Autoimmune arthritis affects many people worldwide. It involves the immune system attacking healthy joints.
Understanding autoimmune arthritis is key to managing it effectively. This condition includes several types, each with unique symptoms. Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to better treatment outcomes. Diagnosing autoimmune arthritis involves various tests and procedures. Accurate diagnosis helps in creating a proper treatment plan.
In this blog post, we explore the different types of autoimmune arthritis. We will also discuss the common symptoms and how doctors diagnose this condition. This information can help you or a loved one recognize and seek treatment for autoimmune arthritis. Stay tuned to learn more about this complex condition.
Introduction To Autoimmune Arthritis
Autoimmune arthritis is a group of diseases where the immune system attacks the joints. This causes inflammation, pain, and damage. Understanding this condition helps in managing symptoms and improving life quality.
What Is Autoimmune Arthritis?
Autoimmune arthritis is a chronic condition. The immune system mistakenly targets the body's own tissues. This leads to joint inflammation and damage. Common types include:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Affects joints symmetrically and may impact organs.
- Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA): Linked to psoriasis, causes joint and skin issues.
- Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS): Affects the spine, causing stiffness and pain.
Prevalence And Impact
Autoimmune arthritis affects millions worldwide. Rheumatoid Arthritis impacts about 1% of the global population. Women are more likely to be affected than men. The impact is significant:
| Type | Estimated Prevalence | Common Age of Onset |
|---|---|---|
| Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) | 1% of the global population | 30-60 years |
| Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) | 30% of people with psoriasis | 30-50 years |
| Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) | 0.1-1.4% of the population | Teenage years to early 40s |
Autoimmune arthritis can affect daily life. It limits movement and causes pain. Early diagnosis and treatment help manage symptoms. This improves overall well-being.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder. It causes inflammation in the joints. This can lead to pain, swelling, and stiffness. RA affects people of all ages. It is more common in women than men.
Symptoms Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The symptoms of RA vary from person to person. They can include:
- Joint pain and swelling
- Stiffness in the morning or after inactivity
- Fatigue and weakness
- Fever
- Weight loss
- Small lumps under the skin near joints
These symptoms often start in the small joints of the hands and feet. They can spread to other joints over time. The symptoms can be mild or severe. They can also come and go, known as flare-ups.
Diagnosis Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Doctors use several methods to diagnose RA. These include:
- Medical History: The doctor will ask about symptoms and family history.
- Physical Exam: The doctor will check for swollen joints and test their range of motion.
- Blood Tests: These can detect markers of inflammation and specific antibodies.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, ultrasounds, or MRIs can show joint damage.
Early diagnosis is crucial. It helps start treatment sooner, which can slow the disease's progress.
| Diagnostic Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Medical History | Identify symptoms and family history |
| Physical Exam | Check for swollen joints |
| Blood Tests | Detect inflammation markers |
| Imaging Tests | Show joint damage |
Proper diagnosis and treatment can improve quality of life. It helps manage symptoms and prevent joint damage.
Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) is a type of autoimmune arthritis. It occurs in some people with psoriasis. Psoriasis is a skin condition that causes red, scaly patches. PsA causes joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. It can affect any part of the body. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent joint damage.
Symptoms Of Psoriatic Arthritis
PsA symptoms can vary from person to person. Here are some common symptoms:
- Joint pain and stiffness
- Swelling in fingers and toes
- Red and scaly skin patches
- Fatigue
- Nail changes, such as pitting or separation from the nail bed
- Eye problems, such as redness and pain
Symptoms can be mild or severe. They may affect one or many joints. It is important to recognize these symptoms early.
Diagnosis Of Psoriatic Arthritis
Diagnosing PsA involves several steps. Here are the common methods used:
- Medical History: The doctor will ask about your symptoms and family history of psoriasis or arthritis.
- Physical Examination: The doctor will check for swelling, redness, and joint tenderness.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound can show joint damage.
- Blood Tests: These tests can rule out other types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. If you have psoriasis and experience joint pain, see a doctor. They can help determine if you have PsA and recommend a treatment plan.

Credit: www.pacehospital.com
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) is a form of autoimmune arthritis. It primarily affects the spine, causing inflammation. This inflammation can lead to chronic pain and discomfort. Over time, it may cause the spine to fuse, leading to a loss of flexibility.
Symptoms Of Ankylosing Spondylitis
The symptoms of AS can vary from person to person. Common symptoms include:
- Chronic back pain that worsens with rest and improves with activity
- Stiffness, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity
- Fatigue and tiredness
- Limited movement in the spine
- Pain in the hips and shoulders
- Swelling in the joints
These symptoms may develop gradually. They can often be mistaken for other conditions. Early diagnosis is crucial for managing AS effectively.
Diagnosis Of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Diagnosing AS involves multiple steps. Doctors use a combination of clinical examination and imaging tests.
- Medical History: The doctor will ask about your symptoms and family history.
