Rheumatic diseases affect millions worldwide, causing pain and limiting movement. These conditions often involve inflammation and swelling of the joints.
Understanding rheumatic diseases is crucial for managing their impact on daily life. They encompass a variety of disorders, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus. Each disease presents unique challenges, but they share common symptoms like joint pain and stiffness. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve quality of life.
Knowing the causes and risk factors helps in prevention and management. This blog will explore different types of rheumatic diseases, their causes, and effective treatments. Let’s delve into the world of rheumatic diseases and find ways to manage them better.
Credit: www.nature.com
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis, a common rheumatic disease, affects millions worldwide. It causes joint pain and stiffness, often worsening with age. Simple activities can become difficult, impacting daily life.
, a common form of arthritis, affects millions. It involves the wear and tear of joint cartilage, leading to pain and stiffness. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments can help manage this condition better.
Causes Of Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis often results from various factors. These include:
- Age: The risk increases as people get older.
- Joint injury: Past injuries can lead to joint damage.
- Overuse: Repetitive stress on joints can break down cartilage.
- Genetics: Family history can play a role.
- Obesity: Extra weight adds stress to weight-bearing joints.
Symptoms Of Osteoarthritis
The symptoms of osteoarthritis can vary. Common signs include:
- Joint pain: Especially after movement or at the end of the day.
- Stiffness: Often more noticeable upon waking up or after inactivity.
- Swelling: Inflammation around the affected joint.
- Reduced flexibility: Difficulty moving joints through their full range.
- Grating sensation: Feeling or hearing a grinding sensation.
Diagnosis Of Osteoarthritis
Doctors diagnose osteoarthritis through a combination of methods. They may use:
- Medical history: Discussing symptoms and previous injuries.
- Physical examination: Checking for joint tenderness and swelling.
- Imaging tests: X-rays and MRIs to see joint damage.
- Joint fluid analysis: Testing fluid from the joint for inflammation.
Treatment Options For Osteoarthritis
Various treatments can help manage osteoarthritis. They aim to relieve pain and improve joint function.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Physical therapy: Exercises to strengthen muscles around joints.
- Lifestyle changes: Weight loss and low-impact activities.
- Assistive devices: Braces, shoe inserts, or canes.
- Surgery: In severe cases, joint replacement or repair.
Living With Osteoarthritis
Managing osteoarthritis involves making lifestyle adjustments. These can improve quality of life.
- Regular exercise: Keeps joints flexible and muscles strong.
- Healthy diet: Supports weight control and overall health.
- Pain management: Using heat, cold, or relaxation techniques.
- Support groups: Connecting with others who have similar challenges.
- Education: Learning more about the condition and self-care strategies.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
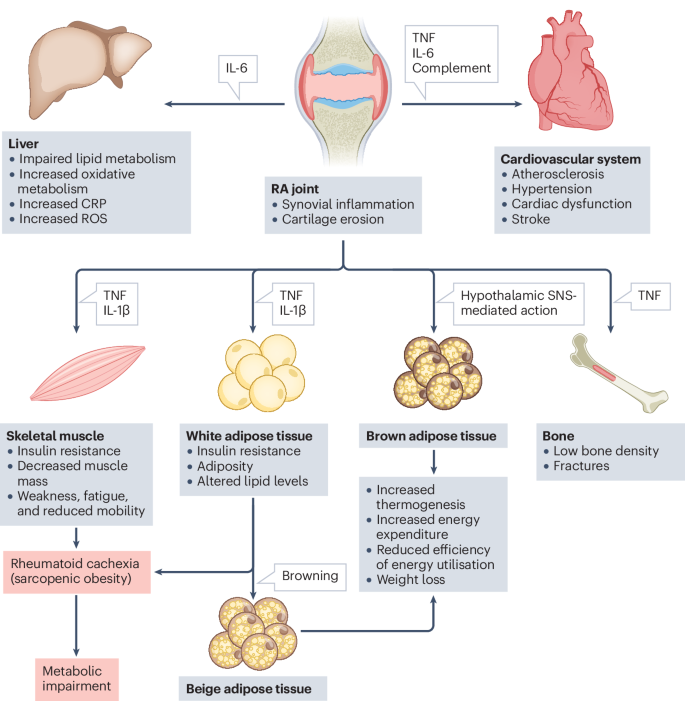
Rheumatoid arthritis is a type of rheumatic disease causing joint inflammation. It leads to pain, swelling, and stiffness. Early diagnosis and treatment help manage symptoms effectively.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder. It primarily affects the joints. The condition can cause pain, swelling, and stiffness. It often leads to joint damage and physical disabilities.
