Managing type 2 diabetes can feel overwhelming. Diet plays a crucial role in control.
A type 2 diabetes diet focuses on maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. It isn't about strict limitations but making smart food choices. Eating the right foods can help manage your blood sugar and keep you healthy. This diet involves balancing carbs, proteins, and fats to avoid spikes.
It's about eating nutritious, whole foods that support your overall well-being. Understanding what to eat and what to avoid is key. This guide will help you navigate the best dietary choices for type 2 diabetes. By following these guidelines, you can take charge of your health and feel better every day. Ready to learn more? Let's dive in!
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/type-2-diabetes-nutrition-and-weight-loss-4014311-f124cff6544d4b1cbb98b81ac9db0ab0.png)
Credit: www.verywellhealth.com
Introduction To Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a common condition that affects how the body processes blood sugar. Managing this condition often involves dietary changes. In this blog post, we will discuss the basics of Type 2 diabetes and the importance of diet in controlling it.
What Is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition where the body does not use insulin properly. This leads to high levels of blood sugar. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose enter the cells for energy. In Type 2 diabetes, the body either resists the effects of insulin or doesn't produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels.
Key points about Type 2 diabetes:
- Most common form of diabetes.
- Usually occurs in adults, but can appear in children.
- Related to obesity, poor diet, and lack of exercise.
Symptoms of Type 2 diabetes may include:
- Increased thirst and hunger.
- Frequent urination.
- Fatigue.
- Blurred vision.
Here is a simple table that outlines the differences between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes:
| Type 1 Diabetes | Type 2 Diabetes |
|---|---|
| Body doesn't produce insulin. | Body resists insulin or doesn't produce enough. |
| Usually diagnosed in childhood. | Usually diagnosed in adulthood. |
| Requires insulin therapy. | Managed with diet, exercise, and sometimes medication. |
Importance Of Diet
Diet plays a crucial role in managing Type 2 diabetes. Eating the right foods can help control blood sugar levels and prevent complications. A balanced diet helps maintain a healthy weight, which is vital for managing diabetes.
Key components of a diabetes-friendly diet include:
- Plenty of vegetables and fruits.
- Whole grains instead of refined grains.
- Lean proteins like chicken, fish, and beans.
- Healthy fats from nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
- Limited intake of sugary foods and drinks.
Here are some tips for a diabetes-friendly diet:
- Eat smaller portions to avoid overeating.
- Choose foods with a low glycemic index.
- Stay hydrated by drinking water instead of sugary drinks.
- Include fiber-rich foods to help control blood sugar.
- Plan meals to include a variety of nutrients.
Maintaining a balanced diet can help manage blood sugar levels effectively. Regular monitoring and adjustments are essential for long-term health.
Key Nutritional Principles
Living with Type 2 Diabetes requires careful attention to diet. Understanding key nutritional principles can help manage blood sugar levels and improve overall health. These principles include balancing macronutrients and being aware of the glycemic index of foods. Let's explore these concepts in detail.
Balanced Macronutrients
A balanced intake of macronutrients is vital for maintaining blood sugar levels. Macronutrients include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Each plays a crucial role in our body's function.
Carbohydrates provide energy but can spike blood sugar levels. Choose complex carbs, such as whole grains, vegetables, and legumes. These digest slowly, providing a steady energy release.
- Whole grains: brown rice, quinoa, oatmeal
- Vegetables: broccoli, spinach, carrots
- Legumes: lentils, chickpeas, black beans
Proteins are essential for muscle repair and growth. They have a minimal effect on blood sugar. Opt for lean protein sources like:
- Chicken breast
- Fish: salmon, tuna
- Plant-based: tofu, tempeh
Fats are necessary for energy and cell function. Focus on healthy fats that support heart health. Good sources include:
- Avocados
- Nuts: almonds, walnuts
- Seeds: chia, flax
Here's a simple table to summarize:
| Macronutrient | Healthy Sources |
|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | Whole grains, Vegetables, Legumes |
| Proteins | Lean meats, Fish, Plant-based proteins |
| Fats | Avocados, Nuts, Seeds |
Glycemic Index Awareness
The glycemic index (GI) measures how quickly foods raise blood sugar levels. Low-GI foods are better for managing diabetes as they cause slower and smaller increases in blood sugar.
