Neurodivergent and neurotypical are terms used to describe different ways of thinking. Neurodivergent refers to people whose brains function differently, while neurotypical describes those whose brains function in a more common way.
Understanding these terms is important. It helps us appreciate the diversity in human thinking and behavior. Neurodivergent individuals may include those with autism, ADHD, dyslexia, and other neurological differences. Neurotypical people generally follow more standard patterns of thought and behavior.
Knowing the differences can improve communication and relationships. It also helps create inclusive environments where everyone feels valued. This blog will explore these concepts in detail, helping you understand what sets them apart. Stay with us as we dive deeper into the fascinating world of neurodiversity.
Defining Neurodivergent And Neurotypical
Understanding the terms neurodivergent and neurotypical helps in recognizing different ways people think and process information. Neurodivergent refers to individuals whose brain functions differently from what is considered typical. These differences can be in learning, attention, social interactions, and more. Neurotypical, on the other hand, describes those whose neurological development and functioning align with societal expectations.
Neurodivergent Traits
Neurodivergent individuals may exhibit a range of unique traits. Here are some common ones:
- Strong attention to detail
- Exceptional memory
- Intense focus on specific interests
- Sensitivity to sensory inputs
- Different communication styles
These traits can vary widely among individuals. They may also present challenges in certain environments, such as schools or workplaces.
Neurotypical Traits
Neurotypical individuals generally exhibit traits that align with societal norms. Some common traits include:
- Standard learning patterns
- Typical social interactions
- Consistent attention spans
- Predictable responses to sensory inputs
- Common communication styles
These traits often make it easier for neurotypical individuals to navigate conventional systems like education and employment.
| Neurodivergent Traits | Neurotypical Traits |
|---|---|
| Strong attention to detail | Standard learning patterns |
| Exceptional memory | Typical social interactions |
| Intense focus on specific interests | Consistent attention spans |
| Sensitivity to sensory inputs | Predictable responses to sensory inputs |
| Different communication styles | Common communication styles |
Historical Context
Understanding the historical context of neurodivergent and neurotypical helps to grasp their significance. The journey of these terms reveals much about societal shifts and growing awareness.
Origins Of Terms
The term "neurodivergent" was coined by sociologist Judy Singer in the late 1990s. She used it to describe individuals with atypical neurological development. This includes autism, ADHD, and other cognitive differences. The word "neurotypical" emerged around the same time. It refers to individuals with typical neurological development. These terms aimed to reduce stigma and promote acceptance.
Evolution Of Understanding
Early views on neurodivergence were often negative. People saw these differences as defects or disorders. Over time, perspectives shifted. The neurodiversity movement began to emphasize the value of diverse minds. Advocates pushed for recognizing strengths, not just challenges.
Today, many see neurodivergence as a natural variation of the human brain. This shift has influenced education, employment, and social policies. It has fostered a more inclusive society. Understanding and acceptance continue to grow, bridging gaps between neurodivergent and neurotypical communities.
Common Neurodivergent Conditions
Neurodivergent conditions refer to variations in the human brain that influence how individuals think, learn, and interact with others. Understanding these conditions helps foster a more inclusive society. Below are some common neurodivergent conditions that many people live with daily.
Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a developmental condition. It affects social skills, communication, and behavior. People with ASD may have unique ways of learning. They may also have special interests. Some individuals might excel in areas such as math or art. Early diagnosis and support can make a significant difference.
Adhd
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a condition marked by inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. People with ADHD might find it hard to focus on tasks. They can also be very energetic. This can make school or work challenging. Nonetheless, many with ADHD are creative and dynamic. They often think outside the box.
Dyslexia
Dyslexia is a learning disorder that affects reading and writing. People with dyslexia may struggle with spelling, reading speed, and comprehension. However, they often have strong reasoning skills. Many are also very creative. With the right support, they can excel in many areas.
Other Conditions
There are many other neurodivergent conditions. Some of these include:
- Dyspraxia: Affects physical coordination and motor skills.
- Dyscalculia: Impacts the ability to understand numbers and math.
- Tourette Syndrome: Characterized by repetitive movements or sounds (tics).
- Hyperlexia: Advanced reading skills in young children, often linked with ASD.
Understanding these conditions helps to create a supportive and inclusive environment for all.
Credit: docvita.com
Neurotypical Characteristics
Understanding neurotypical characteristics helps in appreciating the diversity in cognitive functioning and behavioral patterns. Neurotypical individuals exhibit certain traits and behaviors that can be distinct from those who are neurodivergent. This section will delve into these cognitive and behavioral aspects, shedding light on what it means to be neurotypical.
Cognitive Functioning
Neurotypical people often have cognitive functions that align with societal norms. This means they process information, learn, and solve problems in ways considered standard. Here are some common features:
- Consistent Attention: They can usually maintain focus on tasks for extended periods.
- Problem-Solving Skills: They often use traditional methods to find solutions.