Symptoms Of
Several symptoms can indicate rheumatoid arthritis. Here are some of the main ones:
- Joint pain: Persistent pain in the joints.
- Swelling: Swollen joints that feel warm.
- Stiffness: Especially in the morning or after inactivity.
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired.
- Fever: A low-grade fever may be present.
Causes Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The exact cause is unknown. Yet, several factors may contribute to its development.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing rheumatoid arthritis. Here are some notable ones:
- Genetics: Family history of the disease.
- Gender: More common in women.
- Age: Often develops between ages 40 and 60.
- Smoking: Increases risk and severity.
- Obesity: Excess weight can worsen symptoms.
Diagnosis
Doctors use several methods to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis. They rely on a combination of tests and observations.
Treatment Options
Managing rheumatoid arthritis involves various treatments. Here are some effective approaches:
- Medications: Pain relief and inflammation control.
- Physical therapy: Helps maintain joint function.
- Surgery: In severe cases, joint replacement may be needed.
- Lifestyle changes: Healthy diet and regular exercise.
- Assistive devices: Tools to aid in daily activities.
Living With Rheumatoid Arthritis
Living with this condition requires adjustments. Simple changes can improve quality of life.
Complications
Rheumatoid arthritis can lead to serious complications. Awareness of these is crucial for managing the disease.
Prevention
While there's no sure way to prevent it, some steps can reduce the risk.
Lupus
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects various parts of the body. It is one of many rheumatic diseases, causing inflammation and pain in joints and organs. Early diagnosis and treatment help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Is a complex and often misunderstood rheumatic disease. It affects multiple parts of the body, making it challenging to diagnose and treat. This section delves into key aspects of lupus, helping you understand its symptoms, causes, and management.
What Is Lupus?
Lupus, an autoimmune disease, causes the immune system to attack healthy tissues. This leads to inflammation and damage in various body parts. Commonly affected areas include joints, skin, kidneys, and heart. The disease can be mild or severe, and its symptoms may vary greatly among individuals.
Symptoms Of Lupus
Lupus symptoms can be diverse and sometimes mimic other health issues. Here are some typical symptoms:
- Fatigue: Feeling extremely tired, even after rest.
- Joint pain: Swelling and pain in joints, often in the hands and knees.
- Skin rashes: Red, butterfly-shaped rash on the face or other areas.
- Fever: Unexplained fever without infection.
- Photosensitivity: Sensitivity to sunlight, causing rashes or fatigue.
Causes Of Lupus
The exact cause of lupus remains unknown. However, several factors may contribute to its onset:
- Genetic factors: Family history may increase risk.
- Environmental triggers: Sunlight, infections, and certain medications.
- Hormonal factors: More common in women, suggesting hormones play a role.
- Immune system: Malfunctioning immune response attacking healthy cells.
Diagnosing Lupus
Diagnosing lupus can be tricky due to its varied symptoms. Doctors use several methods to determine the presence of lupus:
- Medical history: Reviewing past health issues and family history.
- Physical exam: Checking for common signs like rashes and joint pain.
- Blood tests: Identifying specific antibodies linked to lupus.
- Urine tests: Detecting kidney problems caused by lupus.
