Chest pain can be scary. It's often linked to heart attacks.
But, not all chest pain means a heart attack. Many other conditions can cause chest pain. Knowing these causes helps you stay calm and find the right treatment. It’s essential to understand your body’s signals. We explore nine different reasons for chest pain that are not heart-related.
By learning more, you can better manage your health and avoid unnecessary worry. Let's dive into these surprising causes of chest pain.
Muscle Strain
Experiencing chest pain can be alarming. Not all chest pain signals a heart attack. One common cause is muscle strain. This happens when chest muscles get overworked or injured. Muscle strain can mimic heart attack pain, causing undue worry.
Symptoms
Muscle strain pain often feels sharp or aching. It can worsen with movement or touch. Breathing deeply or coughing might also increase the pain. The pain is usually localized. It can be felt in a specific area of the chest, unlike heart attack pain, which can radiate.
Treatment
Rest is crucial. Avoid activities that strain the chest muscles. Applying ice can reduce inflammation and pain. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can help. Gentle stretching exercises can also aid recovery. If the pain persists, seek medical advice.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Health-heart-attack-symptoms-7482380-Horiz-V2-ec0945e6f85049c9a6971863e87aed13.jpg)
Credit: www.health.com
Acid Reflux
Experiencing chest pain can be alarming. Many assume it's a heart attack. But, there are other causes. One common cause is acid reflux. This condition, also known as GERD, happens when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus. It can cause discomfort and burning sensations in the chest.
Symptoms
Acid reflux has distinct symptoms. The most common is heartburn. This feels like a burning pain in the chest. It often occurs after eating. Another symptom is regurgitation. This is when acid or food comes back up into the throat. Some people may also experience a bitter or sour taste in their mouth. Difficulty swallowing and a feeling of a lump in the throat are other symptoms.
Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle changes can help manage acid reflux. Start by eating smaller meals. Large meals can increase the chance of acid reflux. Avoid lying down right after eating. Wait at least three hours before lying down. Elevate the head of your bed by six to eight inches. This helps prevent acid from flowing back into the esophagus.
Identify and avoid trigger foods. Common triggers include spicy foods, citrus fruits, and fatty foods. Chocolate, caffeine, and alcohol can also cause problems. Maintain a healthy weight. Excess weight can put pressure on the stomach, causing acid reflux.
Quit smoking. Smoking weakens the lower esophageal sphincter, making acid reflux more likely. Wear loose-fitting clothes. Tight clothing can squeeze the stomach, pushing acid into the esophagus. Drink plenty of water. Staying hydrated can help reduce acid reflux symptoms.
Costochondritis
Chest pain can be alarming. Many people fear it's a heart attack. But there are other causes. One common cause is costochondritis. This condition involves inflammation of the cartilage that connects the ribs to the breastbone. Let's explore the symptoms and treatment options for costochondritis.
Symptoms
Costochondritis causes sharp pain in the chest. The pain can be mistaken for a heart attack. It usually worsens with movement or deep breaths. Pressing on the rib joints might increase the pain. The pain can also spread to the abdomen or back. It's important to note that this pain is usually localized.