- Memory Retention: They typically remember information and events with ease.
Behavioral Patterns
Behavioral patterns in neurotypical individuals are often predictable and align with societal expectations. These behaviors can include:
- Social Interaction: They find it easy to engage in social activities and understand social cues.
- Routine Adherence: They usually follow daily routines without difficulty.
- Emotional Regulation: They often manage their emotions in ways considered typical by society.
Understanding these characteristics can help in recognizing the differences and similarities with neurodivergent individuals. This knowledge promotes empathy and better communication in diverse environments.
Differences In Communication
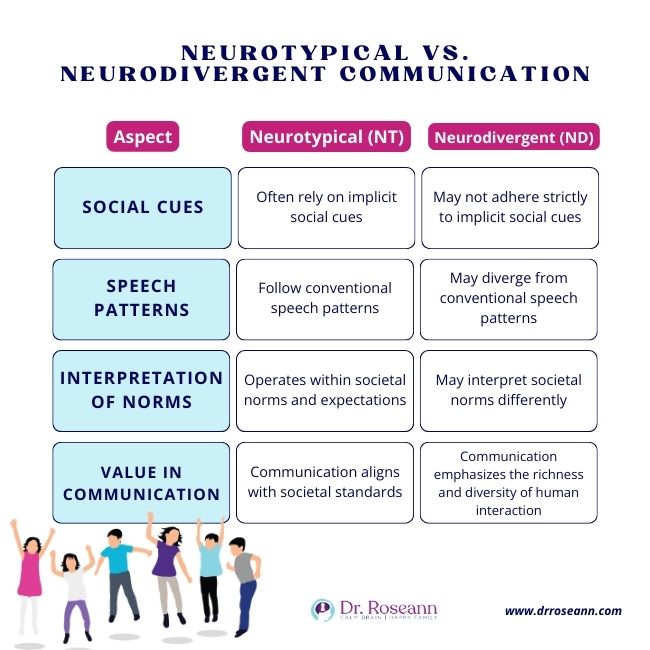
Understanding the differences in communication between neurodivergent and neurotypical individuals can help foster better relationships. These differences often manifest in social interaction and non-verbal communication. Let's explore these aspects to gain a clearer perspective.
Social Interaction
Neurotypical individuals often find social interactions intuitive. They can easily pick up on social cues and respond accordingly. Small talk, making eye contact, and understanding social norms come naturally to them.
Neurodivergent individuals, on the other hand, might approach social interactions differently. They may find it challenging to engage in small talk or understand unspoken social rules. For instance, they might prefer direct communication over subtle hints.
Here is a comparison table to illustrate these differences:
| Aspect | Neurotypical | Neurodivergent |
|---|---|---|
| Small Talk | Easy and natural | Often challenging |
| Eye Contact | Comfortable | May be uncomfortable |
| Social Norms | Intuitive understanding | May require explicit learning |
Non-verbal Communication
Non-verbal communication includes gestures, facial expressions, and body language. Neurotypical individuals typically rely on these cues to convey emotions and intentions.
Neurodivergent individuals may interpret or use non-verbal cues differently. They might not always read facial expressions accurately or use gestures in expected ways. This can lead to misunderstandings in communication.
Consider these bullet points for a quick comparison:
- Facial Expressions: Neurotypical individuals often use and understand them well. Neurodivergent individuals might find them confusing.
- Gestures: Neurotypical individuals use gestures naturally. Neurodivergent individuals might use them less frequently or differently.
- Body Language: Neurotypical individuals often rely on body language. Neurodivergent individuals may not use or read it the same way.
Recognizing these differences can lead to more effective communication strategies. It can also create more inclusive environments.
Credit: docvita.com
Learning And Processing Information
Understanding how individuals learn and process information can help in creating effective educational strategies. Neurodivergent and neurotypical individuals often have different ways of approaching learning and retaining information. Let's explore these differences.
Learning Styles
Neurodivergent individuals might prefer visual aids or hands-on activities. They often excel in environments that offer multi-sensory input. For example, some might benefit from visual schedules or mind maps. Others might learn best through trial and error.
Neurotypical learners usually adapt well to traditional teaching methods. They often succeed with lecture-based learning and textbook reading. Their learning style is generally more consistent with standard educational practices.
| Neurodivergent Learning Styles | Neurotypical Learning Styles |
|---|---|
| Visual aids | Lecture-based |
| Hands-on activities | Textbook reading |
| Multi-sensory input | Standard practices |
| Trial and error | Consistent methods |
Information Retention
Neurodivergent individuals may have unique ways of retaining information. They might remember visual details better. Some may find repetition and routine helpful for retention. Others might use technology like apps and tools.
Neurotypical learners often use traditional methods for information retention. These include note-taking and reviewing materials. They might rely on structured study sessions and mnemonic devices. Their retention strategies align well with conventional educational approaches.