- Biopsy: Examining tissue samples, often from the skin or kidneys.
Managing Lupus
Managing lupus involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medications. Here are some strategies to help manage the condition:
- Medications: Prescribed to control inflammation and symptoms.
- Regular check-ups: Monitoring health and adjusting treatments.
- Healthy diet: Eating balanced meals to support overall health.
- Stress management: Reducing stress through relaxation techniques.
- Exercise: Gentle activities to maintain joint flexibility and strength.
Understanding lupus and its impact is essential for effective management. With proper care, many people with lupus lead fulfilling lives.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing Spondylitis is a type of arthritis affecting the spine. It causes pain and stiffness in the back and neck. This condition can lead to reduced flexibility and posture changes.
(AS) is a type of arthritis that affects the spine. It causes inflammation, leading to pain and stiffness. Over time, the spinal bones can fuse, making the spine less flexible. This can result in a hunched posture. Let's explore some key aspects of this condition.
Symptoms Of Ankylosing Spondylitis
AS symptoms often start gradually. They usually begin in early adulthood. Common symptoms include:
- Back pain: This is often worse in the morning.
- Stiffness: Typically affects the lower back and hips.
- Fatigue: Common due to chronic inflammation.
- Reduced flexibility: Difficulty bending or twisting.
Causes And Risk Factors
Understanding what triggers AS is crucial. The exact cause isn't known, but several factors contribute:
- Genetics: Family history increases the risk.
- Gender: More common in men than women.
- Age: Often begins in late teens or early 20s.
- HLA-B27 gene: Presence of this gene increases risk.
Diagnosing Ankylosing Spondylitis
Doctors use various methods to diagnose AS. These include:
- Physical exam: Checking for pain and stiffness.
- Imaging tests: X-rays or MRI to view spine changes.
- Blood tests: To check for inflammation markers.
Treatment Options
Managing AS focuses on reducing symptoms. Treatment options include:
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain relief.
- Physical therapy: Helps maintain flexibility and strength.
- Exercise: Regular activity can reduce stiffness.
- Surgery: Rarely needed, but an option for severe cases.
Living With Ankylosing Spondylitis
Living with AS requires adjustments. Here are some tips to manage daily life:
- Posture: Maintain good posture to reduce strain.
- Sleep: Use a firm mattress for better support.
- Diet: Eat a healthy diet to reduce inflammation.
- Support: Join support groups for emotional and practical help.
Potential Complications
AS can lead to complications over time. Awareness helps in managing them effectively:
- Eye inflammation: Known as uveitis, causing pain and redness.
- Heart problems: Increased risk of heart disease.
- Lung issues: Reduced capacity due to spinal changes.
- Fractures: Increased risk of spinal fractures.
Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic Arthritis is a type of rheumatic disease. It causes joint pain and skin problems. This condition can affect any part of the body.
Psoriatic arthritis is a type of arthritis that affects some people with psoriasis. Psoriasis is a skin condition causing red, scaly patches. This form of arthritis can affect any joint in the body. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent lasting joint damage.
Symptoms Of
Psoriatic arthritis has various symptoms. Here are some common ones:
- Swollen fingers and toes: Fingers and toes become puffy and sausage-like.
- Joint pain: Pain in joints, often worse in the morning.
- Nail changes: Pitting or separation from the nail bed.
- Eye problems: Redness and pain in the eyes.
Causes And Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors helps in managing the condition effectively. Not everyone with psoriasis will develop psoriatic arthritis.
- Genetics: Family history increases the risk.
- Immune system: Immune system attacks healthy cells.
- Environmental factors: Infections or injuries may trigger it.
- Age: Most common in adults between ages 30 and 50.
Diagnosis
Doctors use several methods to diagnose psoriatic arthritis. Early detection is key to prevent severe damage.
- Physical examination: Checking joints for swelling and tenderness.
- Imaging tests: X-rays or MRI scans to see joint damage.