Treatment Options
There are several treatment options for costochondritis. Rest is crucial. Avoid activities that worsen the pain. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can help. Applying heat or ice packs can reduce inflammation. Gentle stretching exercises might also be beneficial. In severe cases, doctors may recommend physical therapy or steroid injections. Always consult a healthcare provider for persistent pain.
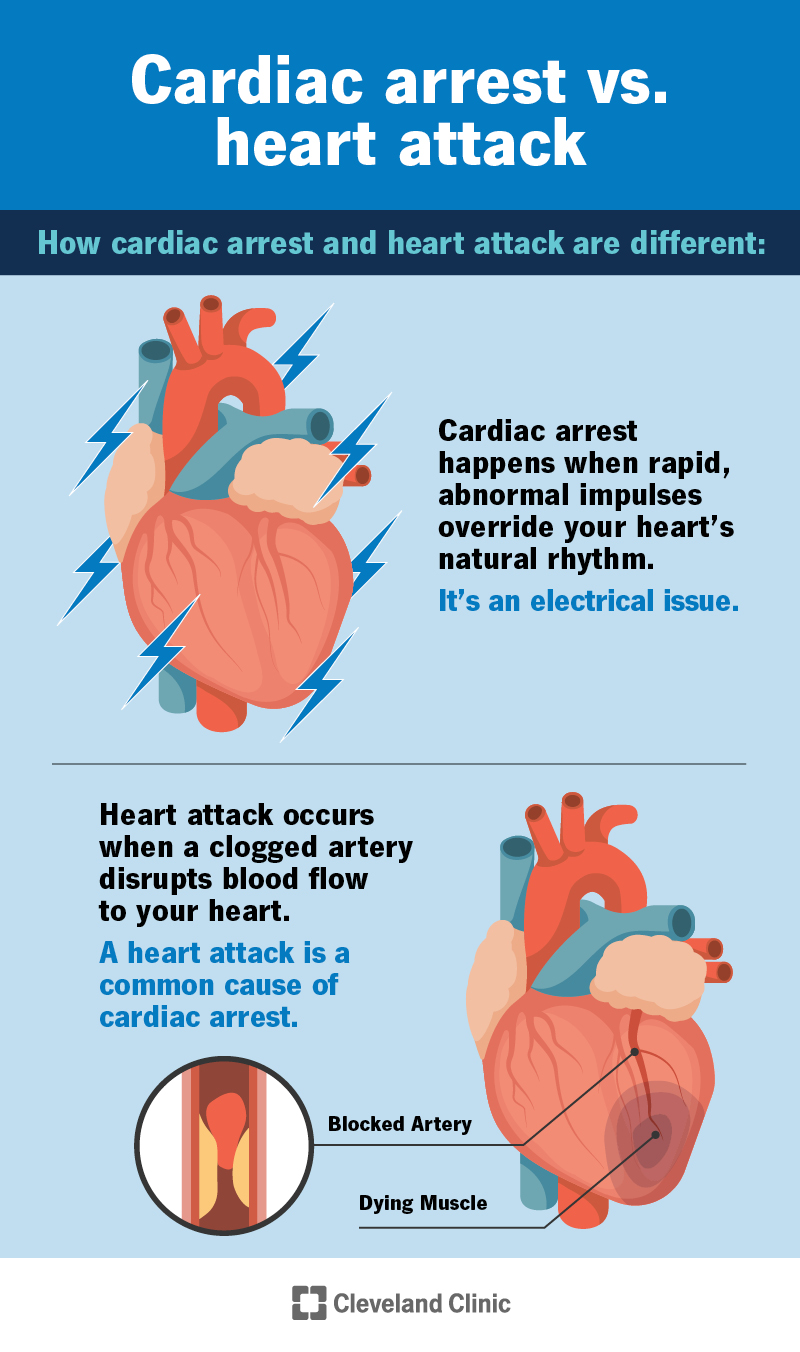
Credit: my.clevelandclinic.org
Pleurisy
Chest pain can be alarming, but not all chest pain means a heart attack. One often overlooked cause is pleurisy. It involves inflammation of the pleura, the lining around the lungs. This can cause sharp pain when you breathe.
Symptoms
Pleurisy symptoms can mimic other conditions. Knowing the specific signs helps in identifying it:
- Sharp chest pain: This pain usually worsens with breathing, coughing, or sneezing.
- Shortness of breath: You may feel breathless because it hurts to take deep breaths.
- Coughing: Often, a dry cough accompanies pleurisy.
- Fever: A mild fever may occur if an infection causes the pleurisy.
Medical Interventions
Treating pleurisy involves addressing the underlying cause. Here are some common medical interventions:
- Medication: Doctors may prescribe pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Antibiotics: If a bacterial infection causes pleurisy, antibiotics are necessary.
- Rest: Adequate rest is crucial to help your body heal.
- Thoracentesis: In severe cases, doctors might remove fluid from the pleural space to relieve symptoms.
If you experience persistent or severe chest pain, seek medical attention. Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential for relief and recovery.
Panic Attack
A panic attack can mimic the intense chest pain of a heart attack. It can be terrifying. Though not life-threatening, it feels very real. Understanding the symptoms and coping strategies helps manage the situation.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a panic attack often strike suddenly. Common signs include:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Rapid heartbeat
- Intense fear or dread
- Sweating
- Shaking or trembling
- Feeling of choking
These symptoms can peak within minutes. They are often accompanied by a sense of losing control.
Coping Strategies
Effective coping strategies can help manage panic attacks. Here are some techniques:
- Deep Breathing: Inhale slowly through your nose. Exhale through your mouth. Repeat until calm.
- Mindfulness: Focus on your surroundings. Notice five things you can see, four things you can touch, three things you can hear, two things you can smell, and one thing you can taste.
- Grounding: Press your feet into the ground. Feel the connection.
- Positive Affirmations: Repeat calming phrases. "This too shall pass" or "I am safe".
- Visualization: Picture a peaceful scene. A beach or a serene forest.
Practicing these techniques regularly can reduce the frequency and intensity of panic attacks.
Pulmonary Embolism
A pulmonary embolism occurs when a blood clot blocks an artery in the lungs. This blockage can reduce blood flow, causing chest pain. Many people mistake this pain for a heart attack. Understanding the symptoms and emergency response is crucial.
Symptoms
Shortness of breath is a common symptom. This can happen suddenly. You might also feel sharp chest pain. The pain may worsen with deep breaths. Some people experience a rapid heartbeat. Coughing, sometimes with blood, may occur. Swelling in one leg is another sign. Look for tenderness or redness in the leg.
