Heart disease is a leading cause of death globally. It affects millions each year.
Understanding heart disease is crucial for better health and prevention. Heart disease includes various conditions affecting the heart. These can range from blood vessel diseases to heart rhythm problems. Knowing the risk factors helps in prevention. Heart disease can stem from lifestyle choices, genetics, or other health conditions.
Symptoms vary, but chest pain and shortness of breath are common. Early detection and lifestyle changes can make a big difference. This blog will explore heart disease in detail, helping you recognize signs and reduce risks. Stay informed to protect your heart health.
What Is Heart Disease
Heart disease is a term that covers various conditions affecting the heart. It includes issues with blood vessels, heart rhythm, and heart structure. Heart disease can lead to serious complications like heart attacks and strokes. Understanding heart disease is key to prevention and treatment.
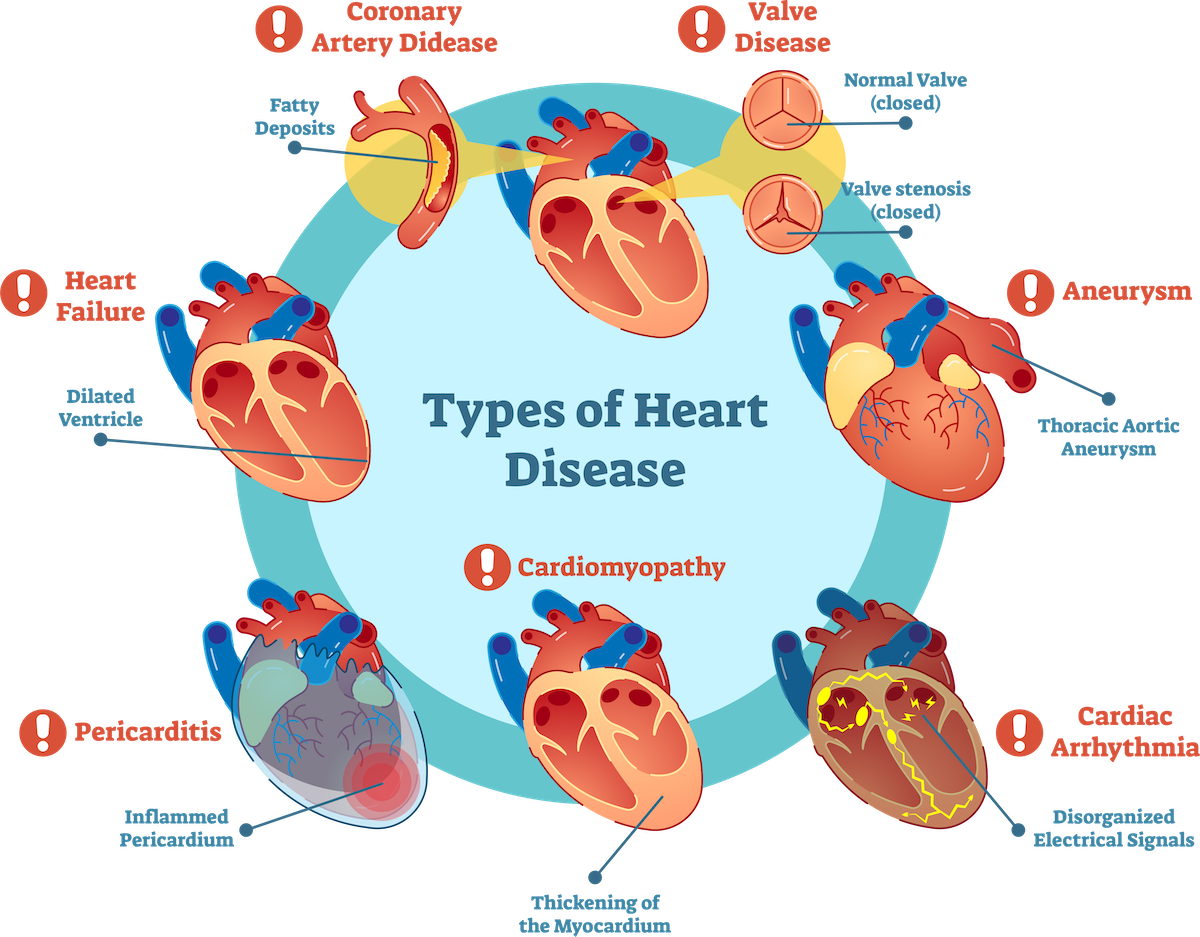
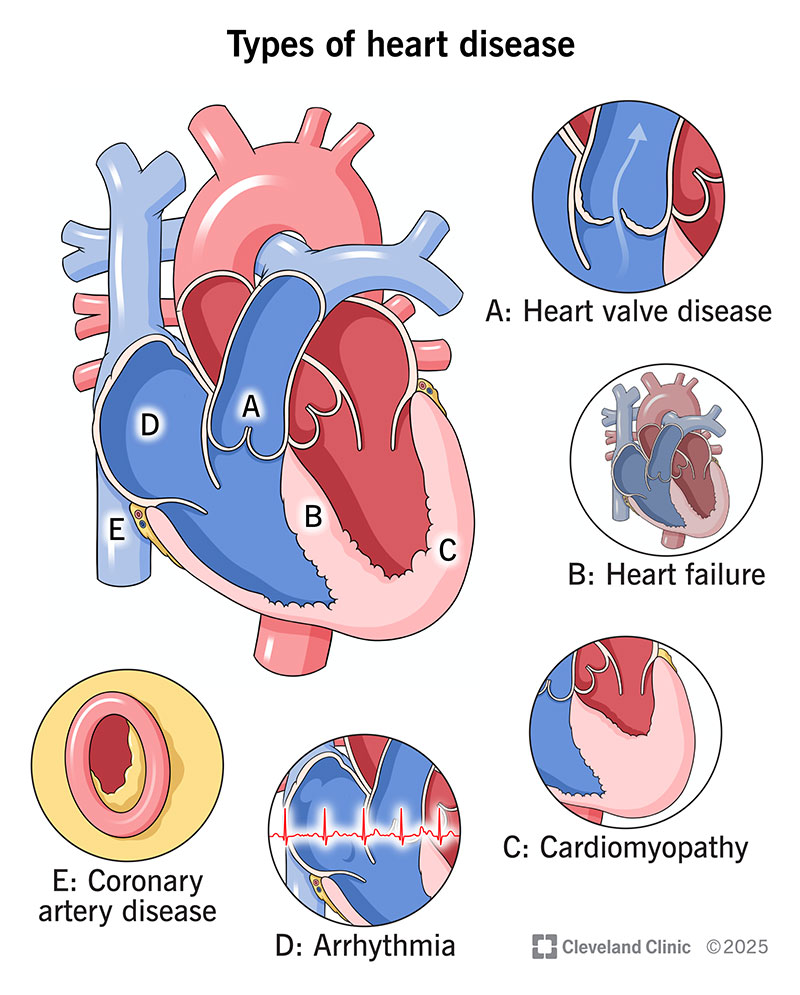
Types Of Heart Disease
Heart disease comes in many forms. Each type affects the heart in different ways. Here are some common types:
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): This is the most common type. It occurs when the arteries supplying blood to the heart become narrow or blocked.
- Heart Arrhythmias: These are problems with the heart's rhythm. The heart may beat too fast, too slow, or irregularly.
- Heart Valve Disease: This involves damage or defects in one or more of the heart valves. Valves help blood flow in the right direction through the heart.
- Heart Failure: This happens when the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's needs.
- Congenital Heart Disease: These are heart problems present at birth. They can affect the heart walls, valves, and blood vessels.
- Cardiomyopathy: This is a disease of the heart muscle. It makes it harder for the heart to pump blood.
Causes And Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors of heart disease can help in prevention. Here are some key points:
- Genetics: Family history can increase the risk of heart disease.
- Age: The risk of heart disease increases with age.
- Gender: Men are generally at higher risk, but women's risk increases after menopause.
- High Blood Pressure: This can damage arteries and lead to heart disease.
- High Cholesterol: Excess cholesterol can build up in the arteries, causing CAD.
- Smoking: Smoking damages the blood vessels and heart, increasing heart disease risk.
- Obesity: Excess weight strains the heart and can lead to heart disease.
