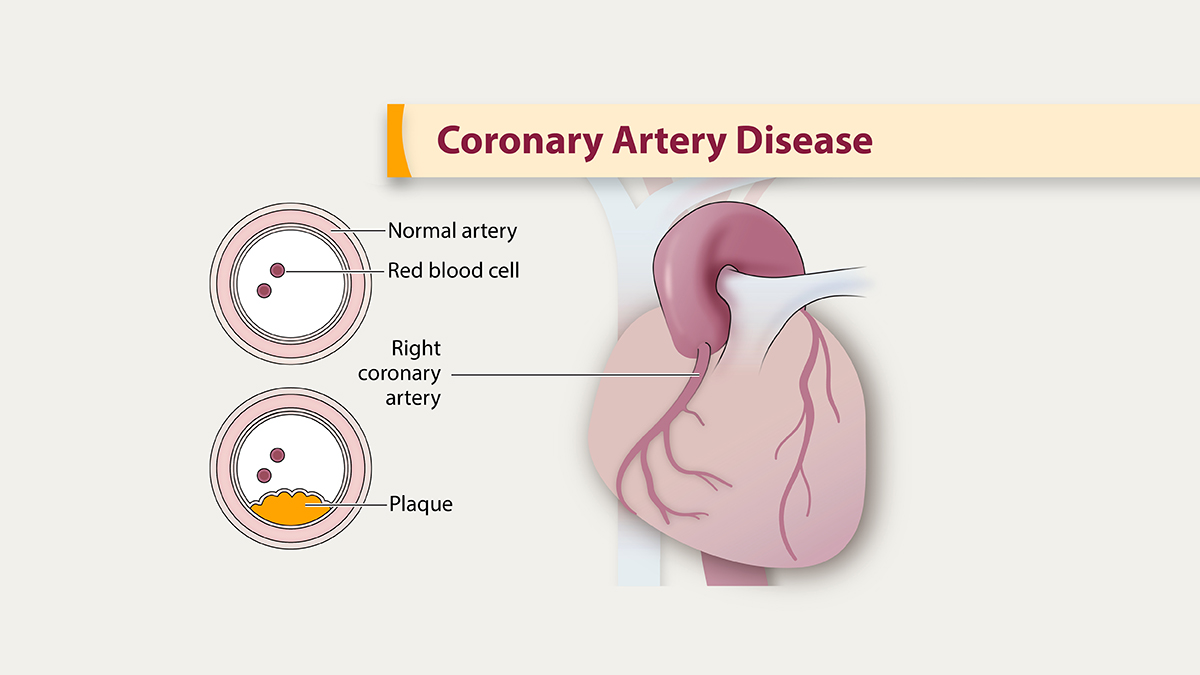
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is a serious heart condition affecting millions worldwide. It occurs when the major blood vessels supplying the heart become damaged or diseased.
Understanding CAD is crucial because it can lead to heart attacks and other severe health issues. This condition develops over time, often without noticeable symptoms until significant damage occurs. Various factors such as lifestyle, genetics, and underlying health conditions contribute to CAD.
Knowing the symptoms, causes, and ways to manage and treat it can save lives. In this blog post, we will explore the essential aspects of Coronary Artery Disease, helping you grasp its impact and how to better care for your heart.

Credit: www.parkwayeast.com.sg
Overview
Coronary artery disease happens when the heart's blood vessels narrow or get blocked. This reduces blood flow and can cause chest pain or heart attacks.
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is a serious condition. It affects the heart's main blood vessels. This disease can lead to heart attacks and other heart problems. Understanding CAD is crucial for maintaining heart health.
What Is Coronary Artery Disease?
Coronary Artery Disease, or CAD, involves the narrowing or blockage of coronary arteries. These arteries supply blood to the heart. When blocked, the heart doesn't get enough oxygen.
Causes Of Cad
Several factors contribute to CAD. Here are some key causes:
- Atherosclerosis: Build-up of plaques in the artery walls.
- High blood pressure: Causes damage to the arteries over time.
- High cholesterol: Leads to plaque formation in the arteries.
- Smoking: Damages the lining of the arteries.
- Diabetes: Increases the risk of plaque build-up.
Symptoms Of Cad
People with CAD may experience various symptoms. These can range from mild to severe:
- Chest pain: Also known as angina.
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing, especially during activities.