- Physical Exam: This includes checking your spine's flexibility and areas of pain.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays and MRI scans help detect changes in the spine and joints.
- Blood Tests: These can check for markers of inflammation and the HLA-B27 gene.
Early diagnosis can help manage the condition better. It can also prevent severe complications.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Medical History | Discuss symptoms and family history |
| Physical Exam | Check spine flexibility and pain areas |
| Imaging Tests | X-rays and MRI scans of spine and joints |
| Blood Tests | Check for inflammation markers and HLA-B27 |
Understanding these steps can help you prepare for a diagnosis. It ensures you get the right treatment plan.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It can affect various parts of the body. Joints, skin, kidneys, and the brain are often involved. The immune system attacks healthy tissues by mistake. This causes inflammation and damage.
Many people with SLE experience arthritis. This type of arthritis is known as lupus arthritis. Lupus arthritis can cause pain and swelling in the joints. Understanding the symptoms and diagnosis of lupus arthritis is important.
Symptoms Of Lupus Arthritis
Lupus arthritis often presents with joint pain and stiffness. The pain may be mild or severe. Swelling is common in the joints. The hands, wrists, and knees are frequently affected. Joint pain can come and go. It can also be worse in the morning.
Fatigue is another common symptom. Many people with lupus arthritis feel very tired. Fever, muscle pain, and skin rashes are also possible. The symptoms can mimic other types of arthritis. This makes diagnosis challenging.
Diagnosis Of Lupus Arthritis
Diagnosing lupus arthritis involves several steps. Doctors first review the patient's medical history. A physical exam follows. Blood tests are crucial for diagnosis. They check for specific antibodies. These antibodies are common in lupus patients.
Imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs can be helpful. They show joint damage or inflammation. Sometimes, a doctor may order a urine test. This checks for kidney problems, which are common in lupus. Early diagnosis and treatment are important. They help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Credit: my.clevelandclinic.org
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) is a type of arthritis that affects children under the age of 16. It is one of the most common chronic illnesses in children. JIA causes joint inflammation and stiffness that can last for a few months or a lifetime. It is crucial to recognize the symptoms early to manage the condition effectively.
Symptoms In Children
Children with JIA often experience various symptoms. These symptoms can vary from mild to severe. Common symptoms include:
- Joint pain and swelling: Often in knees, hands, and feet.
- Stiffness: Especially in the morning or after naps.
- Fever: Low-grade fevers that come and go.
- Rashes: Light-pink rashes may appear and disappear.
- Fatigue: Children may tire easily and lack energy.
These symptoms can affect a child's daily activities. They may have difficulty walking or playing. Early diagnosis is essential for better management.
Diagnosis In Children
Diagnosing JIA involves several steps. Doctors use a combination of medical history, physical exams, and tests. Below is a table outlining the common diagnostic steps:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Medical History | Review family history of autoimmune diseases. |
| Physical Exam | Check for joint swelling, pain, and limited movement. |
| Blood Tests | Look for markers of inflammation and autoantibodies. |
| Imaging Tests | X-rays or MRI scans to view joint damage. |