- Physical Inactivity: Lack of exercise can contribute to heart disease.
- Unhealthy Diet: Diets high in fats, sugars, and salt can increase heart disease risk.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and the heart.
- Stress: Chronic stress can contribute to heart disease.
By managing these risk factors, it is possible to lower the chances of developing heart disease. Regular check-ups and a healthy lifestyle are crucial for heart health.
Symptoms To Watch For
Heart disease is a leading cause of health problems worldwide. Recognizing the symptoms early can help prevent severe complications. This section will guide you on the symptoms to watch for and when to seek medical help.
Common Symptoms
Many symptoms can indicate heart disease. Being aware of these can help catch problems early. Here are some common symptoms to watch for:
- Chest Pain: This is the most common symptom. It can feel like pressure, tightness, or squeezing.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing can happen with or without chest pain.
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired even with simple activities.
- Swelling: Swelling in legs, ankles, or feet can indicate heart problems.
- Irregular Heartbeat: A fast or irregular heartbeat can be a sign of trouble.
Other symptoms can also suggest heart disease. These include:
- Dizziness or light-headedness
- Nausea or vomiting
- Pain in the neck, jaw, or back
When To Seek Help
Knowing when to seek medical help is crucial. If you experience any of the following symptoms, contact a healthcare provider immediately:
- Severe Chest Pain: Especially if it lasts more than a few minutes or goes away and comes back.
- Shortness of Breath: If it occurs suddenly or is severe.
- Fainting: Loss of consciousness can indicate serious heart issues.
Other scenarios that require immediate medical attention include:
- Severe swelling in your legs or ankles
- Sudden, severe headache along with heart-related symptoms
- Palpitations that do not go away or are accompanied by dizziness or chest pain
Regular check-ups can help monitor heart health. If you have risk factors like high blood pressure, diabetes, or family history of heart disease, be extra vigilant.
Diagnosis Methods
Heart disease is a leading cause of death worldwide. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and management. Understanding the various methods used to diagnose heart disease can help individuals recognize the importance of regular check-ups and prompt medical attention. This section delves into the primary methods used to diagnose heart disease, including medical history reviews and diagnostic tests.
Medical History Review
A thorough medical history review is the first step in diagnosing heart disease. Doctors gather detailed information about the patient's health, lifestyle, and family history. This helps identify risk factors and symptoms that may indicate heart problems.
Key areas of focus during a medical history review include:
- Family history: Heart disease can be hereditary. Knowing if close relatives have had heart disease can indicate an increased risk.
- Lifestyle factors: Smoking, diet, exercise, and alcohol consumption can impact heart health.
- Previous medical conditions: Conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol are significant risk factors.
- Symptoms: Patients are asked about symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, and palpitations.
Doctors may use a questionnaire to gather this information more systematically. Here is an example of a table summarizing the key points:
| Focus Area | Details |
|---|---|
| Family History | Presence of heart disease in close relatives |
| Lifestyle Factors | Smoking, diet, exercise, alcohol use |
| Previous Medical Conditions | Diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol |
| Symptoms | Chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, palpitations |
Understanding these aspects helps doctors assess the likelihood of heart disease and decide on further diagnostic tests.
Diagnostic Tests
After reviewing medical history, doctors may recommend various diagnostic tests to confirm the presence of heart disease. These tests provide detailed insights into the heart's function and structure.
Common diagnostic tests include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): Measures the heart's electrical activity. It helps detect irregular heartbeats, heart attacks, and other conditions.
- Echocardiogram: Uses sound waves to create images of the heart. It shows the heart's structure and function.
- Stress Test: Assesses how the heart performs under physical stress. It can reveal problems that are not visible when the heart is at rest.
- Cardiac Catheterization: Involves inserting a catheter into a blood vessel to the heart. It provides detailed information about the coronary arteries and heart function.
- Blood Tests: Measure levels of substances like cholesterol, triglycerides, and enzymes that indicate heart damage.
