Managing diabetes involves more than just watching what you eat. Meal timing plays a crucial role in controlling blood sugar levels.
Understanding when to eat can greatly improve your glucose control. Many people focus solely on their diet, but meal timing is just as important. Eating at the right times helps keep your blood sugar stable throughout the day. This can prevent spikes and drops in glucose levels, which can be harmful.
In this blog post, we will explore why meal timing matters for diabetes management. You will learn how to schedule your meals to keep your blood sugar in check. This information can help you live a healthier, more balanced life with diabetes.
Importance Of Meal Timing
Understanding the importance of meal timing is crucial for individuals managing diabetes. Meal timing can significantly impact blood glucose levels. Eating at specific times can help keep glucose levels stable and within the target range. This can prevent both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia. Let's explore why meal timing matters for glucose control and diabetes management.
Impact On Glucose Levels
Eating regular meals helps maintain stable glucose levels. Skipping meals or eating at irregular times can cause glucose spikes or drops. Consistent meal timing allows the body to process food more efficiently. This helps prevent sudden changes in blood sugar levels. Balanced glucose levels reduce the risk of complications.
Role In Diabetes Management
Proper meal timing is a key component of diabetes management. Eating at regular intervals helps keep blood glucose levels predictable. This makes it easier to manage diabetes with medications or insulin. Consistent meal timing also supports better energy levels. Regular eating patterns can improve overall health and well-being for diabetics.
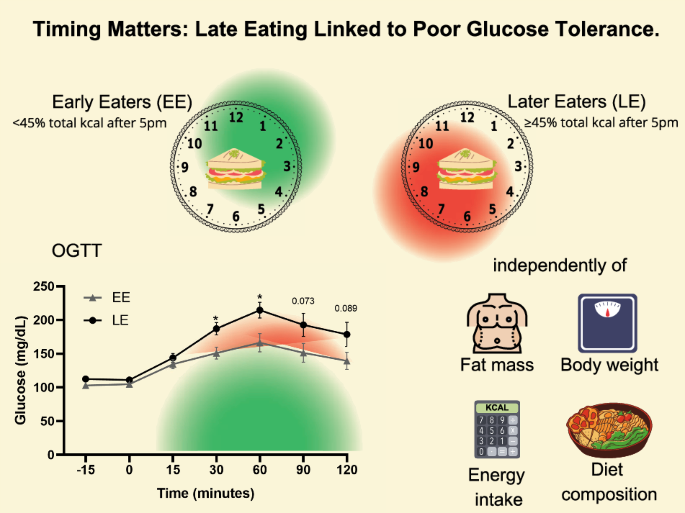
Credit: www.nature.com
Breakfast Timing
Understanding the best time to eat breakfast can help control glucose levels. Breakfast is an important meal for people with diabetes. It sets the tone for the rest of the day. Proper timing can significantly impact blood sugar levels.
Ideal Time To Eat
The ideal time to eat breakfast is within an hour of waking up. This helps keep blood sugar levels stable. Eating soon after waking can prevent glucose spikes. It also supports steady energy levels throughout the morning.
Effects On Morning Glucose
Eating breakfast at the right time can affect morning glucose levels. Skipping breakfast or eating too late can cause blood sugar to rise. A balanced breakfast helps maintain normal glucose levels. This reduces the risk of complications related to diabetes.
Lunch Scheduling
Effective lunch scheduling can play a crucial role in managing diabetes. Eating at consistent times helps maintain stable blood glucose levels. This section explores the benefits and impacts of a well-timed midday meal.
Midday Meal Benefits
Eating lunch at a regular time brings numerous advantages:
- Prevents late afternoon cravings.
- Boosts metabolism for the rest of the day.
- Provides steady energy levels, avoiding post-lunch sluggishness.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Craving Control | Reduces the urge for unhealthy snacks later. |
| Metabolism Boost | Keeps your body's energy-burning process active. |
| Steady Energy | Maintains consistent energy, preventing post-lunch dips. |
Impact On Afternoon Glucose
Timing lunch correctly influences afternoon glucose levels:
- Eating lunch too late can cause glucose spikes.
- Consistent lunch timing helps avoid low blood sugar episodes.
- Balanced meals at lunch ensure gradual glucose release.
