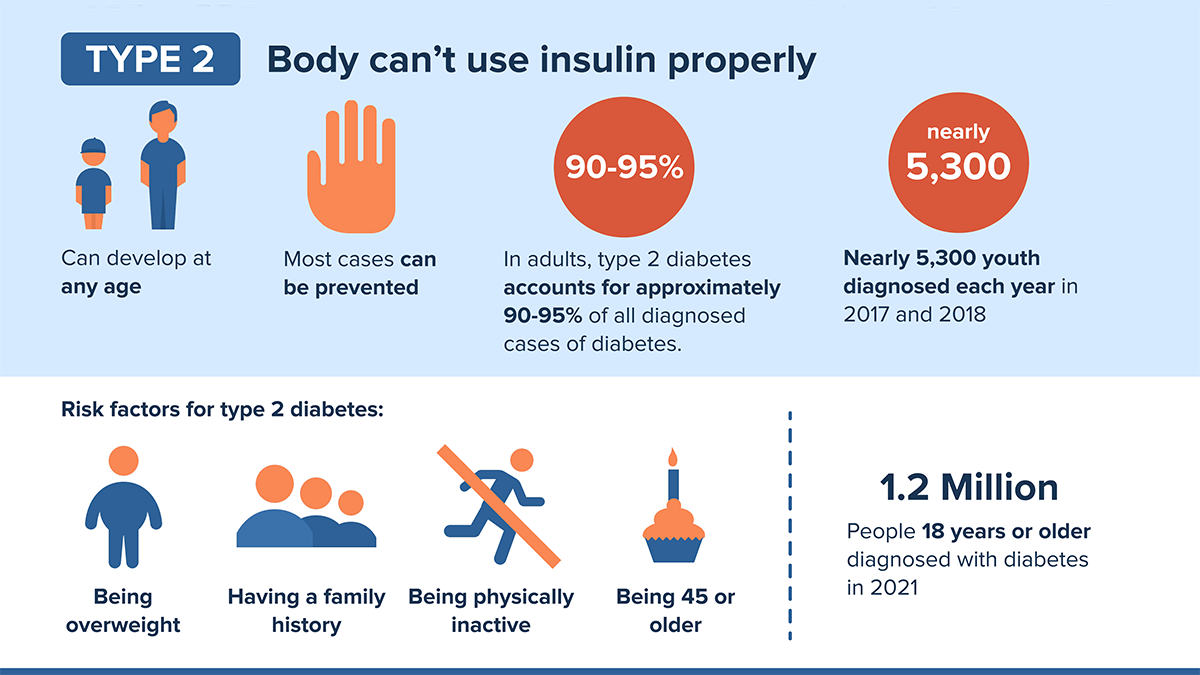
Type 2 diabetes is a common condition affecting millions worldwide. It occurs when the body cannot use insulin properly, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Understanding type 2 diabetes is crucial for managing health and preventing complications. This condition often develops in adults but can affect younger people too. It is linked to lifestyle factors such as diet and physical activity. Early detection and proper management can greatly improve quality of life.
In this blog post, we will explore what type 2 diabetes is, its symptoms, causes, and effective management strategies. By the end, you will have a clearer picture of how to handle this condition and improve your overall well-being. Stay tuned to learn more about type 2 diabetes and how to take control of your health.
Credit: www.cdc.gov
What Is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions worldwide. Understanding this illness is vital for managing and preventing its complications. This section dives into the basics of what Type 2 Diabetes is and the symptoms associated with it.