A summary of these tests can be represented in a table:
| Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Electrocardiogram (ECG) | Detects electrical activity and heart rhythm |
| Echocardiogram | Visualizes heart structure and function |
| Stress Test | Assesses heart performance under stress |
| Cardiac Catheterization | Provides detailed coronary artery information |
| Blood Tests | Measures substances indicating heart health |
These tests help doctors make an accurate diagnosis and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Early detection of heart disease can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/overview-of-heart-disease-4160961_final-152f46073f2242999b771e409973825b.png)
Credit: www.verywellhealth.com
Treatment Options
Heart disease is a serious condition affecting millions of people worldwide. Understanding the treatment options available can help manage the disease and improve quality of life. Treatment options vary based on the type and severity of heart disease. They include medications, surgical procedures, and lifestyle changes. This blog post focuses on two primary treatment options: medications and surgical procedures.
Medications
Medications are often the first line of treatment for heart disease. They help manage symptoms, prevent complications, and improve heart function. Different medications serve various purposes. Here are some common types:
- Beta-blockers: Reduce blood pressure and heart rate.
- ACE inhibitors: Relax blood vessels and lower blood pressure.
- Statins: Lower cholesterol levels.
- Anticoagulants: Prevent blood clots.
- Diuretics: Help the body get rid of excess fluid.
Doctors prescribe these medications based on the patient's specific condition. For instance:
| Condition | Medication Type |
|---|---|
| High Blood Pressure | Beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors |
| High Cholesterol | Statins |
| Risk of Clots | Anticoagulants |
| Fluid Retention | Diuretics |
It's important to follow the doctor's instructions while taking these medications. Missing doses or stopping medication without consulting a doctor can worsen the condition. Regular check-ups are also essential to monitor progress and adjust medications if needed. Medications can help manage heart disease effectively when taken as prescribed.
Surgical Procedures
In some cases, medications alone are not enough. Surgical procedures may be necessary to treat heart disease. These procedures can improve blood flow, repair damaged heart tissue, or replace damaged heart valves. Some common surgical options include:
- Angioplasty: Opens blocked arteries using a balloon.
- Stent Placement: Keeps arteries open after angioplasty.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): Creates a new path for blood flow around blocked arteries.
- Heart Valve Repair or Replacement: Fixes or replaces damaged heart valves.
- Pacemaker Implantation: Regulates heartbeats using a small device.
Each surgical procedure has its own benefits and risks. Doctors will recommend the best option based on the patient's condition. For example:
| Condition | Procedure |
|---|---|
| Blocked Arteries | Angioplasty, Stent Placement, CABG |
| Damaged Valves | Heart Valve Repair or Replacement |
| Irregular Heartbeats | Pacemaker Implantation |
Recovery from heart surgery varies. It depends on the type of procedure and the patient's overall health. Post-surgery, patients may need medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. These steps are crucial for a successful recovery and long-term heart health.
Lifestyle Changes
Heart disease is a leading cause of death worldwide. It affects millions every year. But the good news is, lifestyle changes can help manage and even prevent heart disease. These changes involve adopting a healthier diet, regular exercise, quitting smoking, and managing stress. Let's focus on two key areas: diet and nutrition, and exercise recommendations.
Diet And Nutrition
What you eat plays a significant role in heart health. A balanced diet can reduce the risk of heart disease. Here are some tips to improve your diet:
- Increase fruits and vegetables: Aim for at least five servings a day. They are rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
- Choose whole grains: Replace refined grains with whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread.
- Limit unhealthy fats: Avoid trans fats found in fried foods, pastries, and fast foods. Opt for healthy fats like those in olive oil, avocados, and nuts.
- Reduce sodium intake: High sodium can lead to high blood pressure. Use herbs and spices to flavor food instead of salt.
- Watch your portion sizes: Eating too much can lead to weight gain. Use smaller plates to help control portions.
Here’s a simple table to guide your daily nutrient intake:
| Nutrient | Recommended Daily Intake |
|---|---|
| Fruits and Vegetables | At least 5 servings |
| Whole Grains | 3-6 servings |
| Protein | 2-3 servings |
| Fats | Use sparingly |
| Sodium | Less than 2,300 mg |
Exercise Recommendations
Regular physical activity strengthens the heart. It helps maintain a healthy weight and lowers blood pressure. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week. Here are some activities that can help:
- Walking: A simple and effective way to get moving. Aim for 30 minutes a day, five days a week.