- Blood tests: To rule out other types of arthritis.
- Joint fluid test: Analyzing fluid from the affected joint.
Treatment Options
Treatment aims to control inflammation, reduce pain, and maintain joint function. A combination of treatments often works best.
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs and immune suppressants.
- Physical therapy: Exercises to improve joint mobility.
- Lifestyle changes: Maintaining a healthy weight and diet.
- Surgery: In severe cases, joint replacement may be necessary.
Living With Psoriatic Arthritis
Living with psoriatic arthritis requires lifestyle adjustments. These changes can improve your quality of life.
- Regular exercise: Helps keep joints flexible and reduces pain.
- Balanced diet: Eating healthy foods to maintain weight.
- Stress management: Techniques like yoga and meditation.
- Support groups: Connecting with others facing similar challenges.
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) is a type of rheumatic disease affecting children. It causes joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. Treatment focuses on reducing symptoms and improving quality of life.
(JIA) affects many children worldwide. This chronic condition causes joint inflammation before the age of 16. Understanding its various aspects is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment.
Symptoms Of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
JIA symptoms can vary widely among children. Some common signs include:
- Joint pain: Persistent discomfort in the joints.
- Swelling: Noticeable inflammation in affected areas.
- Stiffness: Difficulty moving joints, especially in the morning.
- Fever: Occasional high body temperature.
- Rash: Skin changes, often pink or red spots.
Types Of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
JIA has several subtypes, each with unique characteristics.
- Oligoarticular JIA: Affects four or fewer joints.
- Polyarticular JIA: Involves five or more joints.
- Systemic JIA: Includes fever and rash alongside joint issues.
- Enthesitis-related JIA: Includes inflammation where tendons attach to bones.
- Psoriatic JIA: Associated with skin psoriasis and joint pain.
Diagnosis Of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Diagnosing JIA involves multiple steps. Doctors use various methods to identify the condition.
- Medical history review: Understanding the child's health background.
- Physical examination: Checking joints for swelling and tenderness.
- Blood tests: Identifying markers like C-reactive protein.
- Imaging tests: Using X-rays or MRIs to view joint damage.
Treatment Options For Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Treatments aim to relieve pain and prevent joint damage. They vary based on the child's specific needs.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroids.
- Physical therapy: Exercises to maintain joint function and flexibility.
- Regular monitoring: Ongoing check-ups to assess disease progression.
Living With Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Children with JIA can lead fulfilling lives. Here are some tips to help manage the condition:
- Stay active: Regular exercise helps maintain joint health.
- Balanced diet: Proper nutrition supports overall well-being.
- Education: Learning about JIA empowers children and families.
- Support system: Emotional and social support is crucial.
Prognosis Of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
The outlook for children with JIA varies. Many achieve remission with proper treatment. Early intervention and ongoing care are key.
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a common rheumatic disease causing widespread pain and tenderness. It often leads to fatigue and sleep issues. Managing symptoms involves medication, exercise, and stress reduction.
Is a chronic condition causing widespread pain. It affects muscles and soft tissues. Understanding its symptoms and treatment options is vital.
Symptoms Of Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia comes with many symptoms. These can vary in intensity and duration:
- Widespread Pain: Pain felt all over the body.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired even after a full night’s sleep.
- Sleep Disturbances: Trouble sleeping or staying asleep.
- Cognitive Difficulties: Trouble thinking clearly or remembering things.
Causes Of Fibromyalgia
The exact cause is unknown. However, several factors may contribute:
- Genetics: It can run in families.
- Infections: Certain illnesses may trigger it.
- Physical or Emotional Trauma: Stressful events may bring it on.
Diagnosing Fibromyalgia
Doctors use several methods to diagnose fibromyalgia. These include:
- Physical Exam: Checking for tender points on the body.
- Blood Tests: Ruling out other conditions.
- Symptom History: Reviewing the patient's symptoms over time.
