Type 1 diabetes is a chronic condition. It affects how your body handles glucose.
Understanding Type 1 diabetes is crucial for managing health. This condition usually starts in childhood or young adulthood. It happens when the pancreas stops making insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose enter cells for energy. Without it, glucose builds up in the blood.
This can lead to serious health issues. Recognizing symptoms early can help with better management. Knowing the causes can aid in prevention and awareness. Treatment options are available that can improve quality of life. This blog will guide you through the symptoms, causes, and treatments of Type 1 diabetes. Stay informed and take control of your health.
Credit: my.clevelandclinic.org
Introduction To Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes is a chronic condition where the pancreas produces little or no insulin. It mostly appears in children and young adults. Unlike Type 2 Diabetes, it is not linked to lifestyle or diet.
The immune system mistakenly attacks insulin-producing cells. This leads to high blood sugar levels. Managing Type 1 Diabetes requires daily insulin injections and careful monitoring.
Brief History
The history of Type 1 Diabetes dates back to ancient times. Greek physicians first described symptoms like excessive thirst and urination. In the 1920s, scientists discovered insulin, transforming diabetes treatment.
Before insulin, people diagnosed with diabetes had a short life expectancy. Insulin therapy provided a lifeline. Since then, research has advanced treatment methods and improved quality of life.
Prevalence And Statistics
Type 1 Diabetes affects millions worldwide. It accounts for about 5-10% of all diabetes cases. In the United States, around 1.6 million people live with Type 1 Diabetes.
The condition is more common in children and young adults. Each year, thousands of new cases are diagnosed. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective management and preventing complications.
| Region | Cases (in millions) |
|---|---|
| North America | 1.6 |
| Europe | 1.4 |
| Asia | 1.0 |

Credit: www.eternalhospital.com
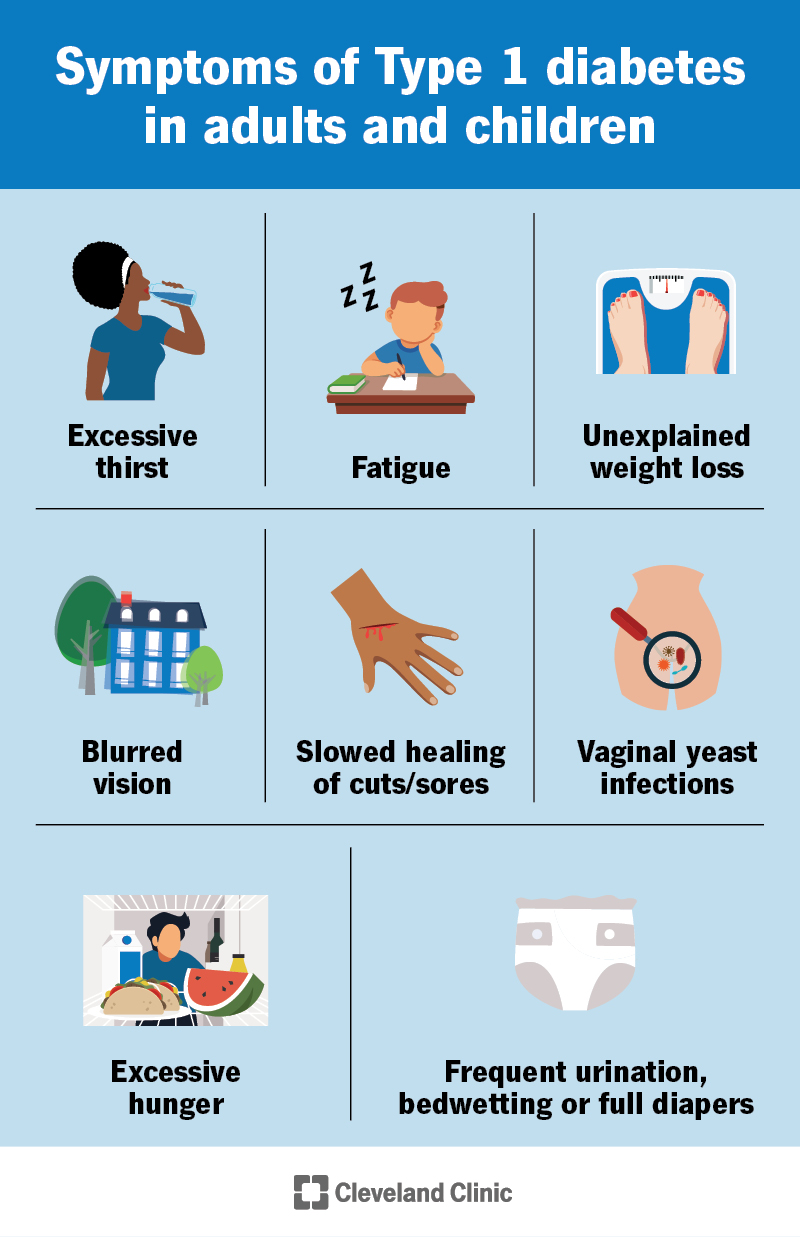
Recognizing Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes early can help manage the condition effectively. The symptoms can vary from mild to severe. Understanding these signs is crucial for timely intervention and treatment.
Early Signs
Some early signs of Type 1 Diabetes may seem harmless. However, they should not be ignored. Here are some common early symptoms:
- Increased Thirst: Feeling thirsty more than usual.
- Frequent Urination: Needing to urinate often, especially at night.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Losing weight without trying.
- Extreme Hunger: Feeling very hungry, even after eating.