Low-GI foods include:
- Non-starchy vegetables: leafy greens, tomatoes
- Fruits: berries, apples
- Whole grains: barley, bulgur
Moderate-GI foods can be included in moderation:
- Sweet potatoes
- Brown rice
- Whole wheat bread
High-GI foods should be limited or avoided:
- White bread
- Rice cakes
- Potatoes
Here's a table for clarity:
| GI Level | Examples |
|---|---|
| Low | Leafy greens, Berries, Barley |
| Moderate | Sweet potatoes, Brown rice, Whole wheat bread |
| High | White bread, Rice cakes, Potatoes |
Being aware of the glycemic index helps make informed choices. This can significantly impact blood sugar management.
Foods To Embrace
Embracing the right foods is essential in managing Type 2 Diabetes. Your diet plays a crucial role in controlling blood sugar levels and maintaining overall health. By focusing on nutrient-dense foods, you can enjoy a variety of flavors while keeping your condition in check. Let's explore the best foods to include in your diet: whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Whole Grains
Whole grains are a fantastic choice for those with Type 2 Diabetes. They are rich in fiber, which helps stabilize blood sugar levels and keeps you feeling full for longer. Unlike refined grains, whole grains are not stripped of their nutrients during processing. This makes them a healthier option.
Consider adding the following whole grains to your diet:
- Brown Rice: A great source of magnesium and fiber.
- Quinoa: High in protein and contains all nine essential amino acids.
- Oats: Can help lower cholesterol levels and improve heart health.
- Barley: Known for its high fiber content and ability to help regulate blood sugar levels.
Here's a quick comparison of some popular whole grains:
| Grain | Fiber (per 100g) | Protein (per 100g) |
|---|---|---|
| Brown Rice | 1.8g | 2.7g |
| Quinoa | 2.8g | 4.4g |
| Oats | 10.1g | 13.2g |
| Barley | 17.3g | 2.3g |
Lean Proteins
Lean proteins are vital for maintaining muscle mass and keeping you satisfied without adding excessive fat or calories. They help stabilize blood sugar levels and provide the necessary energy to fuel your day.
Top choices for lean proteins include:
- Chicken Breast: Skinless chicken breast is an excellent source of lean protein.
- Turkey: Another poultry option that is low in fat and high in protein.
- Fish: Salmon, tuna, and cod are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and protein.
- Plant-Based Proteins: Lentils, beans, and tofu are great for those following a plant-based diet.
Here's a comparison of lean protein sources:
| Protein Source | Calories (per 100g) | Protein (per 100g) |
|---|---|---|
| Chicken Breast | 165 | 31g |
| Turkey | 135 | 29g |
| Salmon | 208 | 20g |
| Tofu | 76 | 8g |
Healthy Fats
Healthy fats are important for heart health and can help manage Type 2 Diabetes. These fats help reduce inflammation and improve cholesterol levels. Choose unsaturated fats over saturated fats to support your health.
Incorporate these healthy fats into your diet:
- Avocado: Packed with monounsaturated fats and fiber.
- Nuts: Almonds, walnuts, and pistachios are great options.
- Seeds: Chia seeds and flaxseeds are rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
- Olive Oil: A staple in the Mediterranean diet, known for its heart-healthy benefits.
A comparison of healthy fat sources:
| Food | Fat (per 100g) | Type of Fat |
|---|---|---|
| Avocado | 15g | Monounsaturated |
| Almonds | 49g | Monounsaturated |
| Chia Seeds | 31g | Polyunsaturated |
| Olive Oil | 100g | Monounsaturated |
Foods To Avoid
Managing Type 2 Diabetes with a proper diet is essential for maintaining blood sugar levels. Understanding which foods to avoid can help you stay healthy and prevent complications. Below, we will discuss key foods that should be limited or excluded from your diet.
