Fat is a crucial part of our diet. It provides energy and helps our body function.
Understanding fat is important for making healthy choices. Fat comes in many forms, each with different effects on our health. Some fats are beneficial, while others can be harmful. Knowing the difference can improve our well-being. This blog will explore various types of fat, their roles, and how to include the right fats in your diet.
By the end, you'll have a clear idea of what fats to eat and which to avoid. Ready to dive in and learn more about fats? Let's get started!
The Science Behind Fat
Fat is an essential part of our diet and body. Understanding the science behind fat helps us make better health choices. This article dives into the types of fat and the functions they serve in our bodies. Let's explore the fascinating world of fat.
Types Of Fat
Not all fats are created equal. Some types of fat are good for you, while others can be harmful. Here are the main types of fat:
- Saturated Fat: Found in animal products like meat and dairy. These fats can raise cholesterol levels.
- Unsaturated Fat: Found in plants and fish. These fats can lower cholesterol levels.
- Trans Fat: Found in processed foods. These fats are harmful and can increase the risk of heart disease.
Here is a table summarizing the different types of fat:
| Type of Fat | Source | Health Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Saturated Fat | Meat, dairy | Raises cholesterol levels |
| Unsaturated Fat | Plants, fish | Lowers cholesterol levels |
| Trans Fat | Processed foods | Increases heart disease risk |
Understanding these fats helps in making better dietary choices. Aim for more unsaturated fats and limit saturated and trans fats.
Functions Of Fat In The Body
Fat plays several vital roles in our body. Here are some key functions:
- Energy Storage: Fat stores energy for future use. It acts as a reserve when food intake is low.
- Insulation: Fat helps insulate the body. It keeps us warm by trapping heat.
- Protection: Fat cushions our organs. It acts as a protective layer against physical impact.
- Vitamin Absorption: Fat helps absorb vitamins A, D, E, and K. These are fat-soluble vitamins.
Here is a summary of the functions of fat in the body:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Energy Storage | Stores energy for future use |
| Insulation | Keeps the body warm |
| Protection | Cushions organs |
| Vitamin Absorption | Helps absorb fat-soluble vitamins |
Fat is essential for many bodily functions. Eating the right type and amount of fat can support overall health.
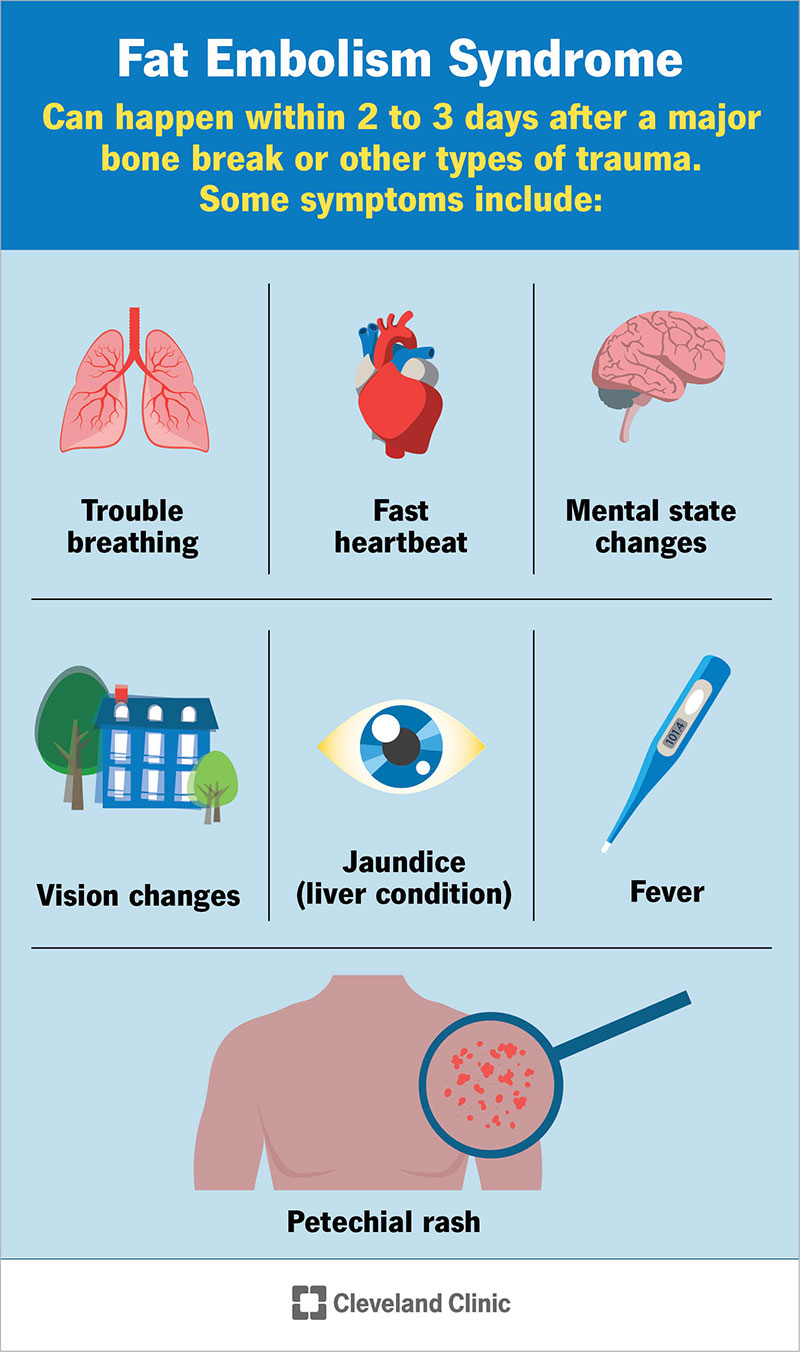
Credit: my.clevelandclinic.org
Health Implications Of Fat Consumption
Fat is an essential part of our diet. It provides energy, supports cell growth, and protects our organs. But not all fats are created equal. Some fats can benefit your health, while others can be harmful. Understanding the health implications of fat consumption can help you make better dietary choices.