Consider these tips to optimize your lunch timing:
- Eat between 12 PM and 1 PM: This window helps maintain a stable glucose level.
- Include protein and fiber: These components slow down glucose absorption.
- Avoid high-sugar foods: They cause rapid glucose spikes and drops.
Use these strategies to make your lunch a powerful tool for managing diabetes.
Dinner Time Considerations
Managing diabetes requires careful attention to meal timing. Dinner is crucial for maintaining balanced glucose levels overnight. Eating at the right time can help prevent blood sugar spikes or drops.
Optimal Evening Meal Time
Dinner time should ideally be two to three hours before bedtime. This allows enough time for digestion and absorption of nutrients. Aim for a consistent schedule to help your body develop a routine. A regular dinner time can help maintain steady glucose levels.
Effects On Overnight Glucose
Eating late can raise blood sugar levels overnight. This happens because the body has less time to process the food. Elevated glucose levels at night can disrupt sleep and lead to higher readings in the morning.
Consider choosing foods with a low glycemic index for dinner. These foods digest slowly and help keep blood sugar levels stable. Here are some examples:
- Non-starchy vegetables
- Lean proteins like chicken or fish
- Whole grains like quinoa or brown rice
It is also essential to monitor portion sizes. Overeating at dinner can cause spikes in blood sugar. Keep meals balanced with a mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
Some people with diabetes may experience the "dawn phenomenon." This is a rise in blood sugar early in the morning. Eating dinner earlier can help counteract this effect. If you experience this, consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
| Timing | Impact on Glucose |
|---|---|
| 2-3 hours before bedtime | Helps maintain stable levels |
| Right before bed | May cause higher overnight levels |
In summary, the timing of your dinner plays a crucial role in managing diabetes. Eating at the optimal time can help maintain balanced glucose levels, leading to better overall health.
Snacking Strategies
Managing diabetes often means paying attention to meal timing. Snacks play an important role in stabilizing blood sugar levels. With the right strategies, you can enjoy snacks while keeping your glucose in check.
Best Times For Snacks
Knowing when to snack is just as important as what to snack on. Here are some ideal times:
- Mid-morning: A small snack can prevent blood sugar dips between breakfast and lunch.
- Mid-afternoon: This helps manage energy levels and avoid overeating at dinner.
- Before bedtime: A light snack can prevent nighttime hypoglycemia.
Healthy Snack Options
Choosing the right snacks can make a big difference. Here are some healthy options:
| Snack | Serving Size | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Apple slices with peanut butter | 1 medium apple, 1 tbsp peanut butter | Fiber, healthy fats, protein |
| Greek yogurt with berries | 1 cup yogurt, 1/2 cup berries | Probiotics, antioxidants, protein |
| Carrot sticks with hummus | 1 cup carrots, 2 tbsp hummus | Vitamins, fiber, protein |
| Mixed nuts | 1/4 cup | Healthy fats, protein |
| Cheese and whole-grain crackers | 1 oz cheese, 5 crackers | Calcium, fiber, protein |
Remember to listen to your body. Choose snacks that satisfy your hunger and help maintain stable glucose levels.
Exercise And Meal Timing
Balancing exercise and meal timing is crucial for people with diabetes. It helps in controlling blood glucose levels effectively. Proper nutrition before and after exercise can make a significant difference. This section explains the importance of pre-exercise meals and post-exercise nutrition.
Pre-exercise Meals
Eating the right foods before exercise is important. It provides the energy needed to perform well. Here are some tips for a pre-exercise meal:
- Eat a small meal or snack 30-60 minutes before exercising.
- Include a mix of carbohydrates and proteins.
- Avoid high-fat and high-fiber foods. They can slow digestion.
Here are some examples of good pre-exercise meals:
| Food | Portion Size |
|---|---|
| Banana and a handful of nuts | 1 medium banana, 10-15 nuts |
| Greek yogurt with berries | 1 cup yogurt, 1/2 cup berries |
| Whole grain toast with peanut butter | 1 slice toast, 1 tablespoon peanut butter |
Post-exercise Nutrition
Eating after exercise helps replenish energy stores and repair muscles. Aim to eat within 30 minutes to 2 hours post-exercise. Here’s what to include:
- Carbohydrates to restore energy.