Basic Definition
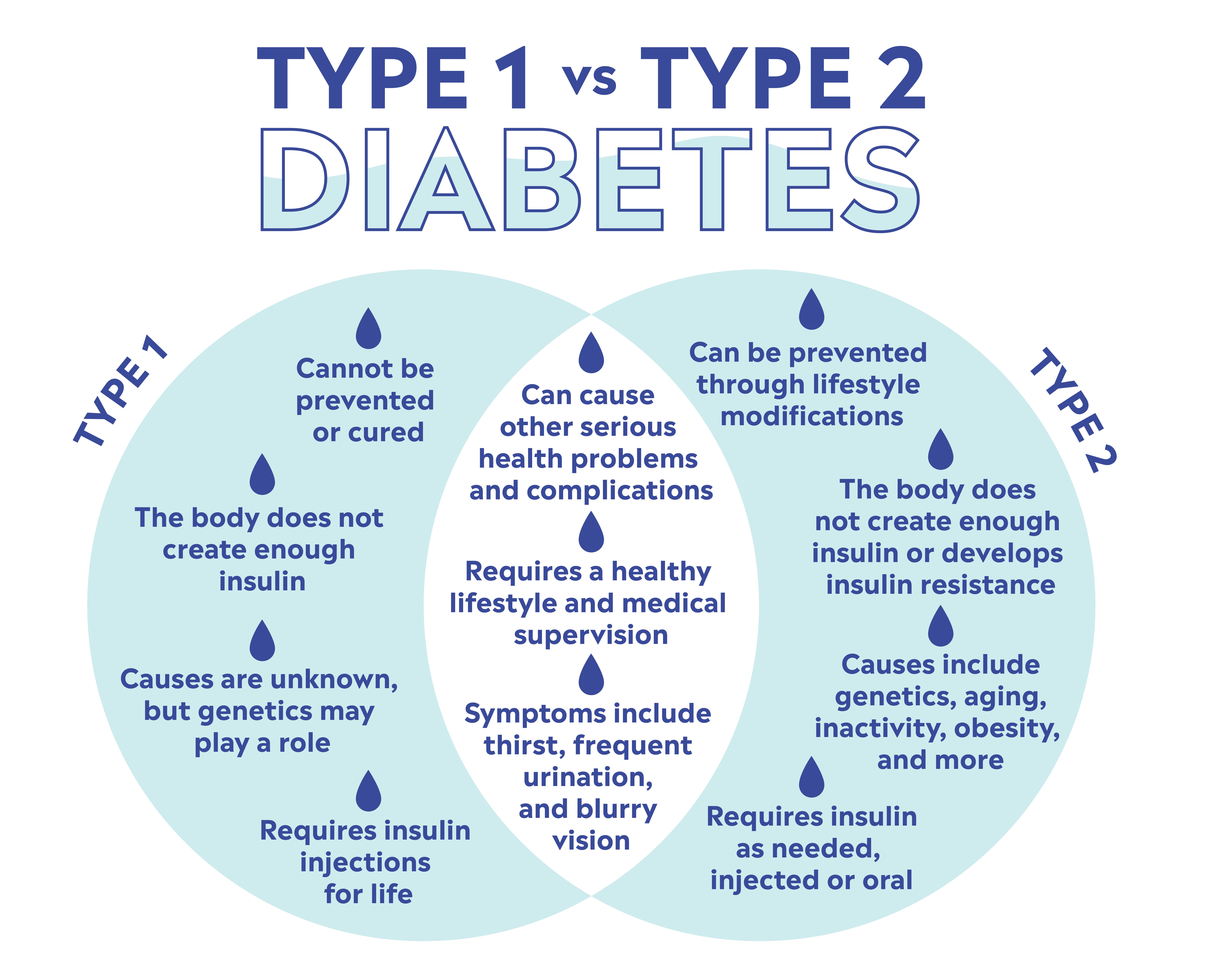
Type 2 Diabetes is a condition where the body fails to use insulin properly. This is known as insulin resistance. Over time, the pancreas cannot make enough insulin to keep blood glucose levels normal. This leads to high blood sugar levels, which can cause various health issues.
Here are some key points about Type 2 Diabetes:
- Insulin resistance: The body's cells do not respond well to insulin.
- High blood sugar: The inability to use insulin effectively leads to elevated blood glucose levels.
- Chronic condition: This is a long-term health issue that requires ongoing management.
Type 2 Diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. It usually develops in adults over 45, but younger people, teens, and children can also develop it. Some risk factors include:
- Being overweight or obese
- Leading a sedentary lifestyle
- Having a family history of diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Abnormal cholesterol levels
Managing Type 2 Diabetes involves lifestyle changes like healthy eating, regular exercise, and sometimes medication. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is also crucial.
Common Symptoms
Type 2 Diabetes often develops slowly. Many people do not notice symptoms initially. Recognizing early signs can help in managing the condition effectively. Common symptoms include:
- Increased thirst: High blood sugar levels cause more fluid to be pulled from tissues.