Emergency Response
If you suspect a pulmonary embolism, act fast. Call emergency services right away. Stay calm and sit still. Do not try to walk or move around. Medical professionals will provide oxygen. They may use blood thinners to dissolve the clot. Quick action can save a life.
Shingles
Chest pain can be alarming, but it doesn’t always mean a heart attack. One less-known cause of chest pain is shingles. Shingles, also known as herpes zoster, is a viral infection that causes a painful rash. It stems from the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus that causes chickenpox. This condition can cause severe discomfort, including chest pain.
Symptoms
The symptoms of shingles can vary, but they often start with pain and burning. This discomfort usually begins on one side of the body or face. In some cases, this pain is mistaken for a heart attack. Shingles also causes a red rash that eventually forms blisters. These blisters can break open and crust over. Other common symptoms include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Chills
- Upset stomach
Early diagnosis is crucial to manage the symptoms effectively.
Antiviral Treatments
Antiviral medications can significantly reduce the severity and duration of a shingles outbreak. Three main antiviral treatments are often prescribed:
- Acyclovir
- Valacyclovir
- Famciclovir
These medications work best if taken within 72 hours of the first symptoms. They help to speed healing and reduce the risk of complications. In addition to antivirals, pain management is essential. Over-the-counter pain relievers and prescription medications can help manage the discomfort.
Shingles can cause chest pain that mimics a heart attack. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking early treatment can help ease the pain. Always consult your doctor if you experience unexplained chest pain.
Pericarditis
Pericarditis is an inflammation of the pericardium, the thin sac surrounding the heart. This condition can cause sharp chest pain that may be mistaken for a heart attack. Understanding the symptoms and treatments of pericarditis can help manage the condition effectively.
Symptoms
Pericarditis symptoms can vary but often include:
- Sharp, stabbing chest pain, usually behind the breastbone or on the left side of the chest.
- Increased pain when lying down or taking deep breaths.
- Pain relief when sitting up and leaning forward.
- Shortness of breath while reclining.
- Low-grade fever.
- Fatigue.
- Swelling in legs or abdomen.
Medical Treatments
Treatment for pericarditis depends on the cause and severity. Common treatments include:
| Treatment | Description |
|---|---|
| Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) | These drugs reduce inflammation and pain. Examples include ibuprofen and aspirin. |
| Colchicine | This medication reduces inflammation and can prevent recurrent episodes of pericarditis. |
| Corticosteroids | Used for severe cases or if symptoms do not improve with NSAIDs or colchicine. |
| Antibiotics | If an infection causes pericarditis, antibiotics may be prescribed. |
| Pericardiocentesis | This procedure involves draining excess fluid from the pericardium to relieve pressure on the heart. |
| Pericardiectomy | Surgical removal of the pericardium may be necessary for chronic or recurrent cases. |
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications. If you experience symptoms of pericarditis, seek medical attention promptly.
Gallbladder Issues
Chest pain can be alarming, especially if you fear a heart attack. Yet, not all chest pain is heart-related. One common cause is gallbladder issues. The gallbladder is a small organ that helps digest fat. When it malfunctions, it can cause significant discomfort, including chest pain.
Symptoms
Gallbladder issues can present a variety of symptoms. These include:
- Severe pain in the upper right abdomen
- Pain that radiates to the back or chest
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever and chills
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin)
It's crucial to notice these symptoms early. They can help differentiate gallbladder pain from heart-related chest pain.
Dietary Adjustments
Managing gallbladder issues often involves changes in diet. Here are some dietary adjustments to consider:
| Foods to Avoid | Foods to Include |
|---|---|
| Fatty foods | Fruits and vegetables |
| Fried foods | Whole grains |
| Processed foods | Lean proteins |
| Dairy products | Healthy fats (olive oil, nuts) |
These dietary changes can reduce gallbladder pain. They also promote overall digestive health.
In conclusion, gallbladder issues can cause chest pain that mimics a heart attack. Recognizing the symptoms and making dietary adjustments can help manage this condition effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Common Causes Of Chest Pain?
Chest pain can be caused by muscle strain, acid reflux, or anxiety. Other causes include lung issues, costochondritis, or panic attacks.
Can Acid Reflux Cause Chest Pain?
Yes, acid reflux can cause chest pain. This happens when stomach acid irritates the esophagus.
Is Chest Pain Always Related To Heart Problems?
No, chest pain isn't always heart-related. It can be due to non-cardiac causes like muscle strain or lung issues.
Can Anxiety Cause Chest Pain?
Yes, anxiety can cause chest pain. This occurs due to stress and tension in the chest muscles.
Conclusion
Chest pain can be scary, but it's not always a heart attack. Understanding the different causes helps reduce anxiety. Conditions like muscle strain, acid reflux, or stress can cause pain too. Knowing these can guide you to the right treatment.
Always consult a doctor for persistent or severe pain. Your health matters most. Stay informed and take care of yourself.