Treatment Options For Fibromyalgia
Treatment focuses on managing symptoms. Here are some common approaches:
- Medications: Pain relievers, antidepressants, and anti-seizure drugs.
- Therapy: Physical therapy and counseling.
- Lifestyle Changes: Exercise, stress management, and better sleep habits.
Living With Fibromyalgia
Living with fibromyalgia can be challenging. Yet, many find ways to cope:
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who have fibromyalgia.
- Education: Learning about the condition and its treatments.
- Self-Care: Prioritizing rest and relaxation.
Impact On Daily Life
Fibromyalgia can affect daily activities. Here are some areas impacted:
- Work: May need adjustments or flexible hours.
- Social Life: May limit social interactions due to fatigue.
- Physical Activities: Exercise may need to be low-impact.
Importance Of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis can improve quality of life. Here’s why it matters:
- Prompt Treatment: Start managing symptoms sooner.
- Better Outcomes: Prevent symptoms from worsening.
- Support Access: Join support groups early on.
Understanding fibromyalgia is key to managing it effectively.
Gout
Gout is a type of rheumatic disease causing severe joint pain, often in the big toe. Crystals form in the joints due to high uric acid levels, leading to inflammation and discomfort. Early treatment can help manage symptoms effectively.
Is a type of arthritis that can cause sudden, severe pain. It often affects the joints, especially the big toe. This condition can be both painful and disabling, making it a significant concern for those affected.
Causes Of Gout
Gout occurs due to high levels of uric acid in the blood. Let's explore the key factors contributing to this condition:
- Diet: Consuming foods rich in purines, like red meat and seafood, can increase uric acid levels.
- Genetics: Family history can play a role in developing gout.
- Medical conditions: Issues like kidney disease can lead to higher uric acid levels.
- Medications: Certain drugs, such as diuretics, may contribute to gout.
Symptoms Of Gout
The symptoms of gout can be quite intense and usually come on suddenly.
- Severe joint pain: Often in the big toe, but can affect other joints.
- Inflammation and redness: The affected area may become swollen and tender.
- Limited range of motion: Movement in the affected joint may be restricted.
- Lingering discomfort: After the severe pain subsides, some discomfort may remain.
Diagnosis Of Gout
Diagnosing gout involves a few key steps to confirm the condition.
Doctors will typically perform a physical exam and review medical history. They might also order specific tests:
- Blood tests: Check uric acid levels in the blood.
- Joint fluid test: Analyze fluid from the affected joint to detect urate crystals.
- X-rays: Rule out other causes of joint inflammation.
- Ultrasound: Detect urate crystals in joints.
Treatment And Management Of Gout
Managing gout involves lifestyle changes and medication. Here are some effective strategies:
- Medications: Pain relievers and drugs that reduce uric acid levels.
- Dietary changes: Avoid high-purine foods and alcohol.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to help flush out uric acid.
- Regular exercise: Maintain a healthy weight and reduce stress on joints.
By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments, you can better manage gout and improve your quality of life.
Other Autoimmune Diseases
Rheumatic diseases encompass various autoimmune conditions affecting joints, muscles, and bones. These diseases often cause pain, stiffness, and swelling, impacting daily activities. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing symptoms effectively.
Rheumatic diseases often bring to mind conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. Yet, many other autoimmune diseases fall under this umbrella. These diseases can cause significant discomfort. They affect various body parts and systems. Let's explore some of these conditions.
Lupus
Lupus is a complex autoimmune disease. It can affect the skin, joints, and organs.
- Symptoms: Include fatigue, joint pain, and skin rashes.
- Diagnosis: Blood tests and a physical exam are necessary.
- Treatment: Involves medication and lifestyle changes.
Sjogren’s Syndrome
Another autoimmune disorder is Sjogren’s syndrome. It primarily affects moisture-producing glands.
- Symptoms: Dry eyes and dry mouth.
- Diagnosis: Blood tests and eye exams help identify it.