- Cycling: Great for cardiovascular health. It’s also low-impact, which is easier on the joints.
- Swimming: A full-body workout that strengthens the heart and muscles.
- Strength training: Include weights or resistance bands twice a week to build muscle and boost metabolism.
- Stretching: Keeps muscles flexible and helps prevent injuries. Include stretching exercises daily.
Here’s an example of a weekly exercise plan:
| Day | Activity |
|---|---|
| Monday | 30-minute walk |
| Tuesday | 30-minute cycling |
| Wednesday | Strength training |
| Thursday | 30-minute walk |
| Friday | Swimming |
| Saturday | Strength training |
| Sunday | Rest and stretching exercises |
Making these lifestyle changes can significantly improve your heart health. Start small and gradually build up your habits. Your heart will thank you!
Credit: www.udmi.net
Preventive Measures
Heart disease is a leading cause of death worldwide. However, there are several preventive measures that can help reduce the risk. Taking proactive steps can improve heart health and ensure a longer, healthier life. Two important preventive measures are regular check-ups and health screenings.
Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups are crucial for maintaining heart health. These visits allow doctors to detect early signs of heart disease and provide necessary treatments. Here are some key reasons why regular check-ups matter:
- Early Detection: Doctors can identify risk factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes.
- Personalized Advice: Doctors offer tailored advice on diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes.
- Monitoring Progress: Regular visits help track health progress and adjust treatments as needed.
During a check-up, expect your doctor to:
| Procedure | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Blood Pressure Check | Detects hypertension |
| Cholesterol Test | Measures cholesterol levels |
| Blood Sugar Test | Checks for diabetes |
| Weight and BMI Measurement | Assesses obesity risk |
It is essential to schedule annual check-ups. This consistency helps in identifying potential problems early. Early intervention can prevent severe complications and improve quality of life.
Health Screenings
Health screenings are another vital preventive measure. They detect conditions that may lead to heart disease. Some important screenings include:
- Cholesterol Screening: High cholesterol can lead to plaque build-up in arteries.
- Blood Pressure Screening: Hypertension increases the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Diabetes Screening: Uncontrolled diabetes can damage blood vessels and the heart.
- Body Mass Index (BMI) Screening: High BMI indicates obesity, a risk factor for heart disease.
These screenings are typically quick and painless. The results help doctors create a personalized care plan. Here is a brief overview of each screening:
| Screening | Frequency | Age Group |
|---|---|---|
| Cholesterol | Every 4-6 years | Adults 20+ |
| Blood Pressure | Every 2 years | Adults 18+ |
| Diabetes | Every 3 years | Adults 45+ |
| BMI | Every 2 years | Adults 18+ |
Health screenings are crucial for early detection and prevention. They offer a clear picture of heart health and allow timely interventions. Make sure to discuss with your doctor which screenings are right for you.
Living With Heart Disease
Living with heart disease can be challenging, but it is possible to lead a fulfilling life with the right approach. Understanding how to manage your condition and seeking support are crucial steps in this journey. Below, we explore effective coping strategies and the importance of support systems for those living with heart disease.
Coping Strategies
Adopting effective coping strategies can significantly improve the quality of life for those with heart disease. Here are some practical tips:
- Follow a Heart-Healthy Diet: Incorporate fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into your meals. Avoid high-sodium and high-fat foods.
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in moderate physical activities like walking, swimming, or cycling. Aim for at least 30 minutes a day, five days a week.
- Take Medications as Prescribed: Adhere to your doctor's recommendations for medications. This helps manage symptoms and prevent complications.
- Monitor Your Health: Keep track of your blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and weight. Use a journal or app to record your readings.
- Manage Stress: Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga. Reducing stress can lower your risk of heart-related issues.
To further illustrate the importance of a balanced lifestyle, consider the following table:
| Activity | Frequency | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Walking | 30 minutes/day | Improves cardiovascular health |
| Healthy Eating | Daily | Reduces cholesterol and blood pressure |
| Medication | As prescribed | Controls symptoms |
Support Systems
Having a strong support system is vital for individuals with heart disease. Here are some key support mechanisms:
- Family and Friends: Lean on your loved ones for emotional support. They can help you stay motivated and provide assistance when needed.