Sugary Beverages
Sugary beverages are high in glucose and can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels. These drinks provide empty calories and lack essential nutrients. Here are some common sugary beverages to avoid:
- Regular Soda
- Fruit Juices
- Energy Drinks
- Sweetened Coffee and Tea
Consider the following table for healthier alternatives:
| Sugary Beverage | Healthier Alternative |
|---|---|
| Regular Soda | Diet Soda or Sparkling Water |
| Fruit Juices | Whole Fruits |
| Energy Drinks | Herbal Tea |
| Sweetened Coffee and Tea | Black Coffee or Unsweetened Tea |
Opting for these alternatives can help manage your blood sugar levels effectively. Always check labels for hidden sugars in beverages.
Processed Foods
Processed foods often contain high levels of unhealthy fats, sodium, and sugars. These ingredients can adversely affect blood sugar levels and overall health. Some examples of processed foods include:
- Packaged Snacks
- Frozen Meals
- Processed Meats
- Fast Food Items
Processed foods are often low in fiber and essential nutrients. They can lead to weight gain and increased insulin resistance. Here are some tips to avoid processed foods:
- Read ingredient labels carefully.
- Choose whole, unprocessed foods.
- Cook meals at home using fresh ingredients.
- Snack on nuts, seeds, and fresh vegetables.
Making these changes can improve your diet and help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Refined Carbs
Refined carbohydrates, such as white bread and pasta, can cause blood sugar spikes. These foods have been stripped of most nutrients and fiber, leading to quick digestion and absorption. Examples of refined carbs to avoid include:
- White Bread
- White Rice
- Pastries
- Breakfast Cereals
Refined carbs can increase hunger and lead to overeating. They can also contribute to weight gain and poor blood sugar control. Here is a table with better alternatives:
| Refined Carbs | Healthier Alternative |
|---|---|
| White Bread | Whole Grain Bread |
| White Rice | Brown Rice or Quinoa |
| Pastries | Fruit with Greek Yogurt |
| Breakfast Cereals | Oatmeal |
Switching to these healthier options can help keep your blood sugar levels in check.
Meal Planning Tips
Managing Type 2 Diabetes involves making smart food choices. A well-planned diet can help maintain blood sugar levels. Here are some meal planning tips to keep your diet on track and support your health.
Portion Control
Controlling portion sizes is crucial for managing Type 2 Diabetes. Eating too much, even of healthy foods, can spike blood sugar levels. Here are some tips to help with portion control:
- Use Smaller Plates: Smaller plates can make portions look bigger, tricking your brain into feeling satisfied with less.
- Measure Your Food: Use measuring cups and spoons to ensure accurate portions.
- Read Nutrition Labels: Check serving sizes on packaged foods to avoid overeating.
Here's a simple table to guide you on portion sizes:
| Food Type | Portion Size |
|---|---|
| Grains | 1/2 cup cooked |
| Vegetables | 1 cup raw or 1/2 cup cooked |
| Fruits | 1 small piece or 1/2 cup |
| Protein | 3 oz cooked meat or 1/2 cup beans |
By keeping portions in check, you can better manage your blood sugar levels. It helps to eat slowly and savor your food. This allows your body to signal when it’s full, preventing overeating.
Smart Snacking
Snacking can be part of a healthy diet, but it’s important to choose snacks wisely. Unhealthy snacks can cause blood sugar spikes. Here are some tips for smart snacking:
- Choose Whole Foods: Opt for fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds.
- Pair Protein with Carbs: Combine a small apple with a tablespoon of peanut butter.
- Avoid Sugary Snacks: Skip candy, cookies, and sugary drinks.
Here are some smart snack ideas:
| Snack | Description |
|---|---|
| Greek Yogurt | Low in sugar, high in protein |
| Carrot Sticks | Crunchy and rich in fiber |
| Almonds | Good source of healthy fats |
| Berries | Low glycemic and full of antioxidants |
Planning ahead can help you make healthier snack choices. Keep healthy snacks on hand to avoid reaching for unhealthy options. Drinking water can also help you feel full between meals.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Incorporating Exercise
Managing Type 2 Diabetes involves more than just monitoring blood sugar levels. A balanced diet, combined with regular exercise, plays a crucial role in managing this condition. Incorporating exercise into your daily routine can significantly improve your overall health and help you manage Type 2 Diabetes more effectively.