- Fatigue: Feeling more tired than usual.
Advanced Symptoms
If Type 1 Diabetes is not diagnosed early, symptoms can become more severe. Some advanced symptoms include:
- Blurred Vision: Vision may become unclear or blurry.
- Slow-Healing Sores: Cuts or sores that heal slowly.
- Frequent Infections: Getting infections more often, such as skin or urinary tract infections.
- Fruity-Smelling Breath: Breath may have a sweet, fruity odor.
- Stomach Pain: Experiencing stomach pain or discomfort.
Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to better management of Type 1 Diabetes. If you notice any of these signs, consult a healthcare provider promptly.
Causes And Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors of Type 1 diabetes is crucial. This knowledge can help manage and possibly prevent the condition. Type 1 diabetes results from a mix of genetic and environmental factors.
Genetic Factors
Genetic makeup plays a significant role in Type 1 diabetes. If you have a family history of the condition, your risk increases. Specific genes can make you more susceptible. Researchers have identified certain genes linked to this autoimmune disease. These genes can affect how your immune system functions.
The HLA genes are one key group. They help your body distinguish between its own cells and foreign invaders. Variations in these genes can confuse your immune system. This confusion can lead to the body attacking insulin-producing cells.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors can also influence the onset of Type 1 diabetes. These triggers are still not fully understood. Viruses are one possible factor. Some viral infections can trigger the immune response that leads to Type 1 diabetes.
Diet in early life is another potential trigger. For instance, cow's milk protein has been studied as a possible factor. Early exposure to certain foods might increase risk. Stress and toxins are also being studied. They might affect the immune system in ways that increase risk.
Understanding these factors can help in early detection. It can also aid in creating preventive strategies. Knowing your risk can encourage proactive health measures.

Credit: www.freedomfromdiabetes.org
Diagnosis Process
Diagnosing Type 1 Diabetes involves a series of medical evaluations. The process helps determine if you have the condition and understand its severity. This early detection is crucial for effective management. Below, we discuss the steps involved in the diagnosis process.
Medical Tests
Doctors rely on several medical tests to diagnose Type 1 Diabetes. Blood tests are the most common. They measure blood sugar levels. Another test is the Hemoglobin A1c test. This test shows average blood sugar levels over the past three months. A fasting blood sugar test is also common. It measures blood sugar after not eating for at least eight hours.