- Healthcare Team: Regular check-ups with your cardiologist and other healthcare professionals ensure your condition is monitored and managed effectively.
- Support Groups: Join local or online support groups. Connecting with others who share similar experiences can be comforting and informative.
- Community Resources: Utilize community programs that offer exercise classes, nutritional counseling, and educational workshops.
- Mental Health Professionals: Seek help from therapists or counselors. They can assist in coping with the emotional aspects of living with heart disease.
Building a network of support involves various layers of assistance. Here's a breakdown:
| Support Type | Role |
|---|---|
| Family | Emotional support, daily assistance |
| Healthcare Team | Medical guidance, monitoring |
| Support Groups | Peer support, shared experiences |
| Community Resources | Programs, workshops |
| Mental Health Professionals | Emotional and psychological support |
Remember, the journey with heart disease is unique for everyone. Establishing coping strategies and a strong support system can make a significant difference in managing your condition and enhancing your overall quality of life.
Future Of Heart Disease Research
Heart disease remains a leading cause of death worldwide. But, the future of heart disease research looks bright. Scientists and doctors are working hard to find better ways to treat and prevent this condition. New treatments and technologies are on the horizon, promising hope for many. Let's explore some of the exciting developments in heart disease research.
Innovative Treatments
Many new treatments for heart disease are being developed. These treatments aim to improve heart health and quality of life. Some of the most promising ones include:
- Gene Therapy: This treatment involves changing genes to prevent or treat disease. For heart disease, scientists are looking at ways to fix or replace faulty genes.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Stem cells can become different types of cells in the body. Researchers are studying how to use them to repair damaged heart tissue.
- New Medications: Many new drugs are being tested. These drugs aim to lower cholesterol, reduce blood pressure, and prevent blood clots.
Here is a table summarizing some of the innovative treatments:
| Treatment | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Gene Therapy | Alter genes to prevent/treat heart disease |
| Stem Cell Therapy | Repair damaged heart tissue |
| New Medications | Lower cholesterol, blood pressure, prevent clots |
These treatments offer new hope. They can help people live longer, healthier lives. The future looks promising with these innovations.
Emerging Technologies
Technology is changing how we understand and treat heart disease. Many new tools and devices are being developed. These technologies can help doctors diagnose and treat heart disease more effectively. Some of the most exciting emerging technologies include:
- Wearable Devices: These devices can track heart rate, blood pressure, and other vital signs. They can alert users to potential problems before they become serious.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI can analyze large amounts of data quickly. It can help doctors make better decisions about treatment and care.
- 3D Printing: This technology can create custom implants and devices for heart patients. It can also be used to make models of the heart for surgical planning.
Wearable devices are particularly popular. They allow continuous monitoring of heart health. This can lead to early detection of problems. Early detection can save lives.
AI is also making a big impact. It can process data from many sources, including medical records and imaging studies. This helps doctors spot patterns and make accurate diagnoses. Here is a table summarizing these technologies:
| Technology | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Wearable Devices | Track vital signs, alert to problems |
| Artificial Intelligence | Analyze data, assist in diagnosis |
| 3D Printing | Create custom implants, plan surgeries |
These technologies are changing the future of heart disease care. They offer new ways to monitor, diagnose, and treat the condition. This means better outcomes for patients and a brighter future for heart health.
Credit: my.clevelandclinic.org
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Heart Disease?
Heart disease refers to various heart conditions. It includes coronary artery disease, heart attacks, and heart failure.
What Causes Heart Disease?
Heart disease is caused by plaque buildup in arteries. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, and diabetes.
How Can I Prevent Heart Disease?
To prevent heart disease, maintain a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and avoid smoking. Regular check-ups are important.
What Are Heart Disease Symptoms?
Symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue. In some cases, there are no symptoms.
Conclusion
Taking care of your heart is essential for a healthy life. Simple changes can make a big difference. Eat well, exercise regularly, and avoid smoking. Regular check-ups help catch problems early. Remember, your heart health impacts your overall well-being. Small steps lead to lasting benefits.
Make heart health a priority today. Protect your heart, protect your future. Live a heart-healthy life and enjoy many happy, healthy years.