- Frequent urination: The body tries to get rid of excess glucose through urine.
- Increased hunger: Without enough insulin, muscles and organs become energy-deprived.
- Fatigue: When cells are deprived of sugar, you may become tired and irritable.
- Blurred vision: High blood sugar levels can pull fluid from the lenses of the eyes, affecting vision.
- Slow-healing sores: High blood sugar levels can affect blood flow and cause nerve damage, making it hard for your body to heal wounds.
- Frequent infections: Type 2 Diabetes can lower the body's ability to resist infections.
Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to timely diagnosis and treatment. If you notice any of these signs, consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management.
Causes And Risk Factors
Type 2 Diabetes is a chronic condition affecting millions worldwide. Understanding its causes and risk factors is crucial for prevention and management. This post will explore the genetic factors and lifestyle choices that contribute to the development of Type 2 Diabetes.
Genetic Factors
Genetics play a significant role in Type 2 Diabetes. If you have a family history of diabetes, your risk increases. Certain genes affect how your body makes insulin, a hormone that controls blood sugar levels.
Here are some key points about genetic factors:
- Family history: If your parents or siblings have Type 2 Diabetes, you are more likely to develop it.
- Ethnicity: Some ethnic groups, like African Americans, Hispanics, Native Americans, and Asians, have a higher risk.
- Genetic mutations: Specific gene mutations can affect insulin production and usage.
Researchers have identified several genes linked to Type 2 Diabetes. These genes influence how your body responds to insulin. For example, mutations in the TCF7L2 gene increase the risk of diabetes.
| Gene | Impact |
|---|---|
| TCF7L2 | Increases risk of diabetes |
| SLC30A8 | Affects insulin secretion |
| KCNJ11 | Impacts insulin production |
Understanding your genetic risk can help you take steps to prevent Type 2 Diabetes. Regular check-ups and early detection are essential.
Lifestyle Choices
Lifestyle choices significantly impact the risk of Type 2 Diabetes. Poor diet, lack of exercise, and obesity are major contributors.
Consider these factors:
- Diet: Consuming high-calorie foods, sugary beverages, and processed foods can lead to obesity and diabetes.
- Physical inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle increases the risk of insulin resistance and Type 2 Diabetes.
- Obesity: Excess weight, especially around the abdomen, is a significant risk factor.
- Smoking: Tobacco use can increase blood sugar levels and insulin resistance.
Making healthier choices can reduce your risk:
- Adopt a balanced diet rich in vegetables, fruits, and whole grains.
- Exercise regularly, aiming for at least 30 minutes of moderate activity most days.
- Maintain a healthy weight to improve insulin sensitivity.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
Small changes in lifestyle can have a big impact. By making healthier choices, you can lower your risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes and improve your overall well-being.
Diagnosis Methods
Type 2 Diabetes is a common health issue. It affects how your body handles glucose. Early detection is key. Various diagnosis methods help identify this condition. This section will explain blood tests and diagnostic criteria.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are essential for diagnosing Type 2 Diabetes. They measure glucose levels in your blood. There are several types of blood tests:
- Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG) Test: This test checks your blood sugar after fasting for at least 8 hours. A result of 126 mg/dL or higher indicates diabetes.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): For this test, you drink a sugary liquid. Blood sugar levels are then tested over the next 2 hours. A result of 200 mg/dL or higher after 2 hours suggests diabetes.
- Hemoglobin A1c Test: This test measures your average blood sugar over the past 2-3 months. An A1c level of 6.5% or higher indicates diabetes.
- Random Plasma Glucose Test: This test checks your blood sugar at any time of the day. A result of 200 mg/dL or higher, along with symptoms of diabetes, indicates diabetes.
These tests help doctors determine if you have Type 2 Diabetes. Blood tests are quick and reliable. They provide crucial information about your blood sugar levels.
Diagnostic Criteria
Doctors use specific criteria to diagnose Type 2 Diabetes. These criteria are based on blood test results. Here are the main diagnostic criteria:
- Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG): A fasting blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL or higher.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): A 2-hour blood sugar level of 200 mg/dL or higher.
- Hemoglobin A1c: An A1c level of 6.5% or higher.