- Heart attack: Severe chest pain, nausea, and sweating.
Risk Factors For Cad
Certain factors increase the risk of developing CAD. Being aware of these can help in prevention:
- Age: Risk increases as you get older.
- Gender: Men are at higher risk; women’s risk increases post-menopause.
- Family history: Genetics can play a role.
- Unhealthy diet: High in fats and sugars.
- Physical inactivity: Lack of exercise contributes to CAD.
Diagnosis Of Cad
Doctors use various methods to diagnose CAD. The process usually involves several steps:
- Medical history: Discussion of symptoms and family history.
- Physical exam: Checking for signs of heart disease.
- Tests: Includes ECG, stress tests, and imaging.
Treatment Options For Cad
Treating CAD involves lifestyle changes and medical interventions. Common treatments include:
- Medications: Help manage symptoms and prevent complications.
- Lifestyle changes: Diet, exercise, and quitting smoking.
- Surgical procedures: Angioplasty or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG).
Understanding CAD is key to preventing and managing this condition. Regular check-ups and a healthy lifestyle can make a significant difference.
Symptoms And Causes
Chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue are common symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease. This condition is caused by plaque buildup in the arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart.
Coronary artery disease (CAD) affects many people worldwide. Understanding its symptoms and causes can help in managing it effectively.
Symptoms Of Coronary Artery Disease
Symptoms of CAD vary from person to person. Here are the common signs:
- Chest pain or discomfort: Commonly known as angina.
- Shortness of breath: Often felt during physical activity.
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired.
- Heart attack: Severe chest pain and other symptoms.
Causes Of Coronary Artery Disease
Several factors contribute to CAD. These elements can increase risk:
- High cholesterol: Leads to plaque build-up in arteries.
- High blood pressure: Damages artery walls over time.
- Smoking: Harms blood vessels and heart.
- Diabetes: Increases risk of heart disease.
- Obesity: Extra weight strains the heart.
- Lack of exercise: Leads to poor heart health.
Recognizing Early Signs
Early detection of CAD symptoms is crucial. Noticing subtle signs can prevent severe outcomes.
- Mild chest pain: May feel like pressure or squeezing.
- Discomfort in arms or neck: Often accompanies chest pain.
- Nausea or dizziness: Sometimes linked with heart issues.
- Sweating: Unexplained and excessive.
Risk Factors For Coronary Artery Disease
Certain risk factors increase the chance of developing CAD. Understanding these can aid in prevention.
- Family history: A genetic predisposition to heart issues.
- Age: Risk increases as you get older.
- Gender: Men have a higher risk at a younger age.
- Stress: Can harm heart health over time.
- Unhealthy diet: High in fats and sugars.
Managing Symptoms
Managing CAD symptoms helps improve quality of life. Here are some strategies:
- Medication: Prescribed drugs to control symptoms.
- Lifestyle changes: Diet and exercise adjustments.
- Regular check-ups: Monitoring heart health regularly.
- Stress management: Techniques like meditation or yoga.
Preventative Measures
Preventing CAD involves lifestyle adjustments. These measures can reduce risk:
- Healthy eating: Focus on fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
- Regular exercise: At least 30 minutes most days.
- Quit smoking: Seek help if needed.
- Control cholesterol: Keep levels in check.
- Monitor blood pressure: Regular check-ups to maintain normal levels.
Understanding CAD and its symptoms is vital. Early detection and lifestyle changes can make a big difference.
Diagnosis And Tests
Doctors diagnose Coronary Artery Disease using tests like ECG, stress tests, and angiograms. These tests check for blocked or narrowed arteries.
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is a serious condition where the heart's arteries become narrow or blocked. Timely diagnosis and tests are crucial to managing this condition effectively.
Medical History And Physical Exam
Doctors begin by reviewing medical history and conducting a physical exam. They ask about symptoms, lifestyle, and family history.
- Symptoms: Information about chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue.
- Risk Factors: Details on smoking, diet, exercise, and hypertension.
- Family History: Any heart disease cases in close relatives.
Blood Tests
Next, blood tests are often used to check for signs of heart disease. These tests measure various substances in the blood.
- Cholesterol Levels: High levels may indicate a higher risk.
- Blood Sugar: Elevated levels can be a sign of diabetes.
- Inflammatory Markers: Substances like CRP indicate inflammation in the arteries.
