Arthritis and bursitis are common conditions that cause joint pain. Both can affect your daily life and movement.
Arthritis involves inflammation of the joints, leading to pain and stiffness. It can affect people of all ages and is often chronic. Bursitis, on the other hand, is the inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles near your joints.
This condition is usually acute and caused by repetitive motion or pressure. Understanding the differences and similarities between arthritis and bursitis can help you manage these conditions better. In this blog post, we will explore what arthritis and bursitis are, how they differ, and how they are diagnosed. This information will provide you with a clearer picture and help you seek appropriate treatment.
Credit: www.towsonortho.com
What Is Bursitis?
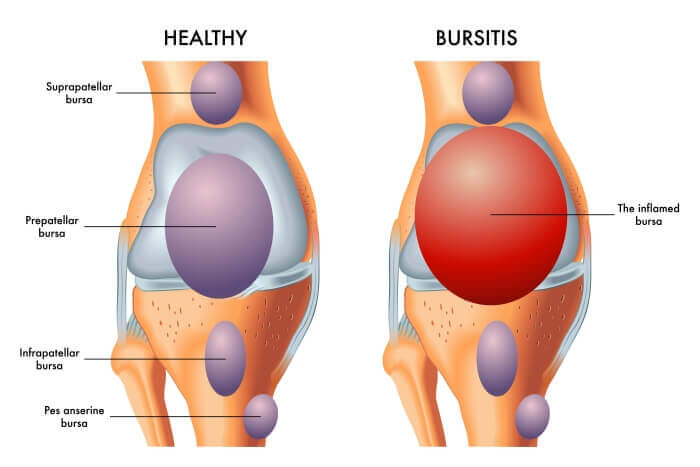
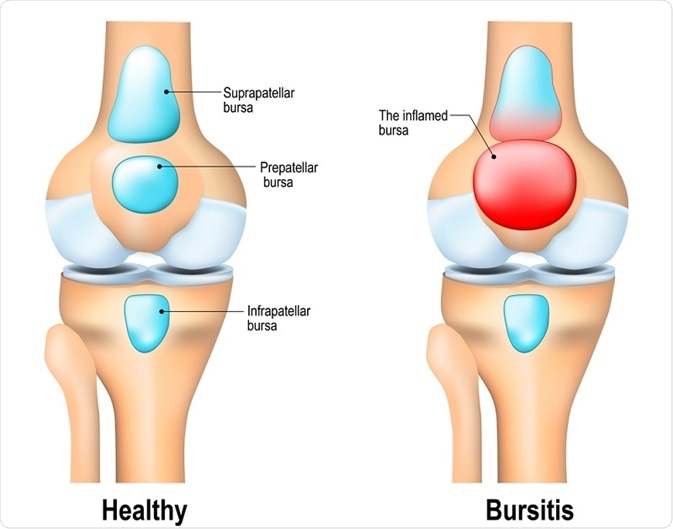
Bursitis is inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion bones, tendons, and muscles. Often linked with arthritis, it causes joint pain and swelling.
Experiencing joint pain can be daunting. Bursitis is a condition that often gets confused with arthritis. To understand it better, let's delve into what bursitis is.
Bursitis is inflammation of the bursa. The bursa is a small fluid-filled sac. It acts as a cushion between bones, tendons, and muscles. Inflammation of the bursa causes pain and discomfort. Let's explore the key facts about bursitis.
Causes Of Bursitis
Different factors can lead to bursitis. Here are some common causes:
- Repetitive Motion: Activities that involve repeated movements can irritate the bursa.
- Trauma or Injury: A sudden impact or injury can inflame the bursa.
- Prolonged Pressure: Continuous pressure on a joint, like kneeling, can cause bursitis.
- Infection: Bacteria can infect the bursa, leading to inflammation.
- Underlying Conditions: Conditions like gout or rheumatoid arthritis can trigger bursitis.
Symptoms Of Bursitis
Recognizing the symptoms of bursitis is crucial. Common signs include:
- Pain: Sharp or aching pain, especially when moving the affected joint.
- Swelling: Visible swelling around the joint area.
- Redness: The area may appear red and feel warm to the touch.
- Limited Movement: Difficulty in moving the joint normally.
- Tenderness: The affected area is sensitive to pressure.
Common Areas Affected By Bursitis
Bursitis can affect various parts of the body. The most common areas include:
- Shoulders: Frequent in people who perform overhead activities.
- Elbows: Often seen in those who lean on their elbows for long periods.
- Hips: Common in runners and athletes.
- Knees: Known as "housemaid's knee" from prolonged kneeling.
- Ankles: Can occur from excessive walking or running.
Treatment Options For Bursitis
Effective treatments can help manage bursitis. Here are some standard options:
- Rest: Avoid activities that worsen the pain.
- Ice Packs: Apply ice to reduce swelling and pain.
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs can help ease symptoms.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen muscles around the joint.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation.
- Surgery: Rarely needed but can remove the inflamed bursa.
Understanding bursitis can aid in managing and preventing this painful condition. Recognize the symptoms early and seek appropriate treatment.
What Is Arthritis?
Arthritis and bursitis are conditions causing joint pain and swelling. Arthritis affects joints directly, while bursitis targets fluid-filled sacs near joints. Both lead to discomfort and can limit movement.