Benefits Of Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity offers numerous benefits for individuals with Type 2 Diabetes. Exercise helps in:
- Lowering blood sugar levels: Physical activity helps your muscles use glucose for energy, which lowers your blood sugar levels.
- Improving insulin sensitivity: Regular exercise can make your body more responsive to insulin, reducing the need for medication.
- Weight management: Exercise aids in maintaining a healthy weight, which is critical for managing diabetes.
- Boosting cardiovascular health: Physical activity strengthens your heart and improves circulation, reducing the risk of heart disease.
To illustrate the impact of exercise on blood sugar levels, consider the table below:
| Activity Level | Reduction in Blood Sugar |
|---|---|
| Light Activity (e.g., walking) | 5-10% |
| Moderate Activity (e.g., brisk walking) | 10-20% |
| Vigorous Activity (e.g., running) | 20-30% |
Types Of Exercises
Various types of exercises can benefit those with Type 2 Diabetes. Here are some recommended activities:
- Aerobic exercises: Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling improve heart health and burn calories. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise per week.
- Strength training: Lifting weights or using resistance bands helps build muscle mass. Strong muscles use glucose more efficiently, reducing blood sugar levels. Try to include strength training exercises at least twice a week.
- Flexibility exercises: Yoga and stretching improve flexibility and reduce stress. These activities can also help with balance, reducing the risk of falls.
- Balance exercises: Activities like Tai Chi can improve balance and coordination. This is especially important for older adults to prevent falls.
Incorporating these exercises into your routine can significantly improve your health. Remember to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise program.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring blood sugar levels is a crucial part of managing type 2 diabetes. Keeping track of your blood sugar helps you understand how food, activity, and medication affect your glucose levels. This understanding allows for better management of your diet and lifestyle to maintain a healthy balance.
When To Test
Testing your blood sugar levels at the right times can provide valuable insights. Here are some key times to consider:
- Before Meals: This helps understand how your body manages glucose without food.
- After Meals: Testing 1-2 hours post-meal shows how your body responds to the food.
- Before Bed: Ensures your levels are safe before sleeping.
- When Feeling Unwell: Illness or stress can affect blood sugar.
- Before and After Exercise: Helps see how physical activity impacts your levels.
Some individuals might need to test more frequently, while others less. Discuss with your doctor to determine the best schedule for you. Regular testing helps you recognize patterns and make adjustments to your diet or medication as needed.
Interpreting Results
Understanding your blood sugar readings is key to managing diabetes effectively. Here are some general guidelines:
| Time | Target Range (mg/dL) |
|---|---|
| Before Meals | 80-130 |
| 1-2 Hours After Meals | Less than 180 |
| Before Bed | 100-140 |
If your readings are consistently outside these ranges, it may be time to adjust your diet or medication. Here are some steps to help:
- Keep a Log: Track your readings, meals, and activities.
- Identify Patterns: Look for trends in your blood sugar levels.
- Consult Your Doctor: Share your log with your healthcare provider for advice.
Understanding your blood sugar patterns can help you make informed decisions about your diet and lifestyle. This proactive approach helps in keeping your diabetes under control.
Long-term Dietary Strategies
Managing Type 2 diabetes requires a long-term dietary strategy. These strategies help control blood sugar levels and maintain overall health. Making sustainable changes and seeking professional guidance are key components of a successful diet plan.
Sustainable Changes
Making sustainable changes is crucial for managing Type 2 diabetes. These changes should be practical and long-lasting. Small, consistent adjustments can lead to significant improvements over time.
Here are some sustainable dietary changes:
- Increase Fiber Intake: Choose whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. Fiber helps control blood sugar levels.
- Control Portion Sizes: Eat smaller, balanced meals. This helps prevent blood sugar spikes.
- Reduce Sugar and Refined Carbs: Avoid sugary drinks and snacks. Choose complex carbohydrates like brown rice and whole wheat bread.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water. Avoid sugary beverages.