- Treatment: Focuses on relieving symptoms.
Scleroderma
Scleroderma involves the hardening of the skin and connective tissues. It can be localized or systemic.
- Symptoms: Thickened skin, stiffness, and digestive issues.
- Diagnosis: Blood tests and skin biopsies are common.
- Treatment: Medications and physical therapy are vital.
Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis combines skin psoriasis and joint inflammation. It can be quite debilitating.
- Symptoms: Joint pain, swelling, and skin lesions.
- Diagnosis: Physical exams and imaging tests.
- Treatment: Medications and lifestyle changes manage symptoms.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis primarily affects the spine. It can lead to severe, chronic pain.
- Symptoms: Back pain and stiffness.
- Diagnosis: X-rays and MRI scans are helpful.
- Treatment: Includes medications and physical therapy.
Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis is a rare inflammatory disease. It affects the muscles and skin.
- Symptoms: Muscle weakness and skin rashes.
- Diagnosis: Blood tests, EMG, and muscle biopsies.
- Treatment: Involves medications and physical therapy.
Understanding these autoimmune diseases is crucial. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve quality of life. They help manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Causes And Risk Factors
Genetics and age often contribute to rheumatic diseases. Joint injuries and infections can also raise risk levels.
Rheumatic diseases affect millions worldwide. Understanding their causes and risk factors can help in early detection and management.
Genetic Factors
Genetics play a significant role in rheumatic diseases.
- Family history: Increased risk if close relatives have rheumatic diseases.
- Specific genes: Certain genes linked to higher chances of developing these conditions.
Environmental Triggers
Various environmental factors can contribute to rheumatic diseases.
- Infections: Bacterial or viral infections may trigger symptoms.
- Smoking: Increases the risk of developing rheumatic conditions.
- Exposure to pollutants: Contact with chemicals or toxins can influence disease onset.
Age And Gender
Age and gender also influence the likelihood of developing rheumatic diseases.
- Age: Risk increases as one gets older.
- Gender: Women are more prone to these conditions than men.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices can significantly impact the risk of rheumatic diseases. Here are some key points to consider:
- Physical activity: Lack of exercise can worsen symptoms.
- Diet: Poor eating habits may contribute to inflammation.
- Weight: Excess weight puts more strain on joints.
Occupational Hazards
Certain jobs can increase the risk of rheumatic diseases.
- Repetitive motions: Jobs requiring repeated movements can damage joints.
- Heavy lifting: Strain from lifting heavy objects can lead to joint issues.
- Vibration exposure: Use of vibrating tools can affect joint health.
Hormonal Factors
Hormones can influence the development of rheumatic diseases.
- Hormonal changes: Fluctuations, especially in women, may trigger symptoms.
- Pregnancy: Can lead to temporary or permanent joint issues.
Understanding these causes and risk factors can help manage rheumatic diseases more effectively. Awareness and early intervention are key.
Rheumatic Disease Treatment At A Glance
Rheumatic diseases affect joints, muscles, and bones, causing pain and inflammation. Effective treatments include medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. Early diagnosis and proper management can improve quality of life.
Rheumatic diseases can be debilitating, but effective treatments offer hope. Different therapies target specific symptoms, helping patients manage their condition. Let's explore some common treatments.
Medications
Medications play a crucial role in managing rheumatic diseases. They help reduce inflammation, pain, and slow disease progression.
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter options like ibuprofen.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: NSAIDs to reduce inflammation.
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs): Slow disease progression.
- Corticosteroids: Reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is essential for improving mobility and strength. Therapists design personalized exercises to aid recovery.
- Range-of-motion exercises: Improve flexibility.
- Strengthening exercises: Build muscle to support joints.
- Aerobic exercises: Enhance overall fitness.
- Balance training: Prevent falls and improve stability.
Lifestyle Changes
Adopting healthier habits can significantly impact disease management. Small changes can lead to big improvements in quality of life.