Arthritis is a common condition that affects many people. It can cause pain, stiffness, and swelling in the joints. Understanding what arthritis is can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Types Of Arthritis
There are several types of arthritis. Here are the main ones:
- Osteoarthritis: This is the most common type. It occurs when cartilage breaks down.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: This type is an autoimmune disorder. It attacks the joints.
- Psoriatic Arthritis: Linked with psoriasis. It causes joint pain and swelling.
- Gout: Caused by excess uric acid. Leads to sudden, severe pain.
Symptoms Of Arthritis
Recognizing symptoms early can help in managing arthritis. Common symptoms include:
- Joint Pain: Often worse with movement.
- Swelling: Joints may become swollen and tender.
- Stiffness: Particularly in the morning or after rest.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Difficulty moving the joint fully.
Causes Of Arthritis
Arthritis has various causes. They can differ based on the type of arthritis:
- Genetics: Family history may increase risk.
- Age: Risk increases with age.
- Previous Joint Injury: Injuries can lead to arthritis.
- Obesity: Extra weight puts more stress on joints.
Diagnosis Of Arthritis
Doctors use several methods to diagnose arthritis. These include:
- Physical Examination: Checking for swelling, warmth, and range of motion.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRIs, and ultrasounds can show joint damage.
- Blood Tests: Identifying specific markers of inflammation or autoimmune conditions.
Treatment Options For Arthritis
Managing arthritis often involves a combination of treatments. Here are some common approaches:
- Medications: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen muscles and improve joint function.
- Lifestyle Changes: Weight loss, healthy diet, and regular exercise.
- Surgery: Joint replacement or repair in severe cases.
Understanding these aspects of arthritis can help in managing the condition effectively.
How Arthritis And Bursitis Are Different
Arthritis is inflammation of the joints, causing pain and stiffness. Bursitis involves inflammation of the bursae, the fluid-filled sacs cushioning joints. Both conditions affect movement but in different ways.
Arthritis and bursitis are often confused due to their similar symptoms. However, they are distinct conditions with unique causes and treatments. Understanding their differences can help in proper diagnosis and management.
Causes
Different factors contribute to each condition. Here's a breakdown:
- Arthritis: Caused by joint inflammation or cartilage wear.
- Bursitis: Results from the inflammation of bursae, fluid-filled sacs cushioning joints.
Symptoms
While both conditions cause pain, their symptoms vary:
- Arthritis: Joint pain, stiffness, and swelling.
- Bursitis: Sharp pain in a specific area, often worse with movement.
Affected Areas
Arthritis and bursitis target different parts of the body.
- Arthritis: Commonly affects joints like knees, hips, and fingers.
- Bursitis: Usually found in shoulders, elbows, and hips.
Treatment Options
Managing these conditions involves different approaches. Here’s a brief overview:
- Arthritis: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and physical therapy.
- Bursitis: Rest, ice packs, and anti-inflammatory medications.
Long-term Effects
Long-term effects also differ between the two conditions:
- Arthritis: Can cause chronic pain and joint damage.
- Bursitis: Usually temporary, but can recur if not treated properly.
Understanding these differences is vital. It ensures accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
How Arthritis And Bursitis Are Diagnosed
Doctors diagnose arthritis and bursitis through physical exams and imaging tests like X-rays. Blood tests also help identify inflammation and other markers.
Arthritis and bursitis can both be painful and debilitating conditions. Getting the right diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Doctors use different methods to identify each condition.
Medical History And Physical Examination
Doctors start by asking about symptoms and medical history. This information helps in understanding the problem better.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests are often used to diagnose arthritis and bursitis. Here are some common types:
- X-rays: They help in identifying joint damage and bone changes.
- MRI: This test shows detailed images of soft tissues and bones.
- Ultrasound: Useful for detecting fluid in the bursae or inflammation.
Blood Tests
Blood tests help diagnose arthritis types. Here are some common tests:
- Rheumatoid factor: Indicates rheumatoid arthritis.
- CRP and ESR: Shows inflammation levels in the body.
- ANA test: Checks for autoimmune diseases affecting joints.
Joint Aspiration
Doctors use joint aspiration to diagnose bursitis. A needle removes fluid from the swollen area. This fluid is then tested for infection or crystals. It is a common and effective method.
Differential Diagnosis
Differentiating between arthritis and bursitis is vital. Doctors look at specific symptoms and test results. They consider other possible conditions too. This thorough approach ensures accurate diagnosis.
By understanding these diagnostic methods, patients can better navigate their treatment journey.
Credit: www.news-medical.net
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Bursitis?
Bursitis is the inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs. These sacs cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles near your joints. It commonly affects the shoulder, elbow, and hip.
What Is Arthritis?
Arthritis is a condition causing inflammation of one or more joints. It leads to pain, swelling, stiffness, and decreased joint function. There are over 100 types of arthritis, including osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
How Are Arthritis And Bursitis Different?
Arthritis affects joints directly, causing inflammation inside the joint itself. Bursitis involves inflammation of the bursae around the joint. Both cause pain and swelling but affect different structures.
How Is Bursitis Diagnosed?
Bursitis is diagnosed through a physical exam and medical history. Doctors may use imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs. Sometimes, they perform fluid tests from the affected bursa to confirm the diagnosis.
Conclusion
Understanding arthritis and bursitis helps manage joint pain better. Both conditions cause discomfort. They affect daily activities. Diagnosing early makes a big difference. Treatments and lifestyle changes offer relief. Stay informed. Consult your doctor for the best advice. Live a healthier, more comfortable life.