Impact Of Saturated Fat
Saturated fat is often found in animal products and some plant oils. These include:
- Butter
- Cheese
- Red meat
- Coconut oil
- Palm oil
Consuming too much saturated fat can raise your LDL cholesterol levels. High LDL cholesterol is linked to an increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
Here are some effects of high saturated fat intake:
- Increased cholesterol levels: Saturated fats can raise total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol levels.
- Heart disease risk: Elevated LDL cholesterol can lead to plaque buildup in arteries, increasing heart disease risk.
- Weight gain: Saturated fats are calorie-dense, which can contribute to weight gain if consumed in excess.
To manage saturated fat intake:
- Choose lean meats and low-fat dairy products.
- Limit consumption of processed foods and baked goods.
- Use healthier cooking oils like olive or canola oil.
Role Of Trans Fat In Health
Trans fats are created through an industrial process that adds hydrogen to liquid vegetable oils. This makes the oils more solid. They are often found in:
- Fried foods
- Baked goods like cookies and cakes
- Margarines
- Snack foods
Trans fats are harmful to your health for several reasons:
- Increased LDL cholesterol: Trans fats raise bad cholesterol levels.
- Decreased HDL cholesterol: They lower good cholesterol levels.
- Inflammation: Trans fats can cause inflammation, which is linked to heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
Reducing trans fat intake is crucial for maintaining good health. Here are some tips:
- Read nutrition labels and avoid products with "partially hydrogenated oils."
- Opt for foods that are labeled as trans fat-free.
- Choose whole, unprocessed foods whenever possible.
Avoiding trans fats can lead to better heart health and lower the risk of chronic diseases.
The Truth About 'good' And 'bad' Fats
Fats are an essential part of our diet, but not all fats are created equal. Understanding the difference between 'good' and 'bad' fats is crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. While some fats provide numerous health benefits, others can increase the risk of various diseases. Let's dive into the truth about 'good' and 'bad' fats.
Unsaturated Fats: The Good Fats
Unsaturated fats are considered good for your health. They are found in various foods and are beneficial in many ways.
There are two main types of unsaturated fats:
- Monounsaturated fats: These are found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts.
- Polyunsaturated fats: These are found in sunflower oil, fish, and walnuts.
Including unsaturated fats in your diet can:
- Reduce bad cholesterol levels.
- Lower the risk of heart disease.
- Provide essential fatty acids that the body cannot produce.