- Random Plasma Glucose: A blood sugar level of 200 mg/dL or higher, with symptoms of diabetes.
These criteria help doctors make an accurate diagnosis. Here is a table summarizing these diagnostic criteria:
| Test | Diabetes Result |
|---|---|
| Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG) | 126 mg/dL or higher |
| Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) | 200 mg/dL or higher |
| Hemoglobin A1c | 6.5% or higher |
| Random Plasma Glucose | 200 mg/dL or higher with symptoms |
These criteria are standard. They help ensure accurate and consistent diagnoses. Early diagnosis allows for better management of Type 2 Diabetes.
Credit: www.prevention.com
Management Strategies
Type 2 Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way the body processes blood sugar (glucose). Managing this condition is crucial to maintain a healthy lifestyle and prevent complications. Effective management strategies include a combination of proper diet, regular physical activity, and sometimes medication. Here, we will explore two main strategies: diet and nutrition, and physical activity.
Diet And Nutrition
A balanced diet is essential for managing Type 2 Diabetes. It helps control blood sugar levels and maintain a healthy weight. Here are key dietary tips:
- Choose complex carbohydrates: Opt for whole grains, vegetables, and legumes instead of simple sugars.
- Monitor portion sizes: Eating smaller portions can help keep blood sugar levels stable.
- Limit sugary drinks: Replace sodas and fruit juices with water or unsweetened beverages.
- Include fiber-rich foods: Fiber slows down the absorption of sugar, helping to keep blood sugar levels in check.
- Eat healthy fats: Avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil are better choices than trans fats.
Here's a sample meal plan:
| Meal | Food |
|---|---|
| Breakfast | Oatmeal with berries and nuts |
| Lunch | Grilled chicken salad with a variety of vegetables |
| Dinner | Steamed fish with quinoa and steamed broccoli |
| Snacks | Carrot sticks, hummus, or a small apple |
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is another key component in managing Type 2 Diabetes. It helps lower blood sugar levels and improves insulin sensitivity. Here are some tips:
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week: This can include activities like brisk walking, swimming, or cycling.
- Incorporate strength training: Lifting weights or using resistance bands twice a week can be beneficial.
- Stay active throughout the day: Try to avoid sitting for long periods by taking short walks or standing up every hour.
Here's a weekly exercise plan:
| Day | Activity |
|---|---|
| Monday | 30-minute brisk walk |
| Tuesday | Strength training (30 minutes) |
| Wednesday | 30-minute swim |
| Thursday | Rest or light yoga |
| Friday | 30-minute cycling |
| Saturday | Strength training (30 minutes) |
| Sunday | 30-minute walk |
Medication Options
Type 2 Diabetes is a condition that affects how the body processes blood sugar. Managing this condition often requires different medication options. These medications help control blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and reduce complications. Let's explore some common medications and insulin therapy used to manage Type 2 Diabetes.
Common Medications
Several medications are available to help manage Type 2 Diabetes. These medications work in various ways to keep blood sugar levels under control. Here are some common options:
- Metformin: This is often the first medication prescribed. It helps lower glucose production in the liver and improves the body's sensitivity to insulin.
- Sulfonylureas: These drugs stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin. Examples include glipizide and glyburide.
- Meglitinides: Similar to sulfonylureas, these drugs also stimulate insulin production but are faster-acting. Examples include repaglinide and nateglinide.
- Thiazolidinediones: These drugs improve insulin sensitivity. Examples are pioglitazone and rosiglitazone. They may have side effects like weight gain and heart issues.
- DPP-4 inhibitors: These drugs help reduce blood sugar levels without causing weight gain. Examples include sitagliptin and saxagliptin.
Each medication has its benefits and potential side effects. Doctors often start with one medication and may add others based on how well blood sugar levels are controlled. Below is a table summarizing the common medications for Type 2 Diabetes:
| Medication | Function | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Metformin | Lowers glucose production, improves insulin sensitivity | Metformin |
| Sulfonylureas | Stimulates insulin production | Glipizide, Glyburide |
| Meglitinides | Stimulates insulin production (fast-acting) | Repaglinide, Nateglinide |
| Thiazolidinediones | Improves insulin sensitivity | Pioglitazone, Rosiglitazone |
| DPP-4 inhibitors | Reduces blood sugar levels | Sitagliptin, Saxagliptin |
Insulin Therapy
Insulin therapy is sometimes necessary for managing Type 2 Diabetes, especially when other medications are not enough. Insulin helps the body use glucose for energy. There are different types of insulin:
- Rapid-acting insulin: Works quickly, usually within 15 minutes. Examples include insulin lispro and insulin aspart.
