Ocular migraines can be alarming and confusing. They involve visual disturbances that might affect one or both eyes.
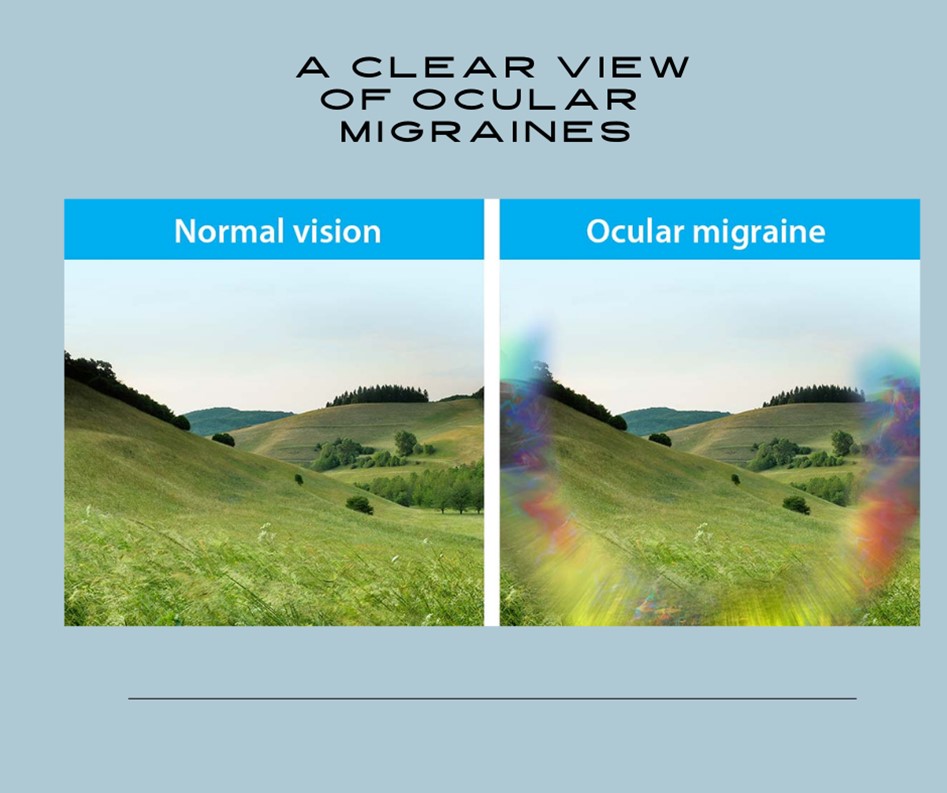
Understanding ocular migraines is key to managing them effectively. These migraines are different from typical migraines, as they primarily affect vision. Individuals may experience flashing lights, blind spots, or zigzag patterns. While these symptoms can be unsettling, they usually resolve on their own within 30 minutes.
Knowing the symptoms and causes can help in recognizing and addressing them promptly. This guide covers everything you need to know about ocular migraines, including how to manage and prevent them. Let's explore this condition and learn how to handle its impact on daily life.
Credit: www.fleyedocs.com
What Is Ocular Migraine?
Ocular migraine causes visual disturbances, such as flashing lights or blind spots. It often occurs without a headache. Symptoms usually last less than an hour.
Ocular migraines can be both intriguing and alarming. They often strike without warning and affect vision temporarily. Let's delve into what ocular migraines are and what you should know about them.