Sometimes, a random blood sugar test is used. This test does not require fasting. High levels of blood sugar can indicate diabetes. Another test is the oral glucose tolerance test. You drink a sugary liquid, and your blood sugar is tested over a few hours.
Diagnostic Criteria
To diagnose Type 1 Diabetes, doctors look for specific criteria. A fasting blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL or higher suggests diabetes. An A1c level of 6.5% or higher also indicates diabetes. A random blood sugar level of 200 mg/dL or higher can confirm the diagnosis if symptoms are present. Symptoms may include increased thirst, frequent urination, or unexplained weight loss.
The oral glucose tolerance test also has its criteria. A blood sugar level of 200 mg/dL or higher after two hours suggests diabetes. Meeting any of these criteria usually leads to a Type 1 Diabetes diagnosis. If the diagnosis is unclear, more tests may be needed.
Daily Management
Managing Type 1 Diabetes daily is vital. It involves monitoring blood sugar and insulin therapy. These tasks help keep blood sugar levels stable. Consistent management reduces complications and promotes overall health.
Insulin Therapy
Insulin therapy is a key part of Type 1 Diabetes management. People with Type 1 Diabetes need insulin daily. The pancreas does not produce insulin in this condition.
There are different types of insulin. They vary in how quickly they work and how long they last. Some common types include:
- Rapid-acting insulin
- Short-acting insulin
- Intermediate-acting insulin
- Long-acting insulin
Your doctor will help choose the right insulin type. They will also guide you on the dosage. Insulin is usually injected using a syringe, pen, or pump. Pumps provide a steady supply of insulin. This helps keep blood sugar levels stable.
Monitoring Blood Sugar
Regular blood sugar checks are essential. They help you understand how well your treatment is working. Monitoring helps prevent hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia.
Use a glucose meter to check blood sugar levels. It involves a small finger prick. Record the readings to track patterns. This data helps your healthcare provider adjust your treatment plan.
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) are also available. They track blood sugar levels throughout the day and night. CGMs provide real-time data. They can alert you to high or low blood sugar levels.
Here is a simple table to help understand blood sugar target ranges:
| Time of Day | Target Blood Sugar Range (mg/dL) |
|---|---|
| Before Meals | 80-130 |
| Two Hours After Meals | Less than 180 |
Maintaining blood sugar within these ranges is crucial. It helps manage Type 1 Diabetes effectively. Discuss your target ranges with your doctor. They may adjust these based on your needs.
Daily management of Type 1 Diabetes requires discipline. But it is essential for a healthy life. Follow your treatment plan closely. Consult your healthcare team regularly. They are your partners in managing this condition.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Managing Type 1 Diabetes requires significant lifestyle adjustments. These changes can help control blood sugar levels and improve overall health. Here, we focus on two critical areas: diet and exercise.
Dietary Considerations
Diet plays a crucial role in managing Type 1 Diabetes. A balanced diet helps maintain stable blood sugar levels. Here are some important dietary tips:
- Carbohydrate Counting: Understanding how many carbs you eat helps in insulin management.
- Low Glycemic Index Foods: Choose foods that don't spike blood sugar quickly.
- Regular Meals: Eating at consistent times aids in better glucose control.
- Healthy Snacks: Opt for nuts, seeds, and vegetables over sugary snacks.
Below is a table of foods to include and avoid:
| Foods to Include | Foods to Avoid |
|---|---|
| Whole grains, lean proteins, leafy greens | Sugary drinks, processed snacks, white bread |
| Fruits with low sugar, nuts, legumes | Fried foods, high-fat dairy, sweets |
Exercise Routines
Exercise is another key component in managing Type 1 Diabetes. Physical activity helps lower blood sugar levels and improves insulin sensitivity. Here are some exercise tips:
- Consistency: Aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise most days.
- Types of Exercise: Include both aerobic and strength training activities.