- Short-acting insulin: Starts working within 30 minutes and lasts about 5-8 hours. Regular insulin is an example.
- Intermediate-acting insulin: Begins working within 1-2 hours and lasts up to 18 hours. NPH insulin is an example.
- Long-acting insulin: Works slowly and lasts up to 24 hours. Examples include insulin glargine and insulin detemir.
Doctors will decide the type of insulin based on individual needs. Sometimes, more than one type of insulin is used. Here is a summary of the different types of insulin therapy:
| Type of Insulin | Onset | Duration | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rapid-acting | 15 minutes | 2-4 hours | Insulin lispro, Insulin aspart |
| Short-acting | 30 minutes | 5-8 hours | Regular insulin |
| Intermediate-acting | 1-2 hours | 18 hours | NPH insulin |
| Long-acting | 1-2 hours | 24 hours | Insulin glargine, Insulin detemir |
Insulin therapy requires careful monitoring of blood sugar levels. Consistent communication with healthcare providers ensures the best results. Managing Type 2 Diabetes effectively involves a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and regular check-ups.
Complications To Monitor
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Managing blood sugar levels is crucial, but it's also important to monitor for potential complications. These complications can affect various parts of the body, leading to serious health issues. Let's explore some of the key complications to monitor.
Heart Disease
Heart disease is a common complication of Type 2 diabetes. High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves that control the heart. This increases the risk of heart problems.
People with Type 2 diabetes should watch for signs of heart disease. These include:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Swelling in the legs
- Irregular heartbeat
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help monitor heart health. Key tests include:
| Test | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Blood pressure | Every visit |
| Cholesterol levels | Annually |
| Electrocardiogram (EKG) | As needed |
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk of heart disease. This includes:
- Eating a balanced diet
- Exercising regularly
- Quitting smoking
- Managing stress
Nerve Damage
Nerve damage, or neuropathy, is another complication of Type 2 diabetes. High blood sugar levels can injure nerves throughout the body. The most common type is peripheral neuropathy, which affects the legs and feet.
Symptoms of nerve damage include:
- Numbness or tingling in the feet or hands
- Sharp pains or cramps
- Muscle weakness
- Loss of balance and coordination
To monitor and manage nerve damage:
- Check feet daily for cuts or sores
- Wear comfortable shoes
- Maintain blood sugar levels within target range
- See a podiatrist regularly
Healthcare providers may suggest specific treatments for nerve damage. These can include:
| Treatment | Description |
|---|---|
| Medications | To manage pain |
| Physical therapy | To improve strength and balance |
| Special foot care | To prevent injuries |
Pay attention to changes in sensation or pain. Early detection and management can prevent severe complications.
Living With Type 2 Diabetes
Living with Type 2 Diabetes means making consistent lifestyle changes. This helps manage blood sugar levels. It also improves overall well-being. Understanding and adapting to these changes is key. This guide will help you navigate daily routines and find emotional support.
Daily Routines
Establishing a daily routine is vital for managing Type 2 Diabetes. It can help keep blood sugar levels stable. Here are some important aspects:
- Diet: Eat balanced meals. Include vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Avoid sugary and processed foods.
- Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity. Aim for at least 30 minutes a day. Walking, swimming, or cycling are great options.
- Medication: Take your medications as prescribed. Set reminders if necessary. This ensures you do not miss doses.
- Blood sugar monitoring: Check your blood sugar levels regularly. Keep a log of your readings. This helps in adjusting your management plan.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water. It helps maintain blood sugar balance. Avoid sugary drinks and excessive caffeine.