Electrocardiogram (ecg Or Ekg)
An ECG records the heart's electrical activity. It helps to detect irregular heartbeats and other problems. This test is quick and non-invasive.
Stress Testing
Stress tests show how the heart works during physical activity. They help to identify problems that might not be visible when the body is at rest.
- Treadmill Test: The patient walks on a treadmill while the heart is monitored.
- Medication-Induced Stress: Drugs are used to simulate exercise in those unable to perform physical activity.
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram uses ultrasound waves to create images of the heart. This test provides detailed information about heart structure and function.
Coronary Angiography
For more detailed images, coronary angiography is performed. A special dye is injected into the arteries, and X-rays are taken to show blood flow.
- Preparation: Fasting and avoiding certain medications before the test.
- Procedure: Involves inserting a catheter into a blood vessel.
Ct Angiography
CT angiography uses a CT scanner to take images of the coronary arteries. This non-invasive test offers detailed views without the need for catheter insertion.
Mri
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) uses magnetic fields to create detailed heart images. This test helps to evaluate heart muscle and blood flow.
Holter Monitoring
Holter monitors record heart rhythms over 24-48 hours. Patients wear this portable device during their daily activities.
- Usage: Detects irregular heartbeats not caught during a standard ECG.
- Comfort: Small and easy to wear under clothing.
Nuclear Stress Test
Nuclear stress tests involve injecting a radioactive substance to highlight areas of the heart. It shows blood flow and areas with poor circulation.
Cardiac Ct
Cardiac CT scans capture detailed images of the heart and its vessels. It helps to identify calcium buildup in the arteries.
- Procedure: Involves lying still on a table while the scanner takes images.
- Comfort: Non-invasive and quick.
Each of these tests provides valuable insights into heart health. Early diagnosis and proper management can make a significant difference in outcomes.
Management And Treatment
Effective management and treatment of Coronary Artery Disease often involves lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes surgery. Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and quitting smoking can significantly reduce risks.
Coronary artery disease, or CAD, affects millions worldwide. Managing and treating CAD is crucial. Here are some effective ways to manage and treat this condition.
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes can significantly impact CAD management.
- Healthy diet: Eat fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Regular exercise: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate activity daily.
- Smoking cessation: Quit smoking to improve heart health.
- Stress management: Practice relaxation techniques like meditation.
Medications
Medications play a key role in treating CAD. Doctors may prescribe:
- Statins: Lower cholesterol levels.
- Aspirin: Reduce the risk of blood clots.
- Beta-blockers: Decrease heart rate and blood pressure.
- ACE inhibitors: Relax blood vessels and lower blood pressure.
Surgical Procedures
Surgical options are available for severe CAD cases. Procedures include:
- Angioplasty: Opens blocked arteries with a balloon.
- Stent placement: Keeps arteries open.
- Coronary artery bypass grafting: Creates a new path for blood flow.
Regular Monitoring
Regular monitoring is essential for managing CAD effectively.
- Routine check-ups: Regular visits with your doctor.
- Blood tests: Monitor cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
- Blood pressure: Keep track of blood pressure readings.
- Stress tests: Assess heart function under stress.
Alternative Therapies
Some people explore alternative therapies to complement conventional treatments.
- Acupuncture: May help reduce chest pain.
- Herbal supplements: Consult a doctor before use.
- Yoga: Enhances physical and mental well-being.
Importance Of Support
Support systems are vital in CAD management.
- Family support: Encourages lifestyle changes.
- Support groups: Share experiences and coping strategies.
- Professional counseling: Helps manage stress and anxiety.
Managing and treating CAD is a multi-faceted process. Implementing lifestyle changes, adhering to medication regimens, considering surgical procedures, and seeking support can significantly improve quality of life. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice.
Prevention
Regular exercise and a healthy diet help prevent coronary artery disease. Avoid smoking and manage stress for better heart health.
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a serious condition. But, the good news is, it can be prevented. By taking certain steps, you can reduce your risk. Let's explore some key prevention strategies.
Healthy Eating Habits
Eating well helps lower your risk of CAD. Here are some tips to follow:
- Consume more fruits and vegetables: They are rich in vitamins and fiber.
- Choose whole grains: Whole grains provide essential nutrients.
- Limit saturated fats: These can raise cholesterol levels.
- Reduce salt intake: Excess salt can lead to high blood pressure.