Symptoms Of Ocular Migraine
Symptoms can vary from person to person. Here's a list of common signs:
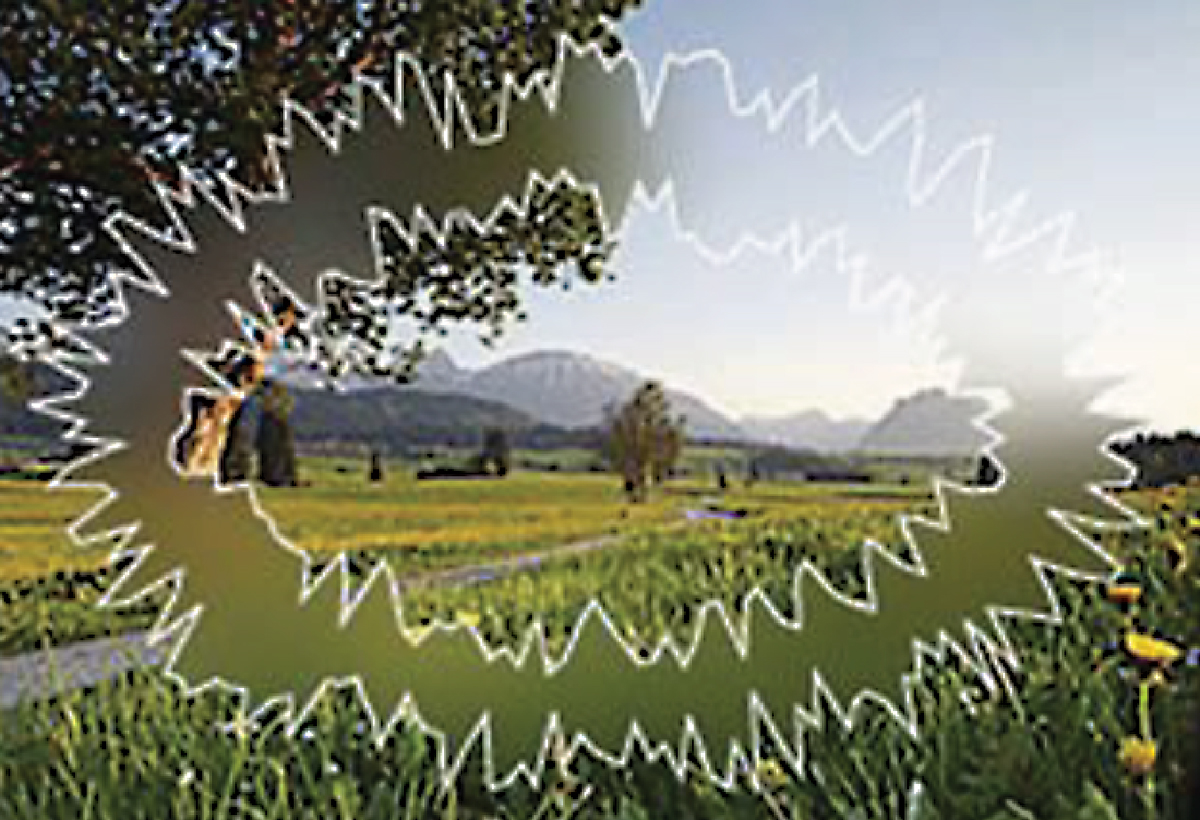
- Visual disturbances: These may include flashing lights or zigzag patterns.
- Vision loss: Temporary blindness in one eye can occur.
- Headache: A mild to severe headache might follow.
Causes Of Ocular Migraine
Understanding the causes can help manage them better. Common triggers include:
- Stress: Heightened levels of stress can trigger an ocular migraine.
- Bright lights: Sudden exposure to bright lights may initiate an episode.
- Hormonal changes: Fluctuations in hormones can be a cause.
Duration Of Ocular Migraine
Typically, ocular migraines are short-lived. They often last between 10 to 30 minutes. Most people regain normal vision after this period. It's unusual for symptoms to persist longer.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of experiencing an ocular migraine. Here are some key points:
- Family history: Genetics can play a role.
- Age: People aged 30-40 are more prone.
- Gender: Women are more likely to suffer from them.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing ocular migraines involves a few steps. Doctors usually perform a comprehensive eye exam. They may also review your medical history. Additional tests like an MRI can be necessary in some cases.