Here's a quick comparison of foods rich in unsaturated fats:
| Food | Type of Unsaturated Fat |
|---|---|
| Olive Oil | Monounsaturated |
| Salmon | Polyunsaturated |
| Avocado | Monounsaturated |
| Walnuts | Polyunsaturated |
Saturated And Trans Fats: The Bad Fats
Saturated and trans fats are considered harmful to your health. They are found in many processed foods and animal products.
Saturated fats can raise the level of cholesterol in your blood, leading to heart disease and stroke. Common sources include:
- Butter
- Cheese
- Red Meat
Trans fats are even worse. They not only raise bad cholesterol but also lower good cholesterol levels. Common sources include:
- Fried foods
- Baked goods
- Margarine
Here is a table to help you identify bad fats:
| Food | Type of Bad Fat |
|---|---|
| Butter | Saturated |
| French Fries | Trans |
| Cheese | Saturated |
| Cookies | Trans |
To maintain good health, limit your intake of saturated and trans fats. Opt for unsaturated fats instead. Your heart will thank you!
Facts Vs. Myths About Fat
Fat often gets a bad reputation in the world of nutrition. Many people believe that all fats are harmful and should be avoided. This is not entirely true. There are many myths about fat that need to be debunked. Understanding the facts about fat can help you make better dietary choices. Let's explore some common myths and facts about fat.
Low-fat Vs. Full-fat Products
Many people think that low-fat products are healthier than full-fat products. This is a common myth. Both have their own benefits and downsides. Here are some key points to consider:
- Low-Fat Products: These products often have added sugars and artificial ingredients to improve taste. This can lead to increased calorie intake.
- Full-Fat Products: Full-fat products are more natural. They often contain fewer artificial ingredients. They can also make you feel full longer, reducing overall calorie consumption.
Let's compare some common low-fat and full-fat products:
| Product | Low-Fat | Full-Fat |
|---|---|---|
| Milk | Contains added sugars | Contains natural fats |
| Yogurt | Often high in sugar | Rich in probiotics |
| Cheese | May contain fillers | Natural source of fat |
Choosing between low-fat and full-fat products depends on your overall diet and health goals. It's important to read labels and be aware of added ingredients.
The Link Between Fat And Weight Gain
Another common myth is that eating fat leads to weight gain. This is not always true. The type of fat and the amount consumed play a big role. Here are some facts:
- Healthy Fats: Unsaturated fats, like those found in olive oil and avocados, can improve heart health. They do not necessarily lead to weight gain.
- Unhealthy Fats: Trans fats and excessive saturated fats can contribute to weight gain and health problems.
It's also important to understand how the body uses fats:
- Energy Source: Fat is a concentrated source of energy. The body uses it for fuel when needed.
- Satiety: Fat helps you feel full and satisfied. This can reduce overall calorie intake.
- Nutrient Absorption: Fat helps in the absorption of essential vitamins like A, D, E, and K.
Balancing fat intake is key. Healthy fats should be part of a balanced diet. Avoiding all fats is not the answer. Understanding the types of fats and their effects can help maintain a healthy weight.
Fat In The Diet
Fat is a vital component of our diet. It provides energy, supports cell growth, and protects our organs. Fat also helps the body absorb certain nutrients. But not all fats are created equal. Understanding the types and sources of fat is key to a healthy diet.
Balancing Fat Intake
Balancing fat intake is essential for overall health. Consuming too much fat can lead to weight gain and other health issues. On the other hand, not getting enough fat can be harmful. Here are some tips for balancing fat intake:
- Limit saturated fats: Found in red meat, butter, and cheese. These fats can raise cholesterol levels and increase heart disease risk.
- Avoid trans fats: Often found in processed foods like snacks and baked goods. Trans fats can increase bad cholesterol and lower good cholesterol.
- Moderate fat intake: Fat should make up about 20-35% of your daily calories.
Consider this sample table to understand daily fat intake based on calorie needs:
| Calorie Needs | Total Fat (grams) | Saturated Fat (grams) |
|---|---|---|
| 1,500 | 33-58 | Less than 15 |
| 2,000 | 44-78 | Less than 20 |
| 2,500 | 56-97 | Less than 25 |
Healthy Fat Sources
Choosing healthy fat sources is crucial for maintaining a balanced diet. Healthy fats can support heart health and provide essential nutrients. Here are some excellent sources of healthy fats:
- Avocados: Rich in monounsaturated fats, avocados can improve heart health.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, and chia seeds are packed with healthy fats, fiber, and protein.