Implementing these changes is easier with a plan. Here is a simple table to guide your meals:
| Meal | Example |
|---|---|
| Breakfast | Oatmeal with berries and nuts |
| Lunch | Grilled chicken salad with mixed greens |
| Dinner | Baked salmon with quinoa and steamed broccoli |
| Snack | Apple slices with almond butter |
Remember, consistency is key. Stick to these changes for the best results.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Consulting a professional can greatly enhance your dietary strategy. Registered dietitians and diabetes educators provide personalized advice. They tailor recommendations to your specific needs.
Benefits of professional guidance include:
- Customized Meal Plans: Professionals create meal plans based on your lifestyle and preferences.
- Education: Learn about the impact of different foods on blood sugar levels.
- Support: Get ongoing support and motivation. Regular check-ins help stay on track.
Professional advice ensures you make informed choices. They help in setting realistic goals and tracking progress. This support system is essential for long-term success.
Here are some tips for finding the right professional:
- Check Credentials: Look for certified dietitians or diabetes educators.
- Read Reviews: Look up reviews or testimonials from other patients.
- Ask Questions: Ensure they understand your needs and goals.
Professional guidance bridges the gap between knowledge and action. It provides the tools and support needed for a healthy lifestyle.
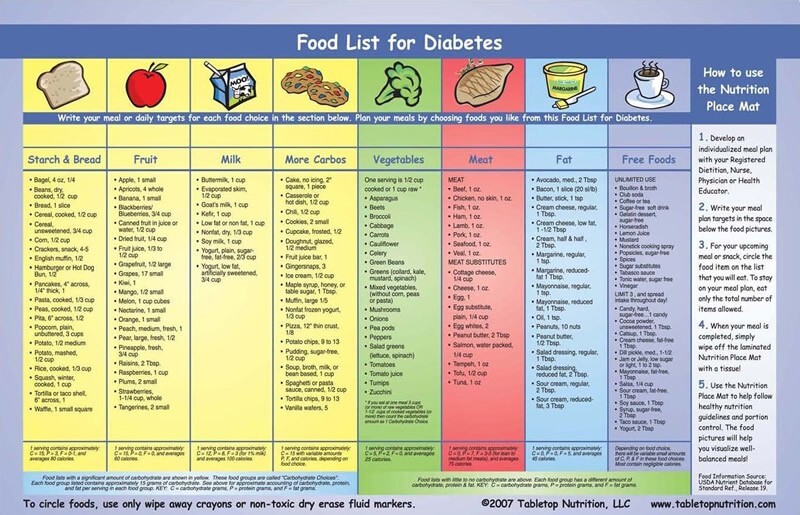
Credit: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Frequently Asked Questions
What Foods Should Type 2 Diabetics Avoid?
Type 2 diabetics should avoid sugary drinks, refined carbs, and trans fats. These foods can spike blood sugar levels. Limit processed snacks and sweets. Choose whole foods instead.
Can Type 2 Diabetes Be Managed With Diet?
Yes, Type 2 diabetes can be managed with a healthy diet. Focus on low-carb, high-fiber foods. Balance protein and fats. Regular meals and healthy snacks help maintain blood sugar levels.
What Is A Good Breakfast For Diabetics?
A good breakfast for diabetics includes eggs, whole grains, and vegetables. Greek yogurt with berries and nuts is also a healthy option. Avoid sugary cereals and pastries.
How Does Fiber Affect Type 2 Diabetes?
Fiber helps manage Type 2 diabetes by controlling blood sugar levels. It slows down sugar absorption. High-fiber foods include vegetables, fruits, and whole grains. Aim for at least 25-30 grams daily.
Conclusion
Managing type 2 diabetes with a good diet is crucial. Choose whole grains, lean proteins, and vegetables. Avoid sugary drinks and processed foods. Listen to your body and make healthy choices. Regular meals and snacks can help maintain blood sugar levels.
Stay active and hydrated for better results. Consult your doctor for personalized advice. Small changes can lead to big improvements. Your health is worth the effort. Take one step at a time.