- Monitor Blood Sugar: Check levels before and after exercise.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to prevent dehydration.
- Have a Plan: Always carry fast-acting carbs like glucose tablets.
Examples of beneficial exercises include:
- Walking
- Jogging
- Cycling
- Swimming
- Weight Training
Regular exercise and a balanced diet are essential for managing Type 1 Diabetes effectively. These lifestyle adjustments can lead to better health outcomes and a more fulfilling life.
Complications And Prevention
Living with Type 1 Diabetes can be challenging. The condition has many complications that affect your health. Understanding these complications and learning how to prevent them is crucial for managing diabetes effectively.
Short-term Complications
Short-term complications of Type 1 Diabetes often arise suddenly. They need immediate attention.
One common issue is hypoglycemia. This happens when blood sugar levels drop too low. Symptoms include sweating, shaking, and confusion.
Another short-term complication is diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). This occurs when the body starts breaking down fat too quickly. Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. DKA can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
Long-term Complications
Long-term complications of Type 1 Diabetes develop over time. They can affect various parts of the body.
High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels, leading to heart disease. This can increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Diabetes can also harm the kidneys, causing diabetic nephropathy. This condition may lead to kidney failure if not managed well.
Another concern is nerve damage, known as diabetic neuropathy. This can cause pain and numbness in the hands and feet.
Eye complications, such as diabetic retinopathy, can lead to vision loss. Regular eye exams are essential to detect and treat this early.
Prevention
Preventing complications involves careful management of blood sugar levels. Regular monitoring and insulin therapy are key.
Adopting a healthy lifestyle helps too. Eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and avoid smoking.
Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are important. They help catch and address complications early.
Current Research And Future Directions
Type 1 diabetes research is advancing rapidly. Scientists are exploring new treatments and potential cures. These efforts aim to improve the quality of life for those affected. Let's delve into the latest innovations and what the future might hold.
Innovative Treatments
Researchers are developing insulin delivery systems. These include smart insulin pens and pumps. These devices help maintain blood sugar levels more effectively.
Another promising area is the development of artificial pancreas systems. These systems automate insulin delivery, reducing the burden on patients.
Additionally, scientists are working on beta cell replacement therapies. This involves transplanting healthy cells to produce insulin naturally.
Potential Cures
Gene therapy is a key area of research for a potential cure. Scientists are exploring ways to correct the genetic defects causing Type 1 diabetes.
Stem cell therapy is another exciting field. Researchers are investigating how to grow new insulin-producing cells from stem cells.
Immunotherapy is also under investigation. This approach aims to retrain the immune system to stop attacking insulin-producing cells.
The future of Type 1 diabetes treatment looks promising. With ongoing research and innovation, we move closer to finding a cure.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Symptoms Of Type 1 Diabetes?
Type 1 Diabetes symptoms include frequent urination, extreme thirst, and unexplained weight loss. Other signs are fatigue, blurred vision, and increased hunger. Early diagnosis is crucial.
What Causes Type 1 Diabetes?
Type 1 Diabetes is caused by an autoimmune reaction. The body's immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This results in little to no insulin production.
How Is Type 1 Diabetes Treated?
Type 1 Diabetes is treated with insulin therapy. Patients need regular blood sugar monitoring and healthy lifestyle choices. A balanced diet and exercise are also important.
Can Type 1 Diabetes Be Prevented?
Currently, Type 1 Diabetes cannot be prevented. It is an autoimmune condition. Researchers are still studying potential prevention methods.
Conclusion
Understanding Type 1 Diabetes is crucial for managing health effectively. Recognize the symptoms early. Seek medical advice if you notice any signs. Causes include genetic factors and immune system issues. Treatment involves insulin therapy, diet, and regular exercise. Adopting a healthy lifestyle is vital.
Stay informed and proactive about your health. Regular check-ups help in managing diabetes better. Supporting loved ones with diabetes also makes a difference. Together, we can manage this condition successfully.