What’s The Difference Between Ocular Migraine And Migraine With Aura?
Ocular migraine causes visual disturbances without a headache. Migraine with aura includes both visual changes and a headache. Both conditions affect vision differently.
Ocular migraines and migraines with aura are often confused. Yet, they have distinct differences. Understanding these can help in managing symptoms better.
Visual Symptoms
Ocular migraines and migraines with aura present different visual symptoms. Here's a breakdown:
- Ocular migraine: Causes vision loss or blindness in one eye.
- Migraine with aura: Includes visual disturbances like flashing lights or zigzag lines.
Duration And Frequency
The duration and frequency of these migraines also vary. Let's explore these aspects:
- Ocular migraine: Typically lasts from a few minutes to an hour.
- Migraine with aura: Visual symptoms usually last 20-60 minutes.
Associated Headache
Not all migraines come with headaches. This distinction is crucial:
- Ocular migraine: May not always lead to a headache.
- Migraine with aura: Often followed by a throbbing headache on one side.
Underlying Causes
Different triggers can cause these types of migraines. Understanding these can aid in prevention:
- Ocular migraine: Often linked to stress, fatigue, or certain foods.
- Migraine with aura: Can be triggered by hormonal changes, stress, or sensory stimuli.
Treatment Options
Treatments vary based on the migraine type. Here are some common approaches:
- Ocular migraine: Resting in a dark room, avoiding triggers, and over-the-counter pain relief.
- Migraine with aura: Prescription medications, lifestyle changes, and avoiding known triggers.
Understanding the differences can help you find the right treatment and manage symptoms more effectively.
How Common Are Ocular Migraines?
Ocular migraines are fairly common and can affect many people. They cause temporary vision disturbances, often with flashing lights or blind spots.
Ocular migraines can be quite unsettling. They cause temporary visual disturbances, making daily activities challenging. But just how common are these ocular migraines?
Frequency Of Ocular Migraines In The General Population
Ocular migraines occur more often than many realize. They affect a broad range of people.
Who Is Most Likely To Experience Ocular Migraines?
Some individuals are more prone to ocular migraines. Here are the groups often affected:
- Women: Higher hormone fluctuations can trigger migraines.
- People aged 30-39: This age group reports more cases.
- Those with a family history: Genetics play a significant role.
How Often Do Ocular Migraines Occur?
The frequency of ocular migraines varies. Some experience them rarely, while others have them more frequently.
Factors Influencing Ocular Migraine Occurrence
Several factors contribute to how often ocular migraines happen. These include:
- Stress: High levels can trigger migraines.
- Diet: Certain foods may be triggers.
- Sleep patterns: Poor sleep can increase occurrences.
- Hormonal changes: Fluctuations can lead to migraines.
Recognizing The Signs Of An Ocular Migraine
It’s essential to identify the signs early. Common symptoms include:
- Visual disturbances: Such as seeing flashes of light.
- Temporary vision loss: In one eye.
- Headache: Often follows the visual symptoms.
Symptoms And Causes
Ocular migraines can cause visual disturbances, such as flashing lights or blind spots. Stress, bright lights, and certain foods often trigger these symptoms.
Ocular migraines can be quite unsettling. They usually involve visual disturbances that can impact daily activities. Understanding the symptoms and causes is key to managing them effectively.
Symptoms
Ocular migraines present with a range of symptoms. These can disrupt your vision and cause discomfort. Here are the most common signs to watch for:
- Visual disturbances: Include flashing lights, zigzag lines, or blind spots.
- Temporary vision loss: Often affects one eye and can last up to an hour.
- Headache: May or may not accompany the visual symptoms.
- Eye pain: Some experience mild to severe pain in the eye.
- Nausea: Feeling nauseous is also common during an episode.
Causes
Several factors can trigger ocular migraines. These triggers vary from person to person. Understanding these can help in managing and preventing episodes:
Certain foods and drinks can also trigger migraines. Here are some common ones:
- Caffeine: Found in coffee, tea, and chocolate.