- Olive oil: A good source of monounsaturated fats, olive oil can reduce inflammation and improve cholesterol levels.
- Fatty fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines provide omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health.
- Dark chocolate: Contains healthy fats and antioxidants when consumed in moderation.
Including these healthy fat sources in your diet can provide numerous benefits. They can enhance brain function, reduce inflammation, and improve overall health. Remember to consume these fats in moderation and balance them with other nutrients for optimal health.
The Role Of Fat In A Balanced Diet
Fat often gets a bad reputation, but it plays a crucial role in a balanced diet. Understanding the importance of fat can help you make healthier food choices. Fat is not only a source of energy but also aids in nutrient absorption and helps you feel full. Let's dive into the role of fat in a balanced diet.
Fat's Contribution To Nutrient Absorption
Fat is essential for absorbing certain nutrients. These nutrients include vitamins A, D, E, and K. These vitamins are fat-soluble, meaning they need fat to be absorbed by your body.
Here are some ways fat helps with nutrient absorption:
- Vitamin A: Important for vision, immune function, and reproduction. Found in foods like liver, fish, and dairy.
- Vitamin D: Crucial for bone health and immune function. Found in fatty fish, fortified dairy, and sunlight exposure.
- Vitamin E: Acts as an antioxidant. Found in nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils.
- Vitamin K: Necessary for blood clotting and bone health. Found in leafy greens and some vegetable oils.
Without enough fat in your diet, your body may struggle to absorb these vitamins. This can lead to deficiencies and related health issues. Including healthy fats in your meals helps ensure you get the most out of your food.
Fat's Impact On Satiety
Fat also plays a significant role in helping you feel full and satisfied. Foods high in fat take longer to digest. This slows down the emptying of your stomach, making you feel full for a longer time.
Here are some ways fat impacts satiety:
- Slow Digestion: Fat slows down the digestive process, keeping you full longer.
- Hormone Regulation: Fat helps regulate hormones like leptin, which controls hunger.
- Calorie Density: Fat is calorie-dense, providing more energy per gram compared to proteins and carbs. This can reduce the need for frequent snacking.
Including healthy fats in your diet can help manage hunger and prevent overeating. This is particularly important for weight management and overall health.
Here is a table showing some sources of healthy fats:
| Food | Type of Fat | Health Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Avocado | Monounsaturated Fat | Heart health, anti-inflammatory |
| Olive Oil | Monounsaturated Fat | Reduces bad cholesterol |
| Salmon | Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Brain health, reduces inflammation |
| Nuts | Polyunsaturated Fats | Heart health, rich in antioxidants |
Incorporate these healthy fats into your meals to benefit from their satiety and nutrient absorption properties.
Fat And Chronic Diseases
Fats are an essential part of our diet, providing energy and supporting cell growth. But not all fats are the same, and their impact on our health can be significant. The type and amount of fat we consume can be linked to chronic diseases, such as heart disease and obesity. Understanding the relationship between fat and these conditions is crucial for making healthier choices.
Heart Disease And Fat Connection
Heart disease is one of the leading causes of death worldwide, and dietary fat plays a significant role in its development. Not all fats are bad, but some can increase the risk of heart disease. Let's break down the connection:
- Saturated Fats: Found in animal products like meat and dairy. These can raise LDL cholesterol levels, leading to plaque buildup in arteries.
- Trans Fats: Often found in processed foods. These fats increase bad cholesterol (LDL) and lower good cholesterol (HDL).
- Unsaturated Fats: Found in plants, nuts, and fish. These fats can help reduce bad cholesterol levels and are beneficial for heart health.
Here's a simple table to understand the impact of different types of fats:
| Type of Fat | Source | Impact on Heart Health |
|---|---|---|
| Saturated Fat | Meat, Butter, Cheese | Increases LDL cholesterol |
| Trans Fat | Fried Foods, Baked Goods | Increases LDL, Lowers HDL |
| Unsaturated Fat | Olive Oil, Fish, Nuts | Reduces LDL cholesterol |
Choosing the right type of fat can make a big difference. Replace saturated and trans fats with unsaturated fats to lower the risk of heart disease.