Early diagnosis helps in starting treatment sooner. This can prevent joint damage and improve a child's quality of life. Parents should consult a pediatric rheumatologist for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
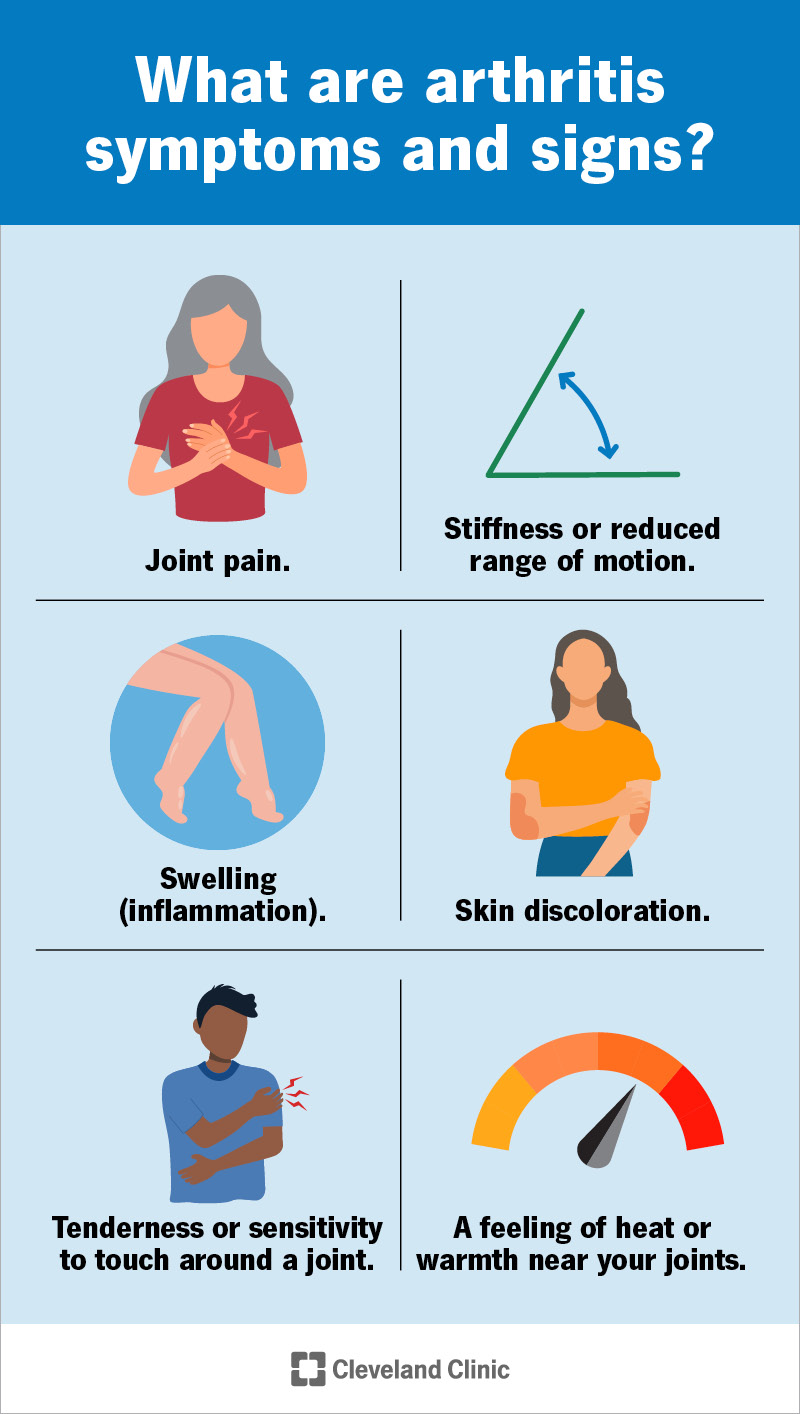
General Symptoms Of Autoimmune Arthritis
Autoimmune arthritis occurs when the body's immune system attacks its own joints. This leads to inflammation, pain, and swelling. Understanding the general symptoms helps in early detection and management.
Early Warning Signs
Early detection can make a significant difference in managing autoimmune arthritis. One of the first signs is joint stiffness, especially in the morning. It can last for more than an hour. Swelling in one or more joints is another early symptom. This swelling often occurs symmetrically, affecting both sides of the body. Mild fever and fatigue can also be early indicators. These symptoms may come and go, making them easy to overlook.
Chronic Symptoms
Chronic symptoms develop as the condition progresses. Persistent joint pain is common. This pain may be constant or flare up at intervals. The affected joints may become deformed over time. This leads to reduced range of motion. Muscle weakness around the affected joints is also frequent. Chronic fatigue becomes more pronounced. It can affect daily activities and overall quality of life. Some people may experience weight loss and dry eyes or mouth.

Credit: www.medicalnewstoday.com
Diagnosing Autoimmune Arthritis
Diagnosing autoimmune arthritis can be challenging. It involves several steps to pinpoint the condition accurately. Early diagnosis is vital. It helps prevent joint damage and manage symptoms. Let's explore the methods used for diagnosis.
Clinical Examinations
Doctors first conduct a clinical examination. They check for joint swelling and tenderness. They assess the range of motion in affected joints. A thorough medical history is also crucial. Doctors ask about family history of autoimmune diseases. They inquire about the duration and severity of symptoms.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests help confirm the diagnosis. Blood tests check for inflammation markers. These include erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP). Other tests identify specific antibodies. Rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) are common ones. They are markers of rheumatoid arthritis.
Additional tests may also be needed. These include a complete blood count (CBC). It helps check for anemia or other abnormalities. Urine tests can also be necessary. They help rule out other conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Autoimmune Arthritis?
Autoimmune arthritis occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the joints. This leads to inflammation and pain. It includes types like rheumatoid arthritis.
What Are Common Symptoms Of Autoimmune Arthritis?
Common symptoms include joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. Fatigue and fever may also occur. Symptoms can vary in severity.
How Is Autoimmune Arthritis Diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a physical exam, blood tests, and imaging studies. Doctors look for inflammation markers and joint damage.
What Types Of Autoimmune Arthritis Exist?
Types include rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. Each type affects the body differently.
Conclusion
Understanding autoimmune arthritis is crucial for managing the condition effectively. Knowing the types and symptoms helps in early detection. Consult a doctor for accurate diagnosis and treatment options. Stay informed and proactive about your health. Regular check-ups ensure better management of autoimmune arthritis.
Living with this condition can be challenging, but proper care makes a difference. Stay strong and seek support when needed.