Understanding these differences can help in creating inclusive learning environments. Tailoring educational strategies to individual needs can enhance learning outcomes for both neurodivergent and neurotypical individuals.
Challenges Faced By Neurodivergent Individuals
Neurodivergent people experience unique challenges. These challenges impact social, educational, and workplace settings. Understanding these difficulties can foster a more inclusive society.
Social Challenges
Social interactions can be tough. Many neurodivergent people struggle with understanding social cues. This can lead to misunderstandings and isolation. Making friends can be difficult. Feeling different can cause anxiety and low self-esteem.
Educational Barriers
Traditional classrooms pose challenges. Neurodivergent students often need different learning methods. Standardized tests might not reflect their true abilities. They might need extra support but feel embarrassed to ask. These barriers can affect their academic success.
Workplace Obstacles
Work environments can be overwhelming. Neurodivergent employees might struggle with office noise or bright lights. They often need clear instructions and routines. Misunderstandings with colleagues can occur. These obstacles can hinder their professional growth.
Credit: drroseann.com
Supporting Neurodivergent Individuals
Supporting neurodivergent individuals means understanding and accommodating their unique needs. This helps them thrive in various environments. Here are some strategies for educational settings, workplaces, and social inclusion.
Educational Strategies
Neurodivergent students often learn differently. Tailored educational strategies can make a big difference. Consider these approaches:
- Individualized Education Plans (IEPs): Create custom learning plans for each student.
- Flexible Teaching Methods: Use visual aids, hands-on activities, and technology.
- Quiet Spaces: Provide areas for students to regroup and focus.
These strategies can help neurodivergent students succeed academically and socially.
Workplace Accommodations
Neurodivergent employees bring unique strengths to the workplace. Accommodations can enhance their productivity:
- Flexible Hours: Allow flexible start and end times.
- Noise-Reducing Headphones: Help with concentration in noisy environments.
- Clear Instructions: Provide written and verbal task details.
Creating a supportive work environment benefits both the employee and the organization.
Social Inclusion
Social inclusion is key for neurodivergent individuals. It fosters a sense of belonging. Here are some ways to promote inclusion:
- Awareness Programs: Educate others about neurodiversity.
- Support Groups: Create groups where neurodivergent people can connect.
- Inclusive Events: Host events that cater to diverse needs.
Encouraging social inclusion helps build a more understanding and empathetic community.
Promoting Neurodiversity
Neurodiversity celebrates the range of human minds. It respects different ways of thinking. This includes both neurodivergent and neurotypical people. Promoting neurodiversity means valuing all types of minds. It means creating spaces where everyone feels included.
Advocacy And Awareness
Advocacy is key to promoting neurodiversity. It involves speaking up for those who might be misunderstood. It means educating others about different ways of thinking. Awareness helps people understand neurodivergent experiences. This can reduce stigma and create a more inclusive society.
Raising awareness can start with simple conversations. Share stories and experiences. Support groups can also help. They provide safe spaces for discussions. Schools and workplaces can offer training. This helps everyone understand and appreciate neurodiversity.
Benefits Of Diverse Perspectives
Diverse perspectives bring many benefits. Different ways of thinking can lead to creative solutions. Neurodivergent people often see things from unique angles. This can help solve complex problems. It can drive innovation in various fields.
Having a mix of neurodivergent and neurotypical minds can enrich teams. It can improve decision-making. Diverse teams can think outside the box. They can challenge the status quo. This diversity fosters a culture of acceptance and growth.
Promoting neurodiversity is not just fair. It is smart. It helps build stronger, more innovative communities. It allows everyone to contribute their best.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Does Neurodivergent Mean?
Neurodivergent refers to individuals whose brain functions differently from the typical norms. This includes conditions like autism, ADHD, and dyslexia. Neurodivergence emphasizes the uniqueness of each person's brain.
How Do Neurotypical Brains Work?
Neurotypical brains function in ways considered standard or typical by societal norms. They follow common patterns in processing information, emotions, and behaviors. This is the neurological norm in most societies.
Can Someone Be Both Neurodivergent And Neurotypical?
No, neurodivergent and neurotypical are distinct categories. Neurodivergent refers to atypical brain function, while neurotypical refers to typical brain function. One cannot be both simultaneously.
What Are Common Neurodivergent Conditions?
Common neurodivergent conditions include autism, ADHD, dyslexia, and dyspraxia. Each condition has unique characteristics and challenges. These conditions highlight the diversity of human brains.
Conclusion
Understanding neurodivergent and neurotypical differences promotes empathy and awareness. Both bring unique strengths and perspectives. Recognizing these differences helps create inclusive environments. Embrace diversity in all its forms. Neurodivergent individuals often offer creative solutions. Neurotypical individuals provide stability and traditional approaches.
Both are essential for a balanced society. Encourage open conversations about neurodiversity. Educate yourself and others. Acceptance and understanding benefit everyone. Celebrate all minds.