- Avoid sugary drinks: These contribute to weight gain and diabetes.
Regular Physical Activity
Exercise is crucial for heart health. It helps keep your arteries clear and strong.
Maintain A Healthy Weight
Keeping a healthy weight is vital. It reduces strain on your heart and lowers blood pressure. A healthy weight also helps control cholesterol and blood sugar levels.
Avoid Smoking
Smoking damages your heart and blood vessels. Quitting smoking can improve your heart health:
- Improves circulation: Better blood flow reduces heart strain.
- Lowers blood pressure: Nicotine raises blood pressure.
- Reduces risk of heart attack: Smokers have a higher risk.
Limit Alcohol Intake
Drinking too much alcohol can harm your heart. Stick to moderate drinking to reduce the risk of CAD.
Manage Stress
Stress affects heart health. Finding ways to manage stress can be beneficial:
- Practice relaxation techniques: Yoga and meditation can help.
- Stay connected: Social support reduces stress.
- Get enough sleep: Good sleep helps manage stress levels.
Regular Health Check-ups
Regular check-ups help detect issues early. This way, you can take action before problems worsen. Keep track of your blood pressure, cholesterol, and glucose levels. Regular tests can spot potential issues early on.
Preventing CAD involves simple, daily habits. Stay committed to these habits for a healthier heart.
Outlook / Prognosis
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) has a varied outlook depending on lifestyle changes and treatment. Early diagnosis and proper management can improve prognosis. Regular check-ups and medication are crucial for maintaining heart health.
Living with coronary artery disease can be challenging. Understanding its outlook and prognosis can help patients manage expectations and improve their quality of life.
Factors Influencing Prognosis
Several factors determine the prognosis of coronary artery disease. Here's a quick look at the main elements:
- Severity of the disease: The extent of artery blockage affects outcomes.
- Age: Older patients may face more complications.
- Lifestyle choices: Smoking, diet, and exercise play significant roles.
- Existing conditions: Diabetes or hypertension can worsen the outlook.
- Timely treatment: Early intervention can improve prognosis.
Treatment Options And Their Impact
Available treatments can greatly influence the prognosis. Let’s explore:
Medications help manage symptoms and prevent complications. Common drugs include:
- Statins: Lower cholesterol levels.
- Beta-blockers: Reduce heart workload.
- Aspirin: Prevent blood clots.
Procedures like angioplasty or bypass surgery can restore blood flow. These interventions significantly improve outcomes.
Long-term Management Strategies
Adopting long-term management strategies is crucial. A few points to consider:
- Regular check-ups: Monitor heart health regularly.
- Healthy diet: Focus on fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Physical activity: Aim for at least 30 minutes daily.
- Quit smoking: Reduces the risk of further complications.
- Stress management: Practices like yoga and meditation help.
Quality Of Life Considerations
Quality of life is a key aspect of managing coronary artery disease. Patients should focus on:
- Emotional well-being: Seek support from friends and family.
- Physical activity: Stay active within comfort levels.
- Social connections: Maintain relationships and engage in community activities.
- Hobbies: Pursue interests to stay mentally engaged.
Regular Monitoring And Follow-up
Ongoing monitoring is essential for managing the disease. Key practices include:
- Routine doctor visits: Keep track of heart health and adjust treatments.
- Blood tests: Monitor cholesterol and blood sugar levels.
- Blood pressure checks: Ensure it stays within a healthy range.
- Heart scans: Detect any changes early.
Understanding these aspects can help patients manage coronary artery disease effectively. With proper care, many can lead fulfilling lives.
How Do I Take Care Of Myself?
Taking care of yourself with coronary artery disease involves a heart-healthy diet and regular exercise. Managing stress and avoiding smoking are also important. Regular check-ups with your doctor help monitor your heart health.
Taking care of yourself when you have coronary artery disease is essential. It helps manage the condition and improves your quality of life. Here are some effective strategies to consider.
Maintain A Heart-healthy Diet
Eating the right foods can make a big difference.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Aim for a variety of colors and types.
- Whole Grains: Choose whole-wheat bread, brown rice, and oats.
- Lean Proteins: Opt for fish, chicken, beans, and nuts.
- Limit Sodium: Use herbs and spices instead of salt.
- Avoid Trans Fats: Check labels and stay away from trans fats.
Regular Physical Activity
Staying active helps your heart stay strong.