- Alcohol: Particularly red wine and beer.
- Aged cheeses: Such as blue cheese, cheddar, and parmesan.
- Processed foods: Like deli meats and canned soups.
- Food additives: Including MSG and artificial sweeteners.
Genetics
Genetics play a significant role in ocular migraines. If you have a family history, you might be more prone to them. This genetic link can explain why some people are more susceptible.
Stress And Anxiety
Stress and anxiety are common triggers. Managing stress can reduce the frequency of migraines. Techniques like meditation and exercise can help. Reducing anxiety can also prevent episodes.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes can trigger ocular migraines. This is often seen in women during menstrual cycles. Birth control pills and hormone replacement therapy can also be factors.
Understanding these symptoms and causes can help you manage ocular migraines better. Identifying your triggers is the first step toward effective management.
Diagnosis And Tests
Doctors diagnose ocular migraines through patient history and symptoms. Tests like eye exams and MRIs help rule out other conditions.
Experiencing an ocular migraine can be unsettling. Understanding the diagnostic process helps ease concerns. Doctors use several tests and criteria to diagnose this condition. Let's explore the key steps involved in identifying ocular migraines.
Medical History And Symptoms
Doctors first gather detailed information about your medical history and symptoms.
- Medical History: This includes past health issues and family history.
- Symptom Description: When and how often symptoms occur.
- Triggers: Identifying factors like stress or food that may provoke migraines.
Comprehensive Eye Exam
A thorough eye examination follows. This helps rule out other eye conditions.
Neurological Examination
Neurological tests are vital. They check for any underlying neurological issues.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests provide detailed pictures of the brain and eyes. These help pinpoint any abnormalities.
- MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging scans the brain for issues.
- CT Scan: Computerized Tomography provides detailed cross-sectional images.
Blood Tests
Doctors may order blood tests. These help identify potential underlying conditions.
Visual Field Test
This test checks for blind spots or loss of vision. It’s crucial for assessing ocular health.
Understanding these diagnostic steps can make the process less daunting. Always consult your doctor for personalized advice.
Management And Treatment
Ocular migraine treatment often involves resting in a dark, quiet room. Medications like pain relievers and anti-nausea drugs can help. Managing stress and avoiding migraine triggers also play a crucial role.
Managing ocular migraines can be challenging. However, there are several effective strategies to ease the symptoms. Below, we'll explore various options for managing and treating ocular migraines.
Lifestyle Changes
Simple adjustments to daily habits can significantly reduce migraine frequency.
- Regular sleep schedule: Ensures your body is well-rested.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps prevent dehydration.
- Balanced diet: Eating regular meals and avoiding trigger foods.
- Stress management: Techniques like yoga or meditation can help.
Medications
Sometimes, medications are necessary to control ocular migraines.
Doctors may prescribe different types of medicines:
- Pain relievers: Such as ibuprofen to alleviate headache pain.
- Anti-nausea drugs: Helps with any nausea or vomiting.
- Preventive medications: Daily drugs to reduce frequency.
Avoiding Triggers
Identifying and avoiding triggers can be a key part of managing ocular migraines.
Common triggers include:
- Bright lights: Avoiding harsh lighting or wearing sunglasses.
- Strong smells: Staying away from perfumes and chemicals.
- Stress: Keeping stress levels in check through relaxation techniques.
Regular Eye Exams
Routine eye check-ups can help in managing ocular migraines.
- Early detection: Identifies any underlying eye issues.
- Proper prescription: Ensures your glasses or contacts are up-to-date.
- Eye health: Monitors overall eye health and addresses problems early.
Rest And Relaxation
Taking time to rest can prevent and ease symptoms.
- Quiet, dark room: Helps reduce light sensitivity.
- Gentle massage: Relieves tension in the head and neck.