- Healthy diet: Anti-inflammatory foods.
- Regular exercise: Maintain joint function.
- Stress management: Techniques like meditation.
- Adequate sleep: Essential for recovery.
Alternative Therapies
Some patients find relief through alternative therapies. These methods can complement traditional treatments.
- Acupuncture: Alleviates pain.
- Massage therapy: Reduces muscle tension.
- Herbal supplements: Natural anti-inflammatory properties.
- Yoga: Enhances flexibility and reduces stress.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery may be necessary for severe cases. It's usually considered when other treatments fail to provide relief.
- Joint replacement: Common for hips and knees.
- Synovectomy: Removes inflamed joint tissue.
- Tendon repair: Fixes damaged tendons.
- Joint fusion: Stabilizes and reduces pain.
Support Groups And Counseling
Emotional support is vital for those with chronic conditions. Connecting with others can provide comfort and practical advice.
- Peer support groups: Share experiences and tips.
- Professional counseling: Address emotional challenges.
- Online forums: Accessible support network.
- Family involvement: Creates a strong support system.
By exploring these treatments, patients can find the best approach for their needs. Rheumatic disease management is a journey, but these options offer a path to a better quality of life.
Managing Flare-ups
Managing flare-ups in rheumatic diseases involves recognizing triggers and maintaining a balanced lifestyle. Regular exercise, proper medication, and stress management can help reduce symptoms.
Managing flare-ups in rheumatic diseases can be challenging. Flare-ups are sudden increases in symptoms that can disrupt daily life. However, with proper strategies, managing them becomes easier.
Identifying Triggers
Recognizing what triggers your flare-ups is crucial. Common triggers may include:
- Stress: Causes physical and emotional strain.
- Weather changes: Temperature shifts can impact joint pain.
- Overexertion: Pushing your body too hard can lead to discomfort.
- Poor diet: Certain foods might worsen symptoms.
Medication Adherence
Taking medication as prescribed is vital.
Doctors recommend staying consistent with your medication schedule. Missing doses can lead to flare-ups. It's also important to discuss any side effects with your healthcare provider. Adjustments might be necessary to find the best regimen.
Physical Therapy
Exercise tailored to your condition helps manage symptoms.
- Low-impact exercises: Swimming and walking reduce stress on joints.
- Stretching routines: Maintain flexibility and reduce stiffness.
- Strength training: Builds muscle to support joints.
Stress Management
Reducing stress plays a significant role in managing flare-ups.
- Mindfulness techniques: Meditation and deep breathing calm the mind.
- Adequate sleep: Restful sleep aids in recovery.
- Hobbies: Engaging in enjoyable activities distracts from pain.
Diet And Nutrition
Healthy eating supports overall well-being.
A balanced diet rich in vegetables, fruits, and lean proteins is essential. Anti-inflammatory foods like fish, nuts, and seeds can help reduce symptoms. Avoiding processed foods and sugars is also beneficial.
Regular Check-ups
Routine visits to your healthcare provider are necessary.
Regular check-ups help monitor your condition. They allow for adjustments in treatment as needed. Your provider can offer new strategies to manage flare-ups. Staying proactive in your care makes a big difference.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Rheumatic Diseases?
Rheumatic diseases are autoimmune and inflammatory diseases affecting joints, muscles, and connective tissues. They cause pain, swelling, and stiffness.
What Is Osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease. It occurs when cartilage wears down, leading to pain and stiffness in joints.
How Is Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated?
Rheumatoid arthritis treatment involves medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial.
What Causes Lupus?
Lupus is caused by an overactive immune system attacking healthy tissues. Genetic and environmental factors contribute to its development.
Conclusion
Understanding rheumatic diseases helps manage symptoms effectively. Early diagnosis is crucial. Treatments like medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes offer relief. Always consult healthcare providers for tailored advice. Stay informed, be proactive, and prioritize your health. This approach can improve quality of life.