A sample daily routine could look like this:
| Time | Activity |
|---|---|
| 7:00 AM | Check blood sugar, take medication, have a balanced breakfast |
| 8:00 AM | 30-minute walk |
| 12:00 PM | Healthy lunch, check blood sugar |
| 3:00 PM | Light snack, such as a piece of fruit |
| 6:00 PM | Check blood sugar, dinner |
| 9:00 PM | Relaxation time, prepare for bed |
Emotional Support
Managing Type 2 Diabetes can be emotionally challenging. Having a support system is crucial. Here are some ways to find and maintain emotional support:
- Family and friends: Share your experiences with loved ones. They can offer encouragement and help with daily tasks.
- Support groups: Join a diabetes support group. It provides a space to share and learn from others. Many groups meet online or in person.
- Professional help: Consult a mental health professional. They can help you cope with stress and anxiety. Therapists and counselors offer valuable tools and strategies.
- Education: Learn about Type 2 Diabetes. Knowledge reduces fear and increases confidence. Attend workshops or read reliable sources.
It's important to take care of your mental health. Here are some self-care tips:
- Meditation: Practice mindfulness or meditation. It helps reduce stress and improves focus.
- Hobbies: Engage in activities you enjoy. This can include reading, gardening, or crafting.
- Rest: Ensure you get enough sleep. A well-rested mind handles challenges better.
Living with Type 2 Diabetes is a journey. Building a solid daily routine and seeking emotional support can make this journey smoother. Remember, you are not alone.
Future Directions
Type 2 Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Managing this disease involves lifestyle changes, medications, and regular monitoring. As we look forward, research and potential therapies offer hope for better management and treatment. Here, we explore the future directions in the fight against Type 2 Diabetes.
Research Advancements
Recent studies have brought significant advancements in understanding Type 2 Diabetes. Scientists have discovered new genetic markers that may predict the risk of developing the disease. These markers can help identify individuals at higher risk early on. Early detection is crucial for effective management.
Key research advancements include:
- Genetic studies: Identifying genes associated with Type 2 Diabetes.
- Microbiome research: Exploring the role of gut bacteria in insulin resistance.
- Cell therapy: Investigating how to regenerate insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
Researchers are also focusing on the impact of diet and exercise. Studies show that a balanced diet and regular physical activity can significantly reduce the risk of Type 2 Diabetes. Understanding the link between lifestyle and disease can lead to better prevention strategies.
| Research Area | Focus |
|---|---|
| Genetic Studies | Identifying risk markers |
| Microbiome Research | Gut bacteria and insulin resistance |
| Cell Therapy | Regeneration of insulin-producing cells |
Potential Therapies
Future therapies for Type 2 Diabetes are promising. New medications are being developed to improve blood sugar control with fewer side effects. These medications aim to enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce glucose production in the liver.
Potential therapies include:
- Incretin-based therapies: These drugs mimic gut hormones to increase insulin production.
- SGLT2 inhibitors: These medications help the kidneys remove glucose from the blood.
- Gene therapy: This aims to correct genetic defects causing the disease.
In addition to medications, technological advancements play a crucial role. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) provide real-time blood sugar readings. Insulin pumps deliver precise doses based on these readings. These devices help individuals manage their blood sugar levels more effectively.
Researchers are also exploring the use of artificial intelligence (AI). AI can analyze large datasets to predict blood sugar trends. This can help in creating personalized treatment plans for patients.
The combination of new medications and advanced technology offers hope. These advancements can improve the quality of life for those living with Type 2 Diabetes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition. It affects how your body processes blood sugar. The body either resists insulin or doesn't produce enough insulin.
What Causes Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is caused by a combination of genetics and lifestyle. Being overweight and inactive increases the risk. Poor diet and lack of exercise also contribute.
What Are Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes?
Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue. Blurred vision and slow-healing sores are also signs. Weight loss or gain can occur.
Can Type 2 Diabetes Be Reversed?
Type 2 diabetes can be managed and even reversed. This often involves lifestyle changes. A healthy diet and regular exercise are crucial.
Conclusion
Managing type 2 diabetes involves lifestyle changes. Healthy eating and regular exercise are key. Monitoring blood sugar levels helps keep them in check. Medication may also be necessary. Support from healthcare providers is essential. Stay informed about your condition. Take control of your health journey.
Small steps can lead to big improvements. Consistency is crucial for managing diabetes. Make choices that support your well-being daily. Stay positive and proactive. Your health matters.