- Deep breathing: Calms the mind and reduces stress.
Consult A Specialist
Seeing a specialist can provide tailored treatment plans.
- Neurologist: Specializes in treating migraines.
- Ophthalmologist: Focuses on eye health and vision-related issues.
- Physical therapist: Assists with exercises to reduce tension.
Hydration And Nutrition
Proper hydration and nutrition play a vital role.
- Water intake: Staying hydrated can prevent migraines.
- Balanced meals: Regular, nutritious meals keep energy levels stable.
- Avoiding caffeine: Reduces the risk of triggering a migraine.
Keeping A Migraine Diary
Tracking your migraines can help identify patterns and triggers.
- Frequency: Note how often they occur.
- Duration: Record how long each migraine lasts.
- Triggers: Identify potential triggers from your daily activities.
By integrating these management strategies, individuals can experience relief and better control over their ocular migraines.
Prevention
Reducing stress levels, maintaining a regular sleep schedule, and avoiding trigger foods can help prevent ocular migraines. Regular eye exams and managing screen time are also beneficial in preventing episodes.
Ocular migraines can be a real nuisance, causing visual disturbances and discomfort. Learning how to prevent them can significantly improve your quality of life. Here are some practical steps to help you avoid these troublesome episodes.
Manage Stress
Stress is a common trigger for ocular migraines. By managing stress, you can reduce the frequency of these episodes. Here are some effective methods:
- Practice relaxation techniques: Deep breathing and meditation can help.
- Maintain a healthy work-life balance: Avoid overworking and take regular breaks.
- Engage in regular physical activity: Exercise can help reduce stress levels.
Maintain A Healthy Diet
A balanced diet can play a key role in preventing ocular migraines. Certain foods can trigger migraines, so it's essential to monitor your diet:
- Avoid trigger foods: Chocolate, cheese, and processed meats might cause migraines.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water to avoid dehydration.
- Eat regular meals: Skipping meals can trigger migraines.
Get Adequate Sleep
Quality sleep is crucial for preventing ocular migraines. Lack of sleep can make you more susceptible to these episodes. Focus on establishing good sleep habits:
- Maintain a regular sleep schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time daily.
- Create a restful environment: Keep your bedroom dark, quiet, and cool.
- Limit screen time before bed: Reduce exposure to screens to promote better sleep.
Monitor Screen Time
Extended screen time can strain your eyes and trigger ocular migraines. It's essential to be mindful of how much time you spend in front of screens:
- Take regular breaks: Follow the 20-20-20 rule (every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds).
- Adjust screen settings: Reduce brightness and increase text size.
- Use proper lighting: Ensure your workspace is well-lit to reduce eye strain.
Stay Physically Active
Regular physical activity can help reduce the occurrence of ocular migraines. Exercise promotes overall health and well-being:
- Engage in aerobic exercises: Walking, swimming, or cycling can be beneficial.
- Practice yoga: Yoga can help reduce stress and improve flexibility.
- Stay consistent: Aim for at least 30 minutes of physical activity most days.
By incorporating these strategies into your daily routine, you can effectively prevent ocular migraines and enjoy a healthier, more comfortable life.
What Is The Prognosis For Ocular Migraine?
Ocular migraine usually has a good prognosis with symptoms resolving on their own. Most people experience temporary vision disturbances without lasting damage.
Experiencing an ocular migraine can be alarming. Bright flashes or zigzag patterns often precede the headache. But what does the future hold for those affected?
Short-term Outlook
The immediate effects of an ocular migraine can be unsettling:
- Visual disturbances: Bright spots or flickering lights.
- Duration: Symptoms usually last 20-30 minutes.
- Headache: May follow the visual changes, but not always.
Long-term Prognosis
Understanding the long-term implications is crucial.
Many individuals find that ocular migraines do not lead to permanent damage. They may experience:
- Recurrence: Some people have frequent episodes, others only occasionally.