- Proteins to help muscle repair.
- Stay hydrated. Drink plenty of water.
Some examples of good post-exercise snacks or meals:
- Grilled chicken with quinoa and vegetables.
- Protein shake with a piece of fruit.
- Cottage cheese with pineapple.
Balance and timing are key to managing diabetes. This ensures you stay healthy and active.
Meal Frequency
Managing diabetes involves more than just watching what you eat. When you eat can be just as important. Choosing the right meal frequency can help control your blood glucose levels. The debate often centers around three meals a day versus small frequent meals. Let’s dive into these options.
Three Meals A Day Vs. Small Frequent Meals
Many people find it easier to stick to a routine of three balanced meals a day. This traditional approach includes breakfast, lunch, and dinner. Each meal is spaced out evenly, providing a structured eating schedule.
On the other hand, some prefer small frequent meals throughout the day. This could mean eating five to six smaller meals instead of three larger ones. The idea is to keep your blood sugar levels stable by not going too long without eating.
| Three Meals a Day | Small Frequent Meals |
|---|---|
| Structured and predictable | More flexible |
| May feel fuller longer | Less likely to feel hungry |
| Potential for larger glucose spikes | Steady glucose levels |
Impact On Glucose Stability
Glucose stability is crucial for managing diabetes. Eating three meals a day can sometimes lead to glucose spikes. This happens if meals are too large or too high in carbs.
Small frequent meals can help keep blood sugar levels stable. Eating more often means smaller amounts of food at each sitting. This can lead to smaller glucose increases.
- Three meals a day: Potential for higher glucose spikes after meals.
- Small frequent meals: Helps maintain steady glucose levels.
Both approaches have their benefits. The right choice depends on individual preferences and lifestyle. Consult with your healthcare provider to find what works best for you.

Credit: www.medicalnewstoday.com
Personalizing Meal Timing
Personalizing meal timing can make a big difference in managing diabetes. Everyone has a different daily schedule and unique glucose patterns. These need special attention. This approach helps in better glucose control and overall health.
Considering Individual Schedules
Each person has a unique routine. Some work early while others work late. Understanding your daily pattern can help you plan meals better. Eating at regular times helps to manage glucose levels. Skipping meals can cause blood sugar spikes. So, it's important to eat on time.
If you have a busy schedule, plan your meals in advance. Keep healthy snacks handy. This way you can eat even if you are busy. Consistency is key. Try to eat your meals at the same time each day. It helps in maintaining stable glucose levels.
Tailoring Based On Glucose Monitoring
Regular glucose monitoring is essential. It helps you understand how your body reacts to different foods. You can use this information to adjust your meal timing. If you notice high glucose levels in the morning, you might need to adjust your breakfast time.
Keep a log of your glucose levels. Note the time you eat and the foods you consume. This can help in identifying patterns. You can then discuss these with your healthcare provider. They can help you make necessary adjustments to your meal timing.
Remember, what works for one person may not work for another. Personalization is key. Tailoring meal timing based on your glucose monitoring can lead to better management of diabetes. It's all about finding what works best for you.
Frequently Asked Questions
When Should Diabetics Eat Meals?
Diabetics should eat meals at regular intervals. Consistent meal timing helps manage blood sugar levels. Aim for balanced meals every 4-5 hours.
Is Breakfast Important For Diabetics?
Yes, breakfast is crucial for diabetics. It helps stabilize blood sugar levels after fasting overnight. Include protein and fiber.
How Late Can Diabetics Eat Dinner?
Diabetics should eat dinner 2-3 hours before bedtime. This helps prevent nighttime blood sugar spikes. Choose balanced, low-glycemic meals.
Are Snacks Necessary For Diabetics?
Snacks can help diabetics manage blood sugar. Healthy snacks between meals can prevent blood sugar dips. Choose low-carb, high-fiber options.
Conclusion
Eating at the right times helps control glucose levels effectively. Consistent meal timing supports stable blood sugar. Plan meals and snacks wisely. Listen to your body's hunger signals. Stay hydrated and choose healthy foods. Maintain a regular eating schedule. This helps with overall health and diabetes management.
Small changes can make a big impact. Focus on balanced meals and timing. This strategy can lead to better glucose control.