Obesity And Fat Consumption
Obesity is a growing concern globally, and the type of fat consumed plays a role in weight gain. While fats are calorie-dense, not all fats contribute to obesity equally:
- Saturated and Trans Fats: These fats are found in many processed and fast foods. Consuming them in large quantities leads to weight gain.
- Unsaturated Fats: These fats, found in nuts, seeds, and fish, can help manage weight. They are more filling and can reduce overall calorie intake.
Here are some tips to manage fat intake for better weight control:
- Read Labels: Check food labels for fat content, especially saturated and trans fats.
- Cook at Home: Home-cooked meals allow you to control the type and amount of fat used.
- Choose Healthy Snacks: Opt for nuts, seeds, or yogurt instead of chips and cookies.
A balanced diet with the right type of fat can help in maintaining a healthy weight. Focus on incorporating more unsaturated fats and limiting saturated and trans fats to combat obesity.

Credit: www.heart.org
Tips For Healthy Fat Consumption
Fats are essential for our bodies, but not all fats are created equal. Consuming healthy fats in the right amounts can improve heart health, support brain function, and provide energy. Here are some tips for healthy fat consumption to help you make better choices for your diet.
Cooking With Healthy Oils
Choosing the right oils for cooking is crucial for maintaining a healthy diet. Not all oils are good for high-heat cooking, and some can add unhealthy fats to your meals. Here are some tips for using healthy oils:
- Olive Oil: Ideal for low to medium-heat cooking. Rich in monounsaturated fats, it helps reduce bad cholesterol.
- Avocado Oil: Great for high-heat cooking. Contains monounsaturated fats and vitamin E.
- Coconut Oil: Suitable for medium-heat cooking. Contains medium-chain triglycerides that provide quick energy.
- Canola Oil: Versatile for various cooking methods. Low in saturated fat and high in omega-3 fatty acids.
Avoid using oils high in saturated and trans fats, such as:
- Butter
- Margarine
- Vegetable shortening
Here is a quick comparison table to help you choose the best oil for your needs:
| Oil Type | Best For | Fat Content |
|---|---|---|
| Olive Oil | Salads, light sautéing | Monounsaturated fats |
| Avocado Oil | High-heat cooking | Monounsaturated fats |
| Coconut Oil | Baking, medium-heat cooking | Saturated fats |
| Canola Oil | Frying, baking | Polyunsaturated fats |
Reading Food Labels For Fat Content
Understanding food labels can help you make healthier choices. Here are some tips to help you read food labels effectively:
- Check the Serving Size: Always look at the serving size first. This helps you understand the amount of fat per serving.
- Total Fat: This includes all types of fats. Aim for foods with lower total fat content.
- Saturated Fat: Limit foods high in saturated fats. These can raise your cholesterol levels.
- Trans Fat: Avoid trans fats completely. These are harmful and can increase the risk of heart disease.
- Unsaturated Fats: Look for monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. These are the healthy fats.
Here is a simple guide to understand the fat content on labels:
| Fat Type | Recommended Amount |
|---|---|
| Total Fat | 20-35% of daily calories |
| Saturated Fat | Less than 10% of daily calories |
| Trans Fat | 0 grams per day |
| Monounsaturated Fat | Up to 15% of daily calories |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | Up to 10% of daily calories |
By paying attention to these details, you can better manage your fat intake and support your overall health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Healthy Fats?
Healthy fats include unsaturated fats found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. They support heart health and brain function.
Why Is Fat Important In Diet?
Fat is essential for energy, nutrient absorption, and cell growth. It also helps protect organs and maintain body temperature.
How Much Fat Should I Eat Daily?
Adults should consume 20-35% of their daily calories from fat. Choose mostly unsaturated fats for optimal health.
Can Fat Help With Weight Loss?
Yes, healthy fats can aid weight loss by providing satiety and reducing hunger. They also support metabolism.
Conclusion
Understanding fat can lead to better health choices. Choose healthy fats for your diet. These include avocados, nuts, and olive oil. Avoid trans fats found in processed foods. Balance is key in a healthy lifestyle. Small changes can make a big difference.
Stay informed and listen to your body. Healthy eating supports overall well-being. Make smart choices and enjoy better health.