- Vision: No lasting harm to eyesight.
- Management: Symptoms often manageable with lifestyle changes.
Impact On Daily Life
Ocular migraines can interfere with daily activities. It's important to recognize the symptoms early:
- Work: Visual disturbances can disrupt tasks.
- Driving: Unsafe to operate a vehicle during an episode.
- Reading: Hard to focus on text.
Treatment And Prevention
Effective management can improve the quality of life. Here are some strategies:
- Medication: Prescribed drugs can help reduce frequency.
- Lifestyle: Regular sleep and reduced stress can prevent episodes.
- Diet: Avoiding trigger foods may decrease occurrences.
Medical Consultation
Consulting a healthcare professional is essential:
- Diagnosis: Confirming ocular migraines and ruling out other issues.
- Treatment plan: Tailored approach for individual needs.
- Monitoring: Regular check-ups to track progress.
Understanding the prognosis for ocular migraines helps manage expectations and plan for the future.
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider About Ocular Migraines?
Experiencing ocular migraines frequently or with severe symptoms calls for a healthcare provider's visit. Sudden changes in vision or persistent headaches also require medical attention.
Ocular migraines can be alarming and disruptive. Knowing when to seek help is crucial. Let's explore when you should see your healthcare provider about ocular migraines.
Severe Or Frequent Symptoms
If your ocular migraines are severe or happen often, it's time to talk to your healthcare provider. These symptoms could indicate a more serious condition. Here are some signs to look out for:
- Severe pain: Pain that is intense and not relieved by over-the-counter medications.
- Frequent episodes: Occurrences more than once a week.
- Long duration: Symptoms lasting longer than an hour.
Unusual Symptoms
Notice any unusual symptoms? These might need immediate attention. Pay attention to the following:
- Vision loss: Complete loss of vision in one or both eyes.
- Weakness: Sudden weakness or numbness in your limbs.
- Speech problems: Trouble speaking or understanding speech.
Changes In Pattern
Any changes in your migraine pattern should be evaluated. If you notice differences in how your migraines present, reach out to your healthcare provider. This can include:
- New triggers: New factors that seem to cause your migraines.
- Different symptoms: Symptoms that differ from your usual migraines.
- Increased severity: Migraines that become more intense over time.
Impact On Daily Life
Migraines affecting daily activities are a red flag. If your ocular migraines disrupt your work, school, or home life, seek professional advice. Consider these points:
- Missed work: Needing to take time off due to migraines.
- Difficulty concentrating: Struggling to focus on tasks.
- Interference with routines: Migraines that make daily activities hard to complete.
Accompanied By Other Symptoms
Ocular migraines paired with other symptoms need medical attention. If you experience any of the following with your migraines, consult your healthcare provider:
- Nausea or vomiting: Feeling sick to your stomach or throwing up.
- Dizziness: Feeling lightheaded or unsteady.
- Sensitivity to light or sound: Difficulty tolerating bright lights or loud noises.

Credit: www.revieweducationgroup.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is An Ocular Migraine?
An ocular migraine causes visual disturbances, like seeing flashes or zigzag patterns. It typically affects one eye.
How Common Are Ocular Migraines?
Ocular migraines are relatively uncommon. They affect around 1-2% of the population.
What Are The Symptoms Of Ocular Migraine?
Symptoms include visual disturbances, light sensitivity, and sometimes mild headache. These symptoms usually resolve within an hour.
How Is Ocular Migraine Diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a thorough eye examination and patient history. Sometimes, additional tests are conducted to rule out other conditions.
Conclusion
Understanding ocular migraines helps you manage and reduce their impact. Recognize symptoms early to seek proper treatment. Simple lifestyle changes can help prevent future episodes. Consult your healthcare provider for persistent or severe symptoms. Stay informed and proactive about your ocular health.
This can significantly improve your quality of life. Take control and minimize the discomfort caused by ocular migraines.