Manage Stress
Chronic stress can harm your heart. Here are some tips to manage it:
- Practice Relaxation: Try meditation or deep breathing exercises.
- Stay Connected: Spend time with friends and family.
- Find a Hobby: Engage in activities that bring joy and relaxation.
- Get Enough Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
Regular Check-ups
Regular doctor visits are crucial.
Take Medications As Prescribed
Medications help control symptoms and prevent complications.
- Follow Instructions: Take your medications exactly as prescribed.
- Set Reminders: Use alarms or apps to remember your doses.
- Inform Your Doctor: Report any side effects immediately.
- Keep a List: Track all your medications and dosages.
- Never Skip Doses: Missing doses can worsen your condition.
Avoid Smoking And Limit Alcohol
Smoking and alcohol can harm your heart.
Stay Informed And Educated
Understanding your condition empowers you to make better choices.
- Learn About CAD: Read reliable sources about coronary artery disease.
- Ask Questions: Don't hesitate to ask your doctor for more information.
- Join Support Groups: Connect with others who have CAD.
- Stay Updated: Keep up with the latest research and treatments.
- Share Knowledge: Educate family and friends about your condition.
Coronary Artery Disease And Mental Health
Coronary artery disease affects blood flow to the heart, causing chest pain and other symptoms. It also impacts mental health, leading to anxiety and depression. Proper management includes lifestyle changes and medical treatments.
Coronary artery disease (CAD) impacts both the heart and the mind. Managing CAD involves more than just physical health. Mental well-being plays a crucial role too.
Stress And Its Impact On Cad
Stress can significantly affect CAD. Elevated stress levels may:
- Increase blood pressure: This adds strain on the heart.
- Promote unhealthy habits: Stress often leads to poor diet and smoking.
- Trigger inflammatory responses: Chronic stress can cause inflammation in arteries.
Anxiety And Cad
Living with CAD can cause anxiety. The following points highlight how anxiety affects CAD patients:
- Raises heart rate: Anxiety can make the heart work harder.
- Interferes with sleep: Poor sleep can worsen heart health.
- Leads to avoidance: Anxiety might prevent patients from seeking care.
Depression And Heart Health
Depression often coexists with CAD. This mental health condition can:
- Reduce motivation for self-care: Depression can hinder healthy lifestyle choices.
- Increase inflammation: Chronic depression can cause inflammation in the arteries.
- Lead to isolation: Depressed individuals may avoid social interactions, worsening their condition.
Coping Strategies For Mental Health
Managing mental health is vital for CAD patients. Effective coping strategies include:
- Regular exercise: Physical activity can reduce stress and anxiety.
- Healthy diet: Nutrition impacts both physical and mental health.
- Mindfulness practices: Techniques like meditation help in managing stress.
- Professional support: Therapy or counseling can provide necessary support.
The Role Of Social Support
Social support plays a significant role in managing CAD and mental health. It provides:
- Emotional comfort: Friends and family can offer emotional support.
- Practical assistance: Loved ones can help with daily tasks and appointments.
- Encouragement: A support system motivates positive lifestyle changes.
Understanding the link between CAD and mental health is essential. Addressing both aspects can lead to better overall health outcomes.
Credit: www.cdc.gov
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Coronary Artery Disease?
Coronary artery disease is a condition where the arteries supplying blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked. This is usually due to plaque buildup, which can lead to chest pain, heart attacks, or other heart-related problems.
What Are The Symptoms Of Coronary Artery Disease?
Common symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue. These symptoms may worsen with physical activity. Some people may also experience pain in the neck, jaw, or back.
How Is Coronary Artery Disease Diagnosed?
Diagnosis often involves a physical exam, blood tests, and imaging tests like an EKG or stress test. Doctors may also use coronary angiography to check for blockages.
What Treatments Are Available For Coronary Artery Disease?
Treatment options include lifestyle changes, medications, and procedures like angioplasty or bypass surgery. Your doctor will recommend the best course based on your condition.
Conclusion
Understanding coronary artery disease is essential for better heart health. Recognize symptoms early and seek medical advice. Regular check-ups and tests help detect issues. Effective management and treatment can improve quality of life. Healthy lifestyle choices, like a balanced diet and exercise, are key.
Remember, mental health also impacts heart health. Stay informed and proactive in your care. Take steps today for a healthier tomorrow.






